ต่อไปนี้เป็นคำชี้แจงการตัดสินใจ -
- ง่าย – คำสั่ง if
- คำสั่ง if – else
- ซ้อน – คำสั่ง if else
- อย่างอื่น – ถ้าบันได
- เปลี่ยนคำสั่ง
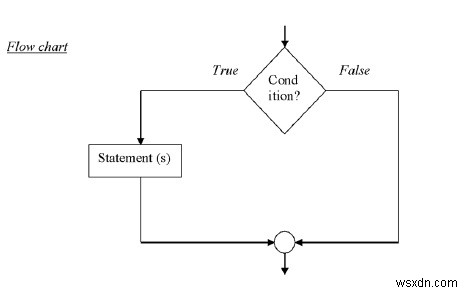
ง่าย – คำสั่ง if
คีย์เวิร์ด 'if' ใช้เพื่อดำเนินการชุดคำสั่งเมื่อเงื่อนไขตรรกะเป็นจริง
ไวยากรณ์
if (condition){
Statement (s)
}
ตัวอย่าง
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้ตรวจสอบว่าตัวเลขมากกว่า 50 หรือไม่
#include<stdio.h>
main (){
int a;
printf (“enter any number:\n”);
scanf (“%d”, &a);
if (a>50)
printf (“%d is greater than 50”, a);
} ผลลัพธ์
1) enter any number: 60 60 is greater than 50 . 2) enter any number 20 no output
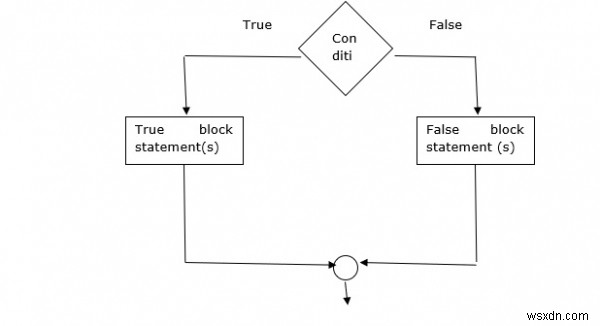
คำสั่ง if else
คำสั่ง if –else ใช้เงื่อนไขจริงหรือเท็จ
ไวยากรณ์
if (condition){
True block statement(s)
}
else{
False block statement(s)
} ผังงาน
ตัวอย่าง
ต่อไปนี้เป็นโปรแกรมตรวจสอบเลขคู่หรือคี่ −
#include<stdio.h>
main (){
int n;
printf (“enter any number:\n”);
scanf (“%d”, &n);
if (n%2 ==0)
printf (“%d is even number”, n);
else
printf( “%d is odd number”, n);
} ผลลัพธ์
1) enter any number: 10 10 is even number
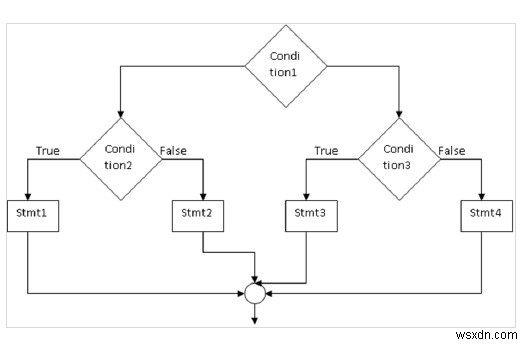
คำสั่ง if - else ซ้อนกัน
ที่นี่ 'if' ถูกวางไว้ในอีก if (หรือ) อื่น -
ไวยากรณ์
if (condition1){
if (condition2)
stmt1;
else
stmt2;
}
else{
if (condition3)
stmt3;
else
stmt4;
} ผังงาน
ตัวอย่าง
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้คือการพิมพ์ตัวเลขที่ใหญ่ที่สุดของ 3 ตัวเลขจากตัวเลขที่กำหนด -
#include<stdio.h>
main (){
int a,b,c;
printf (“enter 3 numbers”);
scanf (“%d%d%d”, &a, &b, &c);
if (a>b){
if (a>c)
printf (“%d is largest”, a);
else
printf (“%d is largest”, c);
} else {
if (b>c)
printf (“%d is largest”, b);
else
printf (“%d is largest”, c);
}
} ผลลัพธ์
enter 3 numbers = 10 20 30 30 is largest
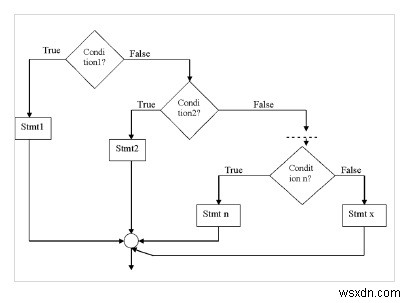
อย่างอื่น – ถ้าแลดเดอร์
เป็นเงื่อนไขการตัดสินใจแบบหลายทาง
ไวยากรณ์
if (condition1) stmt1; else if (condition2) stmt2; - - - - - - - - - - else if (condition n) stmt n; else stmt x;
ผังงาน
ตัวอย่าง
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้จะค้นหารากของสมการกำลังสอง -
#include <math.h>
main (){
int a,b,c,d;
float r1, r2
printf ("enter the values a b c");
scanf (“%d%d%d”, &a, &b, &c);
d= b*b – 4*a*c ;
if (d>0){
r1 = (-b+sqrt(d)) / (2*a);
r2 = (-b-sqrt(d)) / (2*a);
printf (“root1 ,root2 =%f%f”, r1, r2);
}
else if (d== 0){
r1 = -b / (2*a);
r2 = -b/ (2*a);
printf (“root1, root2 = %f%f”, r1, r2);
}
else
printf ("roots are imaginary”);
} ผลลัพธ์
1) enter the values of a b c : 1 4 3 Root 1 = -1 Root 2 = -3
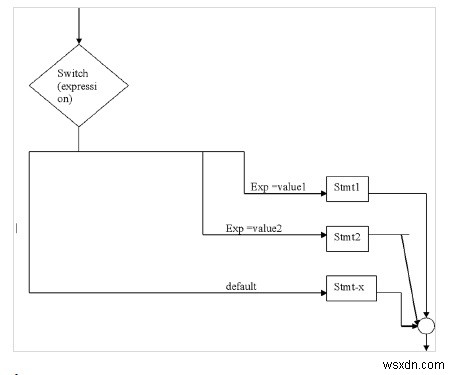
เปลี่ยนคำสั่ง
เป็นประโยชน์ในการเลือกหนึ่งในการตัดสินใจหลาย ๆ ครั้ง
ไวยากรณ์
switch (expression){
case value1 : stmt1;
break;
case value2 : stmt2;
break;
- - - - - -
default : stmt – x;
} ไวยากรณ์
ตัวอย่าง
#include<stdio.h>
main (){
int n;
printf (“enter a number”);
scanf (“%d”, &n);
switch (n){
case 0 : printf (“zero”)
break;
case 1 : printf (‘one”);
break;
default : printf (‘wrong choice”);
}
} ผลลัพธ์
enter a number 1 One


