สมมติว่าเรามีแผนผังการค้นหาแบบไบนารี เราจะรับหนึ่งคีย์ k และเราต้องลบคีย์ที่กำหนด k ออกจาก BST และส่งคืน BST ที่อัปเดต ดังนั้นถ้าต้นไม้เป็นเหมือน −
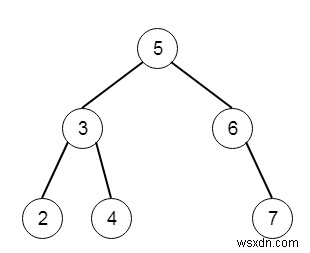
และคีย์ k =3 จากนั้นแผนผังผลลัพธ์จะเป็น −
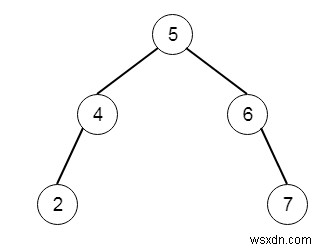
เพื่อแก้ปัญหานี้ เราจะทำตามขั้นตอนเหล่านี้ -
-
กำหนดวิธีการที่เรียกว่า deleteRoot() เพื่อลบรูทโหนด ซึ่งจะทำงานดังนี้
-
ถ้ารูทเป็นโมฆะ ให้คืนค่า null
-
หากรูทไม่มีทรีย่อยที่ถูกต้อง ให้กลับทางซ้ายของรูท
-
x :=ตัวต่อตามลำดับของรูท
-
ตั้งค่าด้านซ้ายของ x เป็น left :=left of root
-
กลับทางขวาของรูท
-
วิธีการลบจะเป็นแบบ
-
หากรูทเป็นค่าว่างหรือค่าของรูทเป็นคีย์ ให้คืนค่า deleteRoot(root)
-
curr :=รูท
-
สร้างหนึ่งวงไม่สิ้นสุดและดำเนินการต่อไปนี้
-
x :=ค่าของโหนดโหนด
-
ถ้าคีย์
-
ถ้า left ofcurr =null หรือ value of left of curr =key แล้ว
-
left ofcurr :=deleteRoot(left of curr) และออกจากลูป
-
-
curr :=เหลือของ curr
-
-
อย่างอื่น
-
ถ้า right ofcurr =null หรือ value of right of curr =key แล้ว
-
right ofcurr :=deleteRoot( right of curr) และออกจากลูป
-
-
curr :=ด้านขวาของสกุลเงิน
-
-
-
คืนค่ารูท
ให้เราดูการใช้งานต่อไปนี้เพื่อความเข้าใจที่ดีขึ้น -
ตัวอย่าง
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class TreeNode{
public:
int val;
TreeNode *left, *right;
TreeNode(int data){
val = data;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
void insert(TreeNode **root, int val){
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(*root);
while(q.size()){
TreeNode *temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if(!temp->left){
if(val != NULL)
temp->left = new TreeNode(val);
else
temp->left = new TreeNode(0);
return;
} else {
q.push(temp->left);
}
if(!temp->right){
if(val != NULL)
temp->right = new TreeNode(val);
else
temp->right = new TreeNode(0);
return;
} else {
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
}
TreeNode *make_tree(vector<int> v){
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(v[0]);
for(int i = 1; i<v.size(); i++){
insert(&root, v[i]);
}
return root;
}
void tree_level_trav(TreeNode*root){
if (root == NULL) return;
cout << "[";
queue<TreeNode *> q;
TreeNode *curr;
q.push(root);
q.push(NULL);
while (q.size() > 1) {
curr = q.front();
q.pop();
if (curr == NULL){
q.push(NULL);
}
else {
if(curr->left)
q.push(curr->left);
if(curr->right)
q.push(curr->right);
if(curr == NULL || curr->val == 0){
cout << "null" << ", ";
} else {
cout << curr->val << ", ";
}
}
}
cout << "]"<<endl;
}
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* deleteNode(TreeNode* root, int key) {
if(root == NULL || root->val == key) return deleteRoot(root);
TreeNode* curr = root;
while(1) {
int x = curr->val;
if(key < x){
if(curr->left == NULL || curr->left->val == key){
curr->left = deleteRoot(curr->left);
break;
}
curr = curr->left;
} else {
if(curr->right == NULL || curr->right->val == key){
curr->right = deleteRoot(curr->right);
break;
}
curr = curr->right;
}
}
return root;
}
TreeNode* deleteRoot(TreeNode* root){
if(!root || root->val == 0)return NULL;
if(root->right == NULL) return root->left;
TreeNode* x = root->right;
while(x->left)x = x->left;
x->left = root->left;
return root->right;
}
};
main(){
vector<int> v = {5,3,6,2,4,NULL,7};
TreeNode *root = make_tree(v);
Solution ob;
tree_level_trav(ob.deleteNode(root, 3));
} อินพุต
[5,3,6,2,4,null,7] 3
ผลลัพธ์
[5, 4, 6, 2, null, 7, ]


