ให้ต้นไม้และเราจำเป็นต้องลบโหนดปลายของเส้นทางที่มีความยาวน้อยกว่า k ที่กำหนดเป็นต้น
อินพุต -
K = 4.
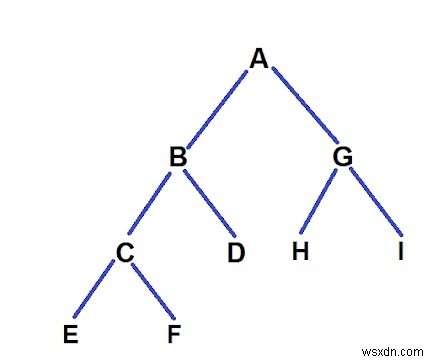
เอาท์พุต -
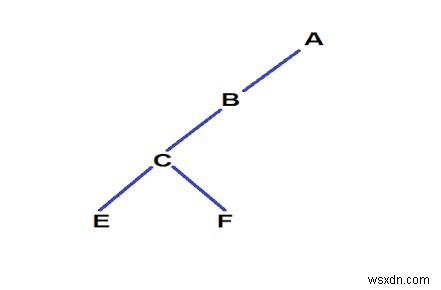
คำอธิบาย
The paths were : 1. A -> B -> C -> E length = 4 2. A -> B -> C -> F length = 4 3. A -> B -> D length = 3 4. A -> G -> H length = 3 5. A -> B -> I length = 3 Now as you can see paths 3, 4, 5 have length of 3 which is less than given k so we remove the leaf nodes of these paths i.e. D, H, I. Now for path 4 and 5 when H and I are removed we notice that now G is also a leaf node with path length 2 so we again remove node G and here our program ends.
เราจะสำรวจต้นไม้ในรูปแบบหลังการสั่งซื้อ จากนั้น เราสร้างฟังก์ชันเรียกซ้ำที่ลบโหนดปลายสุดของเราหากความยาวเส้นทางน้อยกว่า K
แนวทางในการหาแนวทางแก้ไข
ในแนวทางนี้ เราสำรวจผ่านเส้นทางหลังลำดับตอนนี้ เราพยายามลบโหนดปลายสุดที่มีความยาวเส้นทางน้อยกว่า k ซ้ำแล้วซ้ำอีก และดำเนินการต่อในลักษณะนี้
ตัวอย่าง
รหัส C++ สำหรับแนวทางข้างต้น
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node{ // structure of our node
char data;
Node *left, *right;
};
Node *newNode(int data){ // inserting new node
Node *node = new Node;
node->data = data;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
Node *trimmer(Node *root, int len, int k){
if (!root) // if root == NULL then we return
return NULL;
root -> left = trimmer(root -> left, len + 1, k); // traversing the left phase
root -> right = trimmer(root -> right, len + 1, k); // traversing the right phase
if (!root -> left && !root -> right && len < k){
delete root;
return NULL;
}
return root;
}
Node *trim(Node *root, int k){
return trimmer(root, 1, k);
}
void printInorder(Node *root){
if (root){
printInorder(root->left);
cout << root->data << " ";
printInorder(root->right);
}
}
int main(){
int k = 4;
Node *root = newNode('A');
root->left = newNode('B');
root->right = newNode('G');
root->left->left = newNode('C');
root->left->right = newNode('D');
root->left->left->left = newNode('E');
root->left->left->right = newNode('F');
root->right->left = newNode('H');
root->right->right = newNode('I');
printInorder(root);
cout << "\n";
root = trim(root, k);
printInorder(root);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
E C F B D A H G I E C F B A
คำอธิบายของโค้ดด้านบน
ในโค้ดนี้ เรากำลังใช้ฟังก์ชันแบบเรียกซ้ำที่สำรวจทรีของเราและรักษาสถิติของทรีย่อยด้านซ้ายและขวา ตอนนี้เรามาถึงโหนดลีฟ เราตรวจสอบความยาวเส้นทางจนถึงโหนดนั้น หากความยาวพาธน้อยกว่า เราจะลบโหนดนี้ออก จากนั้นเราจะคืนค่าเป็น NULL มิฉะนั้น รหัสจะดำเนินต่อไป
บทสรุป
ในบทช่วยสอนนี้ เราแก้ปัญหาการลบโหนดบนเส้นทางรากถึงปลายที่มีความยาว


