ฟังก์ชันไลบรารี C char *strncpy(char *dest, const char *src, size_t n) คัดลอกอักขระสูงสุด n ตัวจากสตริงที่ชี้ไปที่ โดย src ไปยัง ปลายทาง . ในกรณีที่ความยาวของ src น้อยกว่า n ส่วนที่เหลือของปลายทางจะถูกบุด้วย null ไบต์
อาร์เรย์ของอักขระเรียกว่าสตริง
ประกาศ
ต่อไปนี้เป็นการประกาศอาร์เรย์ -
char stringname [size];
ตัวอย่างเช่น − char string[50]; สตริงที่มีความยาว 50 ตัวอักษร
การเริ่มต้น
- การใช้ค่าคงที่อักขระตัวเดียว −
char string[10] = { ‘H’, ‘e’, ‘l’, ‘l’, ‘o’ ,‘\0’} - การใช้ค่าคงที่สตริง −
char string[10] = "Hello":;
กำลังเข้าถึง − มีสตริงควบคุม "%s" ที่ใช้สำหรับเข้าถึงสตริงจนกว่าจะพบ '\0'
ฟังก์ชัน strncpy( )
-
ฟังก์ชันนี้ใช้สำหรับคัดลอกอักขระ 'n' ของสตริงต้นทางไปยังสตริงปลายทาง
-
ความยาวของสตริงปลายทางมากกว่าหรือเท่ากับสตริงต้นทาง
ไวยากรณ์มีดังนี้ −
strncpy (Destination string, Source String, n);
ตัวอย่างโปรแกรม
ต่อไปนี้เป็นโปรแกรม C สำหรับฟังก์ชัน strncpy() -
#include<string.h>
main ( ){
char a[50], b[50];
printf ("enter a string");
gets (a);
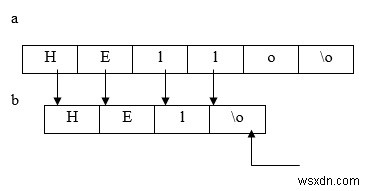
strncpy (b,a,3);
b[3] = '\0';
printf ("copied string = %s",b);
getch ( );
} ผลลัพธ์
เมื่อโปรแกรมข้างต้นทำงาน มันจะให้ผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้ −
Enter a string : Hello Copied string = Hel
นอกจากนี้ยังใช้สำหรับแยกสตริงย่อยด้วย
ตัวอย่างที่ 1
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดงการใช้ฟังก์ชัน strncpy()
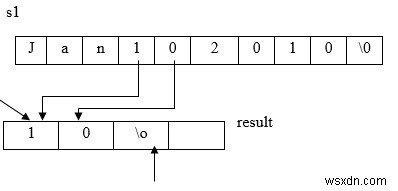
char result[10], s1[15] = "Jan 10 2010"; strncpy (result, &s1[4], 2); result[2] = ‘\0’
ผลลัพธ์
เมื่อโปรแกรมข้างต้นทำงาน มันจะให้ผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้ −
Result = 10
ตัวอย่างที่ 2
มาดูตัวอย่างอื่นใน strncpy
รับด้านล่างเป็นโปรแกรม C เพื่อคัดลอก n จำนวนอักขระจากสตริงต้นทางไปยังสตริงปลายทางโดยใช้ฟังก์ชันไลบรารี strncpy -
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main(){
//Declaring source and destination strings//
char source[45],destination[50];
char destination1[10],destination2[10],destination3[10],destination4[10];
//Reading source string and destination string from user//
printf("Enter the source string :");
gets(source);
//Extracting the new destination string using strncpy//
strncpy(destination1,source,2);
printf("The first destination value is : ");
destination1[2]='\0';//Garbage value is being printed in the o/p because always assign null value before printing O/p//
puts(destination1);
strncpy(destination2,&source[8],1);
printf("The second destination value is : ");
destination2[1]='\0';
puts(destination2);
strncpy(destination3,&source[12],1);
printf("The third destination value is : ");
destination3[1]='\0';
puts(destination3);
//Concatenate all the above results//
strcat(destination1,destination2);
strcat(destination1,destination3);
printf("The modified destination string :");
printf("%s3",destination1);//Is there a logical way to concatenate numbers to the destination string?//
} ผลลัพธ์
เมื่อโปรแกรมข้างต้นทำงาน มันจะให้ผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้ −
Enter the source string :Tutorials Point The first destination value is : Tu The second destination value is : s The third destination value is : i The modified destination string :Tusi3


