ฟังก์ชันไลบรารีสตริง
ฟังก์ชันที่กำหนดไว้ล่วงหน้าซึ่งออกแบบมาเพื่อจัดการกับสตริงมีอยู่ในไลบรารี "string.h" พวกมันคือ −
- strlen ()
- strcmp ()
- strcpy ()
- strncmp ()
- strncpy ()
- strrev ()
- strcat ()
- strstr ()
- strncat ()
ฟังก์ชัน strlen ()
ส่งกลับจำนวนอักขระในสตริง
ไวยากรณ์
int strlen (string name)
ตัวอย่าง
#include <string.h>
main (){
char a[30] = “Hello”;
int l;
l = strlen (a);
printf (“length of the string = %d”, l);
getch ();
} ผลลัพธ์
length of the string = 5
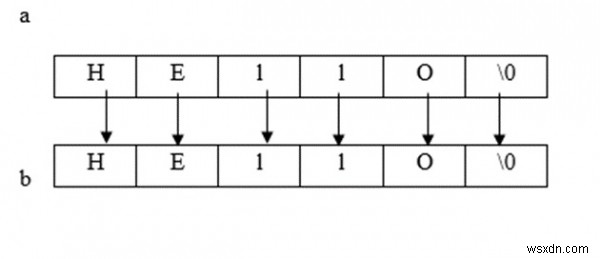
ฟังก์ชัน strcpy ()
- ใช้สำหรับคัดลอกสตริงต้นทางไปยังสตริงปลายทาง
- ความยาวของสตริงปลายทาง>=สตริงต้นทาง
ไวยากรณ์
strcpy (Destination string, Source String);
ตัวอย่างเช่น
1) char a[50]; strcpy (“Hello”,a); o/p: error 2) char a[50]; strcpy ( a,”hello”); o/p: a= “Hello”
ตัวอย่าง
#include <string.h>
main (){
char a[50], b[50];
printf ("enter a source string");
scanf("%s", a);
printf("enter destination string");
scanf("%s",b);
strcpy ( b,a);
printf ("copied string = %s",b);
getch ();
} ผลลัพธ์
Enter a source string : Hello Copied string = Hello
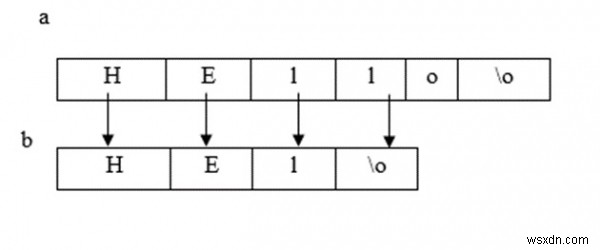
ฟังก์ชัน strncpy ()
-
มันคัดลอกอักขระ 'n' ของสตริงต้นทางไปยังสตริงปลายทาง
-
ความยาวของสตริงปลายทางต้อง>=ของสตริงต้นทาง
ไวยากรณ์
strncpy (Destination string, Source String, n);
ตัวอย่าง
#include<string.h>
main (){
char a[50], b[50];
printf ("enter a string");
gets (a);
gets(b);
strncpy (b,a,3);// copy first 3 char from a string
b[3] = '\0';
printf ("copied string = %s",b);
getch ();
} ผลลัพธ์
Enter a string : Hello Copied string = Hel It is also used for extracting substrings;
ฟังก์ชัน strcat ()
- รวมสองสายเข้าด้วยกัน
- ความยาวของสตริงปลายทางต้องเป็น> กว่าสตริงต้นทาง
ไวยากรณ์
strcat (Destination String, Source string);
ตัวอย่าง
#include <string.h>
main(){
char a[50] = "Hello";
char b[20] = "Good Morning";
clrscr ();
strcat (a,b);
printf("concatenated string = %s", a);
getch ();
} ผลลัพธ์
Concatenated string = Hello Good Morning
ฟังก์ชัน strncat ()
-
ใช้สำหรับการรวมหรือเชื่อมอักขระ n ตัวของสตริงหนึ่งเข้ากับอีกสตริงหนึ่ง
-
ความยาวของสตริงปลายทางต้องมากกว่าสตริงต้นทาง
-
สตริงที่ต่อกันที่เป็นผลลัพธ์จะอยู่ในสตริงปลายทาง
ไวยากรณ์
strncat (Destination String, Source string,n);
ตัวอย่าง
#include <string.h>
main (){
char a [30] = "Hello";
char b [20] = "Good Morning";
clrscr ();
strncat (a,b,4);
a [9] = '\0';
printf("concatenated string = %s", a);
getch ();
} ผลลัพธ์
Concatenated string = Hello Good.
ฟังก์ชัน strcmp() (การเปรียบเทียบสตริง)
-
ฟังก์ชันนี้เปรียบเทียบ 2 สตริง
-
ส่งกลับค่าความแตกต่าง ASCII ของอักขระที่ไม่ตรงกันสองตัวแรกในทั้งสองสตริง
ไวยากรณ์
int strcmp (string1, string2); //If the difference is equal to zero, then string1 = string2 //If the difference is positive, then string1 > string2 //If the difference is negative, then string1 < string2

ตัวอย่าง
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int main (){
char a[50], b [50];
int d;
printf ("Enter 2 strings:");
scanf ("%s %s", a,b);
d = strcmp(a,b);
if (d==0){
printf("%s is (alphabetically) equal to %s", a,b);
}else if (d>0){
printf("%s is (alphabetically) greater than %s",a,b);
}else if (d<0){
printf("%s is (alphabetically) less than %s", a,b);
}
} ผลลัพธ์
Enter 2 strings:apple ball apple is (alphabetically) less than ball
ฟังก์ชัน strnmp ()
ฟังก์ชันนี้ใช้สำหรับเปรียบเทียบอักขระ 'n' ตัวแรกของ 2 สตริง
ไวยากรณ์
strncmp ( string1, string2,2)
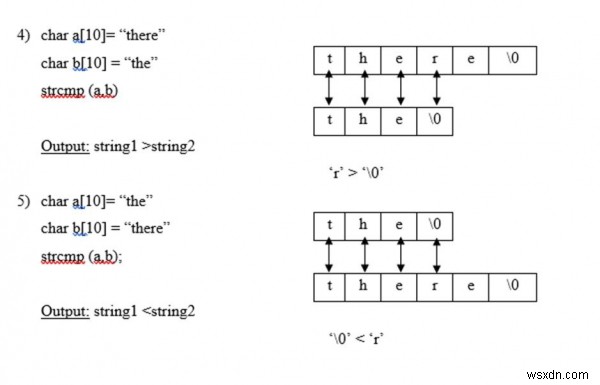
ตัวอย่างเช่น ถ่าน a[10] =“the”;
ถ่าน b[10] =“ที่นั่น”
strncmp (a,b,4);
เอาต์พุต - ทั้งสองสตริงเท่ากัน
ฟังก์ชัน strrev()
- ฟังก์ชันนี้ใช้สำหรับการย้อนกลับสตริง
- สตริงที่ย้อนกลับจะถูกเก็บไว้ในสตริงเดียวกัน
ไวยากรณ์
strrev (string)
ตัวอย่าง
#include<stdio.h>
main (){
char a[50] ;
clrscr();
printf ("enter a string");
gets (a);
strrev (a);
printf("reversed string = %s",a)
getch ();
} ผลลัพธ์
enter a string Hello reversed string = olleH
ฟังก์ชัน strstr()
-
ใช้เพื่อค้นหาว่าสตริงย่อยมีอยู่ในสตริงหลักหรือไม่
-
จะส่งกลับตัวชี้ไปที่การเกิดขึ้นครั้งแรกของ s2 ใน s1
ไวยากรณ์
strstr(mainsring,substring);
ตัวอย่าง
#include<stdio.h>
void main(){
char a[30],b[30];
char *found;
printf("Enter a string:\t");
gets(a);
printf("Enter the string to be searched for:\t");
gets(b);
found=strstr(a,b);
if(found)
printf("%s is found in %s in %d position",b,a,found-a);
else
printf("-1 since the string is not found");
getch();
} ผลลัพธ์
Enter a string: how are you Enter the string to be searched for: you you is found in 8 position


