จากไบนารีทรีโปรแกรมจะต้องค้นหาเส้นทางที่สั้นที่สุดจากรูทไปยังใบไม้ท่ามกลางเส้นทางที่กำหนดจำนวนมาก
เนื่องจากเราสำรวจต้นไม้จากซ้ายไปขวา ดังนั้นหากมีเส้นทางที่สั้นที่สุดหลายเส้นทางจากรากหนึ่งไปยังอีกใบ โปรแกรมจะพิมพ์เส้นทางแรกที่ข้ามผ่านเส้นทางที่สั้นที่สุดทางด้านซ้ายของต้นไม้
เราสามารถใช้คิวที่จะข้ามแต่ละระดับโดยใช้ระดับการข้ามผ่านและเส้นทางที่มีจำนวนระดับน้อยที่สุดจะถูกพิมพ์เนื่องจากจะเป็นเส้นทางที่สั้นที่สุดจากรากไปยังใบ
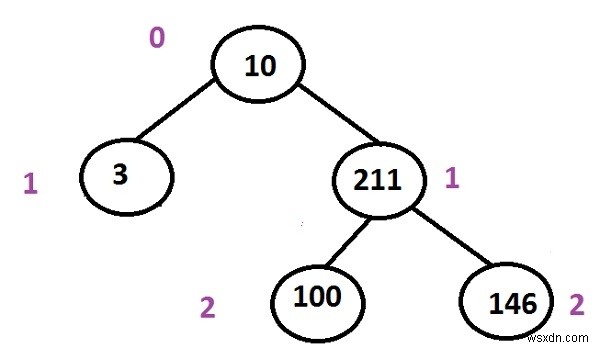
ในต้นไม้ด้านบน มีหลายเส้นทางจากรากสู่ใบ
10 -> 3 (this one is the shortest path amongst all) 10 -> 211 -> 100 10 -> 211 -> 146
ตัวอย่าง
Input : 10 3 211 100 146 Output : 10 3
อัลกอริทึม
Step 1 -> create a structure of a node as struct node struct node *left, *right int data End Step 2 -> function to create a node node* newnode(int data) node *temp = new node temp->data = data temp->left = temp->right= NULL return temp Step 3 -> create function for calculating path void path(int data, unordered_map <int,int> prnt) IF prnt[data] = data Return End path(prnt[data], prnt) print prnt[data] step 4 -> function for finding out the left path void left(Node* root) create STL queue<Node*> que que.push(root) int leaf = -1 Node* temp = NULL Create STL unordered_map<int, int> prnt prnt[root->data] = root->data Loop While !que.empty() temp = que.front() que.pop() IF !temp->left && !temp->right leaf = temp->data break End Else IF temp->left que.push(temp->left) prnt[temp->left->data] = temp->data End IF temp->right que.push(temp->right) prnt[temp->right->data] = temp->data End End End path(leaf, prnt) print leaf Step 5 -> In main() Create tree using Node* root = newnode(90) root->left = newnode(21) call left(root) stop
ตัวอย่าง
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// structure of a node
struct Node {
struct Node *left,*right;
int data;
};
//function to create a new node
Node* newnode(int data){
Node* temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = NULL;
temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
//function to set a path
void path(int data, unordered_map <int,int> prnt) {
if (prnt[data] == data)
return;
path(prnt[data], prnt);
cout << prnt[data] << " ";
}
//function for a leaf path
void left(Node* root) {
queue<Node*> que;
que.push(root);
int leaf = -1;
Node* temp = NULL;
unordered_map<int, int> prnt;
prnt[root->data] = root->data;
while (!que.empty()){
temp = que.front();
que.pop();
if (!temp->left && !temp->right{
leaf = temp->data;
break;
} else {
if (temp->left){
que.push(temp->left);
prnt[temp->left->data] = temp->data;
}
if (temp->right){
que.push(temp->right);
prnt[temp->right->data] = temp->data;
}
}
}
path(leaf, prnt);
cout << leaf << " ";
}
int main(){
Node* root = newnode(90);
root->left = newnode(21);
root->right = newnode(32);
root->left->left = newnode(45);
root->right->left = newnode(52);
root->right->right = newnode(27);
root->left->left->left = newnode(109);
root->left->left->right = newnode(101);
root->right->right->left = newnode(78);
left(root);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
หากเรารันโปรแกรมข้างต้น มันจะสร้างผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้
90 32 52


