สแต็กเป็นประเภทข้อมูลนามธรรม (ADT) ซึ่งมักใช้ในภาษาการเขียนโปรแกรมส่วนใหญ่ มันถูกตั้งชื่อว่า stack ซึ่งมีลักษณะเหมือนสแต็คในโลกจริง เช่น สำรับไพ่หรือจาน เป็นต้น

สแต็กอนุญาตให้ดำเนินการที่ปลายด้านเดียวเท่านั้น คุณลักษณะนี้ทำให้โครงสร้างข้อมูล LIFO LIFO ย่อมาจาก Last-in-first-out ที่นี่องค์ประกอบที่วาง (แทรกหรือเพิ่ม) สุดท้ายสามารถเข้าถึงได้ก่อน ในคำศัพท์เฉพาะของสแต็ก การดำเนินการแทรกเรียกว่าการดำเนินการ PUSH และการดำเนินการนำออกเรียกว่าการดำเนินการ POP
ไดอะแกรมต่อไปนี้แสดงการดำเนินการบนสแต็ก -
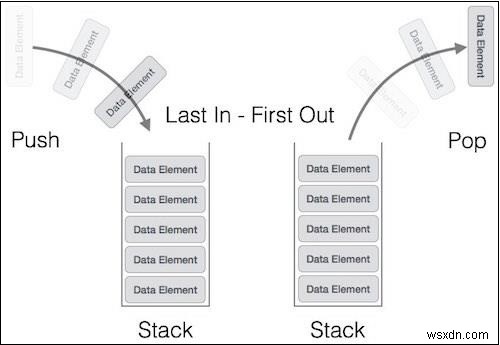
ต่อไปนี้เป็นคลาส Javascript ที่สมบูรณ์เพื่อเป็นตัวแทนของ Stack -
ตัวอย่าง
class Stack {
constructor(maxSize) { // Set default max size if not provided
if (isNaN(maxSize)) {
maxSize = 10;
}
this.maxSize = maxSize; // Init an array that'll contain the stack values.
this.container = [];
}
display() {
console.log(this.container);
}
isEmpty() {
return this.container.length === 0;
}
isFull() {
return this.container.length >= this.maxSize;
}
push(element) { // Check if stack is full
if (this.isFull()) {
console.log("Stack Overflow!") return;
}
this.container.push(element)
}
pop() { // Check if empty
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log("Stack Underflow!") return;
}
this.container.pop()
}
peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
console.log("Stack Underflow!");
return;
}
return this.container[this.container.length - 1];
}
clear() {
this.container = [];
}
} 

