
Python เป็นภาษาโปรแกรมที่ยอดเยี่ยมสำหรับงานดูแลระบบอัตโนมัติบนระบบ Linux ด้วยไลบรารีต่างๆ ที่มีให้เลือกมากมาย หลายไลบรารีจึงสามารถนำไปใช้ในการปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพของงานต่างๆ ได้ จากตัวอย่างด้านล่าง คุณสามารถเรียกใช้คำสั่งระบบ Linux ทำงานกับไฟล์และไดเร็กทอรี ทำงานเครือข่าย และทำให้กระบวนการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์เป็นอัตโนมัติได้ในเวลาเพียงไม่กี่วินาที
Python คืออะไร
Python สามารถอธิบายได้ดีที่สุดว่าเป็นภาษาโปรแกรมทั่วไป ได้รับการพัฒนาโดยนักวิทยาศาสตร์คอมพิวเตอร์ชาวดัตช์ชื่อ Guido van Rossum ในช่วงปลายทศวรรษ 1980 และต้นทศวรรษ 1990 ให้เป็นภาษาการเขียนโปรแกรมที่พิมพ์แบบไดนามิกและสืบทอดต่อจากภาษาการเขียนโปรแกรม “ABC”
ปัจจุบัน ภาษานี้ถือว่าเป็นหนึ่งในภาษาโปรแกรมที่ได้รับความนิยมมากที่สุดในโลก โดยมีการใช้งานตั้งแต่ทุกอย่างในการพัฒนาเว็บ ไปจนถึงคณิตศาสตร์ที่ซับซ้อนและการคำนวณทางวิทยาศาสตร์ นอกจากนี้ยังนิยมใช้ไวยากรณ์ที่หรูหราและเรียนรู้ได้ง่าย
การติดตั้ง Python บน Linux
ลีนุกซ์รุ่นต่างๆ จำนวนมากได้ติดตั้ง Python ไว้แล้วโดยปริยาย. หากต้องการตรวจสอบว่าระบบของคุณติดตั้ง Python 3 หรือไม่ คุณสามารถเรียกใช้ python3 คำสั่งด้วย --version ธง:
python3 --version

หากติดตั้ง Python ไว้ คำสั่งจะแสดงเวอร์ชันของการกำหนดค่า Python ของคุณ
วิธีติดตั้ง Python บนระบบ Ubuntu และ Debian:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y sudo apt install python3.10
หรือจะดาวน์โหลด Python เป็นไฟล์ “.tgz” หรือ “.xz” ก็ได้
การใช้โมดูล “os”
หนึ่งในไลบรารี Python ที่ดีที่สุดสำหรับผู้ดูแลระบบ Linux คือโมดูล "os" คุณสามารถใช้สำหรับการทำงานอัตโนมัติประเภทต่างๆ เช่น การจัดการไดเร็กทอรีและไฟล์ นอกจากนี้ยังสามารถเรียกใช้คำสั่งของระบบได้
ตัวอย่างเช่น คุณสามารถใช้โมดูลเพื่อสร้างไดเร็กทอรีใหม่:
#Import the OS module
import os
#Name of the new directory
dir_name = "example"
try:
#Creates the new directory
os.mkdir(dir_name)
#Prints the result, if the directory was successfully created
print(f"Directory '{dir_name}' created successfully")
#Prints the result, in case the directory already exists
except FileExistsError:
print(f"Directory '{dir_name}' already exists") 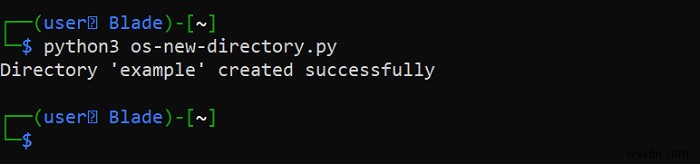
คุณยังสามารถลบไดเร็กทอรีโดยใช้โมดูล:
#Import the OS module
import os
#Name of the directory to be deleted
dir_name = "example"
try:
#Deletes the directory
os.rmdir(dir_name)
#Prints the result, if the directory was successfully deleted
print(f"Directory '{dir_name}' deleted successfully")
#Prints the result, if the directory doesn't exist
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"Directory '{dir_name}' doesn't exist") 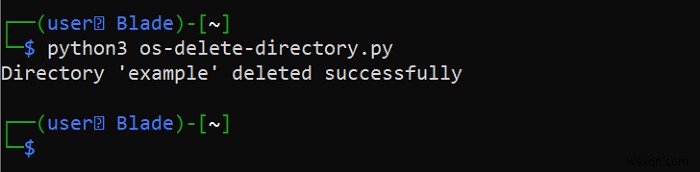
คุณสามารถเปลี่ยนชื่อไฟล์และไดเร็กทอรี:
#Import the OS module
import os
#Current name of the directory or file
current_name = "example"
new_name = "example2.0"
try:
#Renames the directory or file
content = os.rename(current_name, new_name)
#Prints the contents of the directory
print(f"Directory/File '{current_name}' was successfully renamed to '{new_name}'")
#Print the error message, if the directory or file doesn't exist
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"Directory/File '{current_name}' doesn't exist") 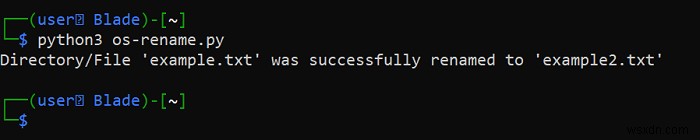
ไฟล์สามารถถอดออกได้ง่ายโดยใช้โมดูล:
#Import the OS module
import os
#Name of the file to be deleted
file_name = "example.txt"
try:
#Deletes the file
os.remove(file_name)
#Prints the result, if the file was successfully deleted
print(f"File '{file_name}' deleted successfully")
#Prints the result, if the file doesn't exist
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"File '{file_name}' doesn't exist") 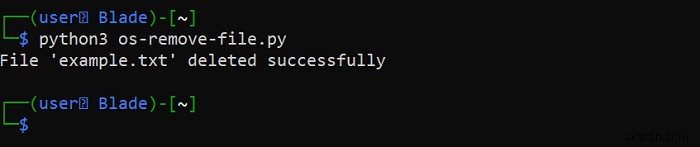
ไดเร็กทอรีการทำงานปัจจุบันสามารถพิมพ์ได้ง่าย:
#Import the OS module
import os
try:
#Gets the current working directory
cwd = os.getcwd()
#The name of the current working directory is printed out
print(cwd)
#If an error occurs, it is printed out
except:
print("An error occurred") 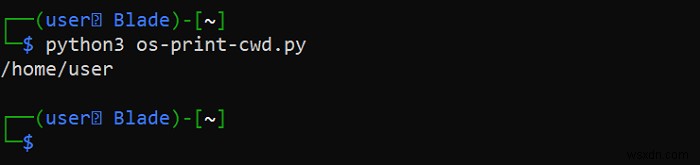
สามารถตรวจสอบเนื้อหาของไดเร็กทอรี เช่น ไฟล์และไดเร็กทอรีย่อยได้อย่างง่ายดาย:
#Import the OS module
import os
#Name of the directory
dir_name = "example"
try:
#Gets the contents of the directory
content = os.listdir(dir_name)
#Prints the contents of the directory
print(content)
#Prints the error, if the directory doesn't exist
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"Directory '{dir_name}' doesn't exist") 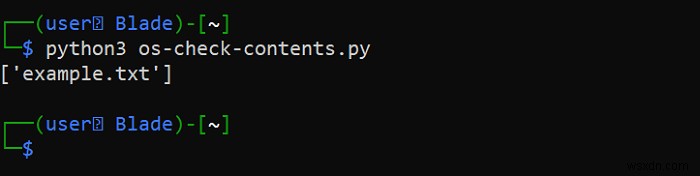
ใช้โมดูลเพื่อพิมพ์ผู้ใช้ปัจจุบัน:
#Import the OS module
import os
try:
#Gets the name of the current user
user = os.getlogin()
#Prints the name of the current user
print(user)
#Prints an error message, in case it occurs
except:
print("An error occurred") รันคำสั่งเชลล์ Linux โดยใช้โมดูล:
#Import the OS module
import os
#The shell command to run
command = "sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y"
try:
#Runs the system command
result = os.system(command)
#Prints the result of the command
print(result)
#Prints an error message, in case an error occurs
except:
print("An error occurred") 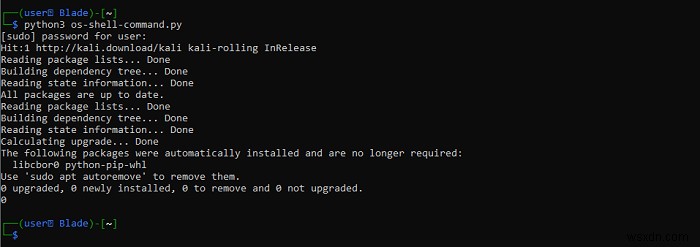
ดำเนินงานเครือข่ายโดยใช้โมดูล “ซ็อกเก็ต”
Python มีโมดูลที่สร้างขึ้นเพื่อทำงานเครือข่ายต่างๆ และสร้างยูทิลิตี้ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับเครือข่ายที่ซับซ้อน เช่น เครื่องสแกนพอร์ตและเซิร์ฟเวอร์วิดีโอเกม ไม่น่าแปลกใจเลยที่โมดูล "ซ็อกเก็ต" ยังสามารถใช้เพื่อทำงานเครือข่ายทั่วไปและขั้นพื้นฐานในระบบของคุณ
ตัวอย่างเช่น คุณสามารถตรวจสอบที่อยู่ IP และชื่อโฮสต์ของระบบ:
#Import the socket module
import socket
try:
#Getting the hostname
host = socket.gethostname()
#Getting the IP address of the host
ip = socket.gethostbyname(host)
#Prints the IP address
print(f"IP address: {ip}")
#Prints the hostname
print(f"Hostname: {host}")
#Prints an error message, if an error occurs
except:
print("An error occurred") คุณยังสามารถใช้โมดูลเพื่อตรวจสอบที่อยู่ IP ของเว็บไซต์:
#Import the socket module
import socket
try:
#Domain to be checked
domain = "duckduckgo.com"
#Getting the IP address of the domain
ip = socket.gethostbyname(domain)
#Prints the IP address
print(f"IP address: {ip}")
#Prints an error message, if an error occurs
except:
print("An error occurred") การใช้ Paramiko สำหรับการเข้าสู่ระบบเซิร์ฟเวอร์ SSH และเรียกใช้คำสั่ง
หากคุณต้องการทำให้กระบวนการล็อกอินเข้าสู่การตั้งค่าเซิร์ฟเวอร์ SSH และรันคำสั่งที่นั่นโดยอัตโนมัติ ไลบรารี Python “Paramiko” จะมีประโยชน์อย่างยิ่ง
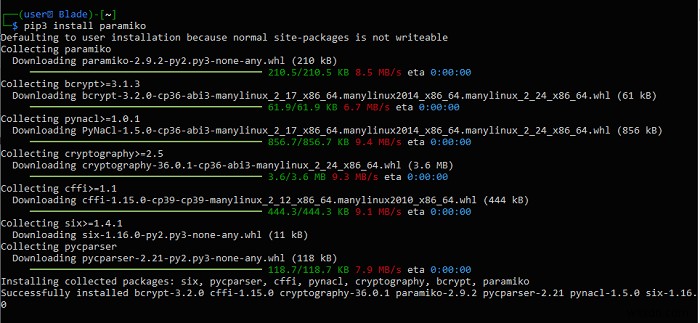
ก่อนอื่นให้ดาวน์โหลดไลบรารี่โดยใช้ pip3 . ของ Python ตัวจัดการแพ็คเกจ:
pip3 install paramiko
ใช้โมดูลเพื่อเข้าสู่ระบบเซิร์ฟเวอร์ SSH และเรียกใช้คำสั่ง:
#Importing the Paramiko library
import paramiko
#Specifying the IP and credentials
ip = '127.0.0.1'
port = 22
user = 'example'
password = 'example'
command = "uname -a"
try:
#Initiating the Paramiko client
ssh = paramiko.SSHClient()
ssh.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
#Connecting to the SSH server
ssh.connect(ip, port, user, password)
#Running a command on the system
stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh.exec_command(command)
#Prints the result of the command
print(stdout.read().decode())
#Prints an error message, in case an error occurs
except:
print("An error occurred") คำถามที่พบบ่อย
1. ฉันต้องใช้ Python 3 เพื่อใช้โมดูลและไลบรารีเหล่านี้หรือไม่
แม้ว่าไลบรารีและโมดูลเหล่านี้ส่วนใหญ่จะทำงานกับ Python 2 ได้ แต่ไวยากรณ์มีความแตกต่างกัน และโค้ดเหล่านี้จะไม่ทำงาน ด้วยการเปลี่ยนแปลงบางอย่าง คุณสามารถปรับเปลี่ยนให้ทำงานใน Python 2 ได้ อย่างไรก็ตาม Python 2 นั้นล้าสมัย ดังนั้นคุณควรใช้ Python 3
2. ฉันจำเป็นต้องติดตั้งโมดูล “os” และ “socket” หรือไม่
โดยทั่วไปไม่มี การติดตั้ง Python ส่วนใหญ่จะมาพร้อมกับโมดูลเหล่านี้ตั้งแต่แกะกล่อง
3. ฉันสามารถใช้ Paramiko เพื่อเข้าสู่ระบบที่ไม่ใช่ Unix ได้หรือไม่
ตามที่ผู้พัฒนา Paramiko บอก ในขณะนี้ ไลบรารีไม่สามารถใช้เพื่อเข้าสู่ระบบที่ไม่ใช่ Unix ด้วย SSH


