คอมพิวเตอร์เป็นเครื่องจักรอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ที่สามารถดำเนินการทางคณิตศาสตร์และตรรกะได้หลายอย่าง เพื่อดำเนินการฟังก์ชันขั้นสูงทั้งหมด คอมพิวเตอร์ต้องการความแข็งแกร่งของหน่วยประมวลผลที่สามารถจัดการกับฟังก์ชันที่ซับซ้อนทั้งหมดที่ดำเนินการโดยผู้ใช้ ดังนั้น หากคุณกำลังจะซื้อระบบคอมพิวเตอร์ใหม่และสงสัยว่าหน่วยประมวลผลกลางแบบใดที่เหมาะกับอุปกรณ์ของคุณ เราขอแนะนำให้คุณอ่านข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับ CPU และ CPU มีประโยชน์อย่างไร
CPU (หน่วยประมวลผลกลาง) คืออะไร
หรือเรียกอีกอย่างว่าโปรเซสเซอร์ โปรเซสเซอร์กลาง หรือไมโครโปรเซสเซอร์ CPU เป็นตัวประมวลผลหลักของคอมพิวเตอร์ ความรับผิดชอบของ CPU ของคอมพิวเตอร์คือการเรียกใช้คำสั่งระหว่างฮาร์ดแวร์และซอฟต์แวร์อย่างราบรื่น เพื่อให้สามารถทำงานได้โดยไม่มีปัญหาใดๆ เรียกอีกอย่างว่าสมองของระบบคอมพิวเตอร์ เพราะหน้าที่ที่สำคัญทั้งหมด เช่น การคำนวณ การเรียกใช้โปรแกรม และการจัดการกิจกรรมต่างๆ ได้รับการจัดการโดย CPU
โปรเซสเซอร์ถูกวางและยึดเข้ากับซ็อกเก็ต CPU ที่เข้ากันได้ซึ่งจัดเก็บไว้ในเมนบอร์ด ความร้อนถูกผลิตขึ้นโดยโปรเซสเซอร์ นั่นคือเหตุผลว่าทำไมจึงปิดด้วยฮีตซิงก์เพื่อป้องกันความร้อนที่ปล่อยออกมา ชิป CPU เป็นรูปสี่เหลี่ยมผืนผ้าเพื่อให้สามารถจัดเก็บไว้ในซ็อกเก็ตได้ง่าย ที่ด้านล่างของชิปมีพินตัวเชื่อมต่อหลายร้อยพินที่เสียบเข้ากับรูที่สอดคล้องกันแต่ละรูในซ็อกเก็ต
วันนี้ CPU ทั้งหมดมีการออกแบบและการทำงานที่คล้ายกันมาก อย่างไรก็ตาม Intel และ AMD มีชิปขนาดใหญ่กว่าที่สามารถจัดเก็บไว้ในเมนบอร์ดได้ นอกจากนี้ ยังมีซ็อกเก็ตต่างๆ มากมายบนเมนบอร์ด และแต่ละซ็อกเก็ตมีเค้าโครงที่แตกต่างกันและมีฟังก์ชันเฉพาะในการจัดเก็บโปรเซสเซอร์
ส่วนประกอบของซีพียู
โปรเซสเซอร์คอมพิวเตอร์เครื่องแรกได้รับการแนะนำโดยนักออกแบบ Intel ชื่อ Ted Hoff ในปี 1970 โปรเซสเซอร์ตัวแรกเรียกว่า 4004 โดย Intel โดยทั่วไปแล้ว โปรเซสเซอร์ของคอมพิวเตอร์ประกอบด้วยส่วนประกอบต่างๆ ดังต่อไปนี้ –
- หน่วยความจำหรือหน่วยเก็บข้อมูล
- ชุดควบคุม
- ALU (หน่วยเลขคณิตลอจิก)
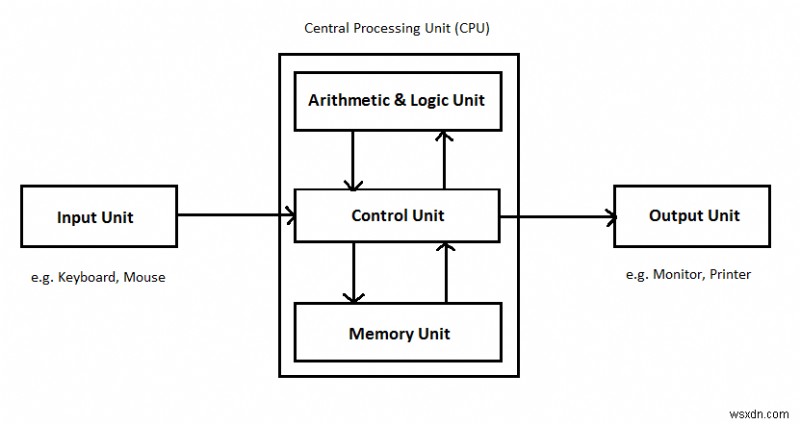
หน่วยเลขคณิตลอจิก (ALU)
หน่วยตรรกะเลขคณิตทำหน้าที่ทางคณิตศาสตร์ ตรรกะ และช่วยในกระบวนการตัดสินใจ หน่วยนี้ประกอบด้วยสองส่วนย่อยคือ
- มาตราเลขคณิต: ฟังก์ชันของส่วนเลขคณิตคือการดำเนินการทางเลขคณิต เช่น การบวก การลบ การคูณ และการหาร การดำเนินการที่ซับซ้อนทั้งหมดทำได้โดยการใช้การดำเนินการข้างต้นซ้ำๆ
- ส่วนตรรกะ: หน้าที่ของส่วนลอจิกคือการดำเนินการทางลอจิก เช่น การเปรียบเทียบ การเลือก การจับคู่ และการรวมข้อมูล
ชุดควบคุม (CU)
หน่วยควบคุมจะดึงคำสั่งจากหน่วยความจำและถอดรหัสและดำเนินการตามนั้น โดยเรียกใช้ ALU เมื่อจำเป็น
ฟังก์ชันของหน่วยนี้คือ -
- มีหน้าที่ควบคุมการถ่ายโอนข้อมูลและคำสั่งระหว่างหน่วยอื่นๆ ของคอมพิวเตอร์
- จัดการและประสานงานหน่วยทั้งหมดของคอมพิวเตอร์
- รับคำสั่งจากหน่วยความจำ แปลความหมาย และสั่งการทำงานของคอมพิวเตอร์
- มันสื่อสารกับอุปกรณ์อินพุต/เอาท์พุตสำหรับการถ่ายโอนข้อมูลหรือผลลัพธ์จากการจัดเก็บ
- ไม่ประมวลผลหรือจัดเก็บข้อมูล
หน่วยความจำหรือหน่วยเก็บข้อมูล
หน่วยนี้สามารถจัดเก็บคำสั่ง ข้อมูล และผลลัพธ์ระหว่างกลาง หน่วยนี้ให้ข้อมูลไปยังหน่วยอื่น ๆ ของคอมพิวเตอร์เมื่อจำเป็น เรียกอีกอย่างว่าหน่วยเก็บข้อมูลภายในหรือหน่วยความจำหลักหรือหน่วยเก็บข้อมูลหลักหรือหน่วยความจำเข้าถึงโดยสุ่ม (RAM)
ขนาดของมันส่งผลต่อความเร็ว พลัง และความสามารถ หน่วยความจำหลักและหน่วยความจำรองเป็นหน่วยความจำสองประเภทในคอมพิวเตอร์ ฟังก์ชันของหน่วยความจำคือ −
- เก็บข้อมูลทั้งหมดและคำสั่งที่จำเป็นสำหรับการประมวลผล
- จัดเก็บผลลัพธ์ขั้นกลางของการประมวลผล
- จัดเก็บผลลัพธ์สุดท้ายของการประมวลผลก่อนที่ผลลัพธ์เหล่านี้จะถูกส่งออกไปยังอุปกรณ์เอาต์พุต
- อินพุตและเอาต์พุตทั้งหมดจะถูกส่งผ่านหน่วยความจำหลัก
ประวัติซีพียู
ในช่วงเวลาแห่งประวัติศาสตร์ ความเร็วและประสิทธิภาพของหน่วยประมวลผลกลางได้พัฒนาไปอย่างมาก CPU ตัวแรกที่เปิดตัวโดย Intel 4004 ซึ่งเปิดตัวเมื่อวันที่ 15 พฤศจิกายน พ.ศ. 2514 มีทรานซิสเตอร์ 2,300 ตัวและดำเนินการ 60,000 ครั้งต่อวินาที และล่าสุด Intel platinum นำเสนอทรานซิสเตอร์ 3,300,000 ตัวและดำเนินการประมาณ 188,000,000 คำสั่งต่อวินาที คุณสามารถเปรียบเทียบความแตกต่างระหว่างประสิทธิภาพและความเร็วของหน่วย CPU ทั้งสองได้อย่างง่ายดาย
ใครคือผู้ก่อตั้งซีพียู
ซีพียูตัวแรก เป็น Intel 4004 ที่ออกโดย Intel ในปี 1971 Federico Faggin เป็นหัวหน้านักออกแบบCPUเชิงพาณิชย์เครื่องแรก . เขาเป็นหนึ่งในบุคคลสำคัญที่ให้เครดิตในการประดิษฐ์ซีพียู| ปี | แนะนำตัวประมวลผลของคอมพิวเตอร์ |
| 1823 | Baron Jons Jackob Berzelius ค้นพบ silicon (Si) ซึ่งปัจจุบันเป็นส่วนประกอบพื้นฐานของโปรเซสเซอร์ |
| 1903 | Nikola Tesla จดสิทธิบัตรวงจรลอจิกไฟฟ้าที่เรียกว่า "เกต" หรือ "สวิตช์" ในปี 1903 |
| พ.ศ. 2490 | John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley invent the first transistor at the Bell Laboratories on December 23, 1947. |
| 1948 | John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley patent the first transistor in 1948. |
| 1956 | John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley were awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for their work on the transistor. |
| 1958 | The first integrated circuit was first developed by Robert Noyce of Fairchild Semiconductor and Jack Kilby of Texas Instruments. The first IC was demonstrated on September 12, 1958. |
| 1960 | IBM developed the first automatic mass-production facility for transistors in New York in 1960. |
| 1968 | Intel Corporation was founded by Robert Noyce and Gordon Moore in 1968. |
| 1969 | AMD (Advanced Micro Devices) was founded on May 1, 1969. |
| 1971 | Intel with the help of Ted Hoff introduced the first microprocessor, the Intel 4004 on November 15, 1971. The 4004 had 2,300 transistors, performed 60,000 OPS (operations per second), addressed 640 bytes of memory, and cost $200.00. |
| 1972 | Intel introduced the 8008 processor on April 1, 1972. |
| 1974 | Intel’s improved microprocessor chip was introduced on April 1, 1974; the 8080 became a standard in the computer industry. |
| 1976 | Intel introduced the 8085 processor in March 1976. |
| 1976 | The Intel 8086 was introduced on June 8, 1976. |
| 1979 | The Intel 8088 was released on June 1, 1979. |
| 1979 | The Motorola 68000, a 16/32-bit processor was released and was later chosen as the processor for the Apple Macintosh and Amiga computers. |
| 1982 | The Intel 80286 was introduced on February 1, 1982. |
| 1985 | Intel introduced the first 80386 in October 1985. |
| 1987 | The SPARC processor was first introduced by Sun. |
| 1988 | Intel 80386SX was introduced in 1988. |
| 1991 | AMD introduced the AM386 microprocessor family in March 1991. |
| 1991 | Intel introduced the Intel 486SX chip in April in efforts to help bring a lower-cost processor to the PC market selling for $258.00. |
| 1992 | Intel released the 486DX2 chip on March 2, 1992, with a clock doubling ability that generates higher operating speeds. |
| 1993 | Intel released the Pentium processor on March 22, 1993. The processor was a 60 MHz processor, incorporates 3.1 million transistors and sells for $878.00. |
| 1994 | Intel released the second generation of Intel Pentium processors on March 7, 1994. |
| 1995 | Intel introduced the Intel Pentium Pro in November 1995. |
| 1996 | Intel announced the availability of the Pentium 150 MHz with 60 MHz bus and 166 MHz with 66 MHz bus on January 4, 1996. |
| 1996 | AMD introduced the K5 processor on March 27, 1996, with speeds of 75 MHz to 133 MHz and bus speeds of 50 MHz, 60 MHz, or 66 MHz. The K5 was the first processor developed completely in-house by AMD. |
| 1997 | AMD released their K6 processor line in April 1997, with speeds of 166 MHz to 300 MHz and a 66 MHz bus speed. |
| 1997 | Intel Pentium II was introduced on May 7, 1997. |
| 1998 | AMD introduced their new K6-2 processor line on May 28, 1998, with speeds of 266 MHz to 550 MHz and bus speeds of 66 MHz to 100 MHz. The K6-2 processor was an enhanced version of AMD’s K6 processor. |
| 1998 | Intel released the first Xeon processor, the Pentium II Xeon 400 (512 K or 1 M cache, 400 MHz, 100 MHz FSB) in June 1998. |
| 1999 | Intel released the Celeron 366 MHz and 400 MHz processors on January 4, 1999. |
| 1999 | AMD released its K6-III processors on February 22, 1999, with speeds of 400 MHz or 450 MHz and bus speeds of 66 MHz to 100 MHz. It also featured an on-die L2 cache. |
| 1999 | The Intel Pentium III 500 MHz was released on February 26, 1999. |
| 1999 | The Intel Pentium III 550 MHz was released on May 17, 1999. |
| 1999 | AMD introduced the Athlon processor series on June 23, 1999. The Athlon would be produced for the next six years in speeds ranging from 500 MHz up to 2.33 GHz. |
| 1999 | The Intel Pentium III 600 MHz was released on August 2, 1999. |
| 1999 | The Intel Pentium III 533B and 600B MHz was released on September 27, 1999. |
| 1999 | The Intel Pentium III Coppermine series was first introduced on October 25, 1999. |
| 2000 | On January 5, 2000, AMD released the 800 MHz Athlon processor. |
| 2000 | Intel released the Celeron 533 MHz with a 66 MHz bus processor on January 4, 2000. |
| 2000 | AMD first released the Duron processor on June 19, 2000, with speeds of 600 MHz to 1.8 GHz and bus speeds of 200 MHz to 266 MHz. The Duron was built on the same K7 architecture as the Athlon processor. |
| 2000 | Intel announces on August 28th that it will recall its 1.3 GHz Pentium III processors due to a glitch. Users with these processors should contact their vendors for additional information about the recall. |
| 2001 | On January 3, 2001, Intel released the 800 MHz Celeron processor with a 100 MHz bus. |
| 2001 | On January 3, 2001, Intel released the 1.3 GHz Pentium 4 processor. |
| 2001 | AMD announced a new branding scheme on October 9, 2001. Instead of identifying processors by their clock speed, the AMD Athlon XP processors will bear monikers of 1500+, 1600+, 1700+, 1800+, 1900+, 2000+, etc. Each higher model number will represent a higher clock speed. |
| 2002 | Intel released the Celeron 1.3 GHz with a 100 MHz bus and 256 kB of level 2 cache. |
| 2003 | Intel Pentium M was introduced in March 2003. |
| 2003 | AMD released the first single-core Opteron processors, with speeds of 1.4 GHz to 2.4 GHz and 1024 KB L2 cache, on April 22, 2003. |
| 2003 | AMD released the first Athlon 64 processors, the 3200+, and the first Athlon 64 FX processor, the FX-51, on September 23, 2003. |
| 2004 | AMD released the first Sempron processor on July 28, 2004, with a 1.5 GHz to 2.0 GHz clock speed and 166 MHz bus speed. |
| 2005 | AMD released their first dual-core processor, the Athlon 64 X2 3800+ (2.0 GHz, 512 KB L2 cache per core), on April 21, 2005. |
| 2006 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E6320 (4 M cache, 1.86 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on April 22, 2006. |
| 2006 | Intel introduced the Intel Core 2 Duo processors with the Core 2 Duo processor E6300 (2 M cache, 1.86 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on July 27, 2006. |
| 2006 | Intel introduced the Intel Core 2 Duo processor for the laptop computer with the Core 2 Duo processor T5500, as well as other Core 2 Duo T series processors, in August 2006. |
| 2007 | Intel released the Core 2 Quad processor Q6600 (8 M cache, 2.40 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) in January 2007. |
| 2007 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E4300 (2 M cache, 1.80 GHz, 800 MHz FSB) on January 21, 2007. |
| 2007 | Intel released the Core 2 Quad processor Q6700 (8 M cache, 2.67 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) in April 2007. |
| 2007 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E4400 (2 M cache, 2.00 GHz, 800 MHz FSB) on April 22, 2007. |
| 2007 | AMD renamed the Athlon 64 X2 processor line to Athlon X2 and released the first in that line, the Brisbane series (1.9 to 2.6 GHz, 512 KB L2 cache) on June 1, 2007. |
| 2007 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E4500 (2 M cache, 2.20 GHz, 800 MHz FSB) on July 22, 2007. |
| 2007 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E4600 (2 M cache, 2.40 GHz, 800 MHz FSB) on October 21, 2007. |
| 2007 | AMD released the first Phenom X4 processors (2 M cache, 1.8 GHz to 2.6 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on November 19, 2007. |
| 2008 | Intel released the Core 2 Quad processor Q9300 and the Core 2 Quad processor Q9450 in March 2008. |
| 2008 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E4700 (2 M cache, 2.60 GHz, 800 MHz FSB) on March 2, 2008. |
| 2008 | AMD released the first Phenom X3 processors (2 M cache, 2.1 GHz to 2.5 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on March 27, 2008. |
| 2008 | Intel released the first of the Intel Atom series of processors, the Z5xx series, in April 2008. They are single-core processors with a 200 MHz GPU. |
| 2008 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E7200 (3 M cache, 2.53 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on April 20, 2008. |
| 2008 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E7300 (3 M cache, 2.66 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on August 10, 2008. |
| 2008 | Intel released several Core 2 Quad processors in August 2008:the Q8200, the Q9400, and the Q9650. |
| 2008 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E7400 (3 M cache, 2.80 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on October 19, 2008. |
| 2008 | Intel released the first Core i7 desktop processors in November 2008:the i7-920, the i7-940, and the i7-965 Extreme Edition. |
| 2009 | AMD released the first Phenom II X4 (quad-core) processors (6 M cache, 2.5 to 3.7 GHz, 1066 MHz or 1333 MHz FSB) on January 8, 2009. |
| 2009 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E7500 (3 M cache, 2.93 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on January 18, 2009. |
| 2009 | AMD released the first Phenom II X3 (triple core) processors (6 M cache, 2.5 to 3.0 GHz, 1066 MHz or 1333 MHz FSB) on February 9, 2009. |
| 2009 | Intel released the Core 2 Quad processor Q8400 (4 M cache, 2.67 GHz, 1333 MHz FSB) in April 2009. |
| 2009 | Intel released the Core 2 Duo processor E7600 (3 M cache, 3.06 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) on May 31, 2009. |
| 2009 | AMD released the first Athlon II X2 (dual-core) processors (1024KB L2 cache, 1.6 to 3.5 GHz, 1066 MHz or 1333 MHz FSB) in June 2009. |
| 2009 | AMD released the first Phenom II X2 (dual-core) processors (6 M cache, 3.0 to 3.5 GHz, 1066 MHz or 1333 MHz FSB) on June 1, 2009. |
| 2009 | AMD released the first Athlon II X4 (quad-core) processors (512 KB L2 cache, 2.2 to 3.1 GHz, 1066 MHz or 1333 MHz FSB) in September 2009. |
| 2009 | Intel released the first Core i7 mobile processor, the i7-720QM, in September 2009. It uses the Socket G1 socket type, runs at 1.6 GHZ, and features 6 MB L3 cache. |
| 2009 | Intel released the first Core i5 desktop processor with four cores, the i5-750 (8 M cache, 2.67 GHz, 1333 MHz FSB), on September 8, 2009. |
| 2009 | AMD released the first Athlon II X3 (triple-core) processors in October 2009. |
| 2010 | Intel released the Core 2 Quad processor Q9500 (6 M cache, 2.83 GHz, 1333 MHz FSB) in January 2010. |
| 2010 | Intel released the first Core i5 mobile processors, the i5-430M and the i5-520E in January 2010. |
| 2010 | Intel released the first Core i5 desktop processor over 3.0 GHz, the i5-650 in January 2010. |
| 2010 | Intel released the first Core i3 desktop processors, the i3-530, and i3-540 on January 7, 2010. |
| 2010 | Intel released the first Core i3 mobile processors, the i3-330M (3 M cache, 2.13 GHz, 1066 MHz FSB) and the i3-350M, on January 7, 2010. |
| 2010 | AMD released the first Phenom II X6 (hex/six core) processors on April 27, 2010. |
| 2010 | Intel released the first Core i7 desktop processor with six cores, the i3-970, in July 2010. It runs at 3.2 GHz and features 12 MB L3 cache. |
| 2011 | Intel released seven new Core i5 processors with four cores, the i5-2xxx series in January 2011. |
| 2011 | AMD released the first mobile processors in their A4 line, the A4-3300M and the A4-3310MX on June 14, 2011. |
| 2011 | AMD released the first mobile processors in their A6 line, the A6-3400M and the A6-3410MX on June 14, 2011. |
| 2011 | AMD released the first mobile processors in their A8 line, the A8-3500M,the A8-3510MX, and the A8-3530MX on June 14, 2011. |
| 2011 | AMD released the first desktop processor in their A6 line, the A6-3650 (4 M L2 cache, 2.6 GHz, 1866 MHz FSB) on June 30, 2011. |
| 2011 | AMD released the first desktop processor in their A8 line, the A8-3850 (4 M L2 cache, 2.9 GHz, 1866 MHz FSB) on June 30, 2011. |
| 2011 | AMD released the first desktop processors in their A4 line, the A4-3300 and the A4-3400 on September 7, 2011. |
| 2012 | AMD released the first desktop processors in their A10 line, the A10-5700 and the A10-5800K on October 1, 2012. |
| 2013 | AMD released one of their fastest desktop processors to date, the Athlon II X2 280, on January 28, 2013. It has two cores and runs at 3.6 GHz. |
| 2013 | Intel released their first processor to utilize the BGA-1364 socket and feature an Iris Pro Graphics 5200 GPU. Released in June 2013, it runs at 3.2 GHz and has 6 MB of L3 cache. |
| 2014 | AMD introduced the socket AM1 architecture and compatible processors, like the Sempron 2650, in April 2014. |
| 2014 | AMD released their first Pro A series APU processors, the A6 Pro-7050B, A8 Pro-7150B, and A10 Pro-7350B, in June 2014. They feature on or two cores and run at 1.9 GHz to 2.2 GHz. |
| 2017 | AMD released their first Ryzen 7 processors, 1700, 1700X, and 1800X models, on March 2, 2017. They have eight cores, run at 3.0 to 3.6 GHz, and feature 16 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | AMD released their first Ryzen 5 processors, 1400, 1500X, 1600, and 1600X models, on April 11, 2017. They have four to six cores, run at 3.2 to 3.6 GHz, and feature 8 to 16 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | Intel released the first Core i9 desktop processor, the i9-7900X, in June 2017. It uses the LGA 2066 socket, runs at 3.3 GHZ, has 10 cores, and features 13.75 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | AMD released their first Ryzen 3 processors, the Pro 1200 and Pro 1300 models, on June 29, 2017. They have four cores, run at 3.1 to 3.5 GHz, and feature 8 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | Intel released the first desktop processor with 12 cores, the Core i9-7920X, in August 2017. It runs at 2.9 GHZ and features 16.50 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | AMD released their first processor with 16 cores, the Ryzen Threadripper 1950X, on August 10, 2017. It runs at 3.4 GHz and features 32 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | Intel released the first desktop processor with 14 cores, the Core i9-7940X, in September 2017. It runs at 3.1 GHZ and features 19.25 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | Intel released the first desktop processor with 16 cores, the Core i9-7960X, in September 2017. It runs at 2.8 GHZ and features 22 MB L3 cache. |
| 2017 | Intel released the first desktop processor with 18 cores, the Core i9-7980X, in September 2017. It runs at 2.6 GHZ and features 24.75 MB L3 cache. |
| 2018 | Intel released the first Core i9 mobile processor, the i9-8950HK, in April 2018. It uses the BGA 1440 socket, runs at 2.9 GHZ, has six cores, and features 12 MB L3 cache. |


