จากแผนผังการค้นหาแบบไบนารี และเราจำเป็นต้องย้อนกลับเส้นทางจากคีย์ใดคีย์หนึ่ง ตัวอย่างเช่น
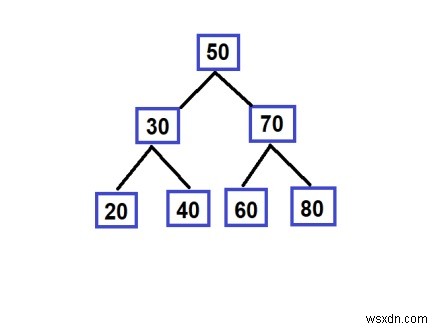
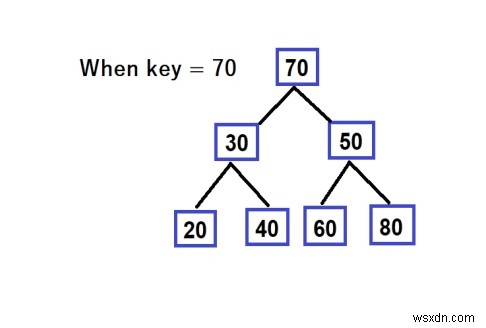
แนวทางในการหาแนวทางแก้ไข
ในแนวทางนี้ เราจะสร้างคิวและพุชโหนดทั้งหมดจนกว่าจะได้รูท
ตัวอย่าง
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int key;
struct node *left, *right;
};
struct node* newNode(int item){
struct node* temp = new node;
temp->key = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void inorder(struct node* root){
if (root != NULL) {
inorder(root->left);
cout << root->key << " ";
inorder(root->right);
}
}
void Reversing(struct node** node,
int& key, queue<int>& q1){
/* If the tree is empty then
return*/
if (node == NULL)
return;
if ((*node)->key == key){ // if we find the key
q1.push((*node)->key); // we push it into our queue
(*node)->key = q1.front(); // we change the first queue element with current
q1.pop(); // we pop the first element
}
else if (key < (*node)->key){ // if key is less than current node's value
q1.push((*node)->key); // we push the element in our queue
Reversing(&(*node)->left, key, q1); //we go to the left subtree using a recursive call
(*node)->key = q1.front(); //we reverse the elements
q1.pop(); // we pop the first element
}
else if (key > (*node)->key){ // if key greater than node key then
q1.push((*node)->key);// we push node key into queue
Reversing(&(*node)->right, key, q1);// we go to right subtree using a recursive call
(*node)->key = q1.front();// replace queue front to node key
q1.pop(); // we pop the first element
}
return;
}
struct node* insert_node(struct node* node, // function to insert node nodes in our BST
int key){
if (node == NULL)
return newNode(key); // if tree is empty we return a new node
if (key < node->key) // else we push that in our tree
node->left = insert_node(node->left, key);
else if (key > node->key)
node->right = insert_node(node->right, key);
return node; // returning the node
}
int main(){
struct node* root = NULL;
queue<int> q1;
int k = 80;
/****************Creating the BST*************************/
root = insert_node(root, 50);
insert_node(root, 30);
insert_node(root, 20);
insert_node(root, 40);
insert_node(root, 70);
insert_node(root, 60);
insert_node(root, 80);
cout << "Before Reversing :" << "\n";
inorder(root);
cout << "\n";
Reversing(&root, k, q1);
cout << "After Reversing :" << "\n";
// print inorder of reverse path tree
inorder(root);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
Before Reversing : 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 After Reversing : 20 30 40 80 60 70 50
คำอธิบายของโค้ดด้านบน
ในแนวทางนี้ เราจะทำการค้นหาคีย์ที่ให้มา เมื่อเราเดินผ่านต้นไม้ เราผลักโหนดทั้งหมดในคิว และตอนนี้เมื่อเราพบโหนดที่มีค่าของคีย์ เราจะสลับค่าของโหนดเส้นทางทั้งหมดที่คิวอยู่ข้างหน้า และในกระบวนการนี้ เส้นทางของเรา จะกลับด้าน
บทสรุป
เราแก้ปัญหาในการย้อนกลับเส้นทางใน BST โดยใช้คิวและใช้การเรียกซ้ำ นอกจากนี้เรายังได้เรียนรู้โปรแกรม C++ สำหรับปัญหานี้และแนวทางที่สมบูรณ์ (ปกติ) ซึ่งเราแก้ไขปัญหานี้ เราสามารถเขียนโปรแกรมเดียวกันในภาษาอื่นๆ เช่น C, java, python และภาษาอื่นๆ เราหวังว่าคุณจะพบว่าบทช่วยสอนนี้มีประโยชน์


