สมมติว่าเรามีอาร์เรย์ที่เรียกว่าจุดที่มีบางจุดอยู่ในรูปแบบ (x, y) ตอนนี้ค่าใช้จ่ายในการเชื่อมต่อจุดสองจุด (xi, yi) และ (xj, yj) คือระยะห่างระหว่างจุดแมนฮัตตัน สูตรคือ |xi - xj| + |yi - yj|. เราต้องหาต้นทุนขั้นต่ำเพื่อเชื่อมต่อทุกจุด
ดังนั้น ถ้า input เหมือนกับ points =[(0,0),(3,3),(2,10),(6,3),(8,0)] แล้ว output จะเป็น 22 เพราะ
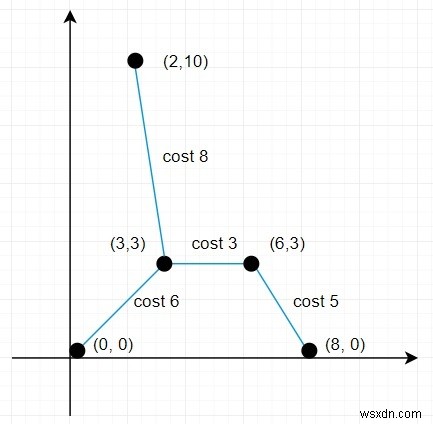
ดังนั้นระยะทางทั้งหมดคือ (6+5+3+8) =22
เพื่อแก้ปัญหานี้ เราจะทำตามขั้นตอนเหล่านี้ -
- points_set :=ชุดใหม่ถือตัวเลขจากช่วง 0 ถึงขนาดของจุด - 1
- heap :=สร้าง heap ด้วยคู่ (0, 0)
- visited_node :=ชุดใหม่
- total_distance :=0
- ในขณะที่ฮีปไม่ว่างเปล่าและขนาดของ visit_node <ขนาดของจุด ให้ทำ
- (ระยะทาง, current_index) :=ลบองค์ประกอบออกจากฮีป
- ถ้า current_index ไม่มีอยู่ใน visit_node แล้ว
- แทรก current_index ลงใน visit_node
- ลบ current_index ออกจาก points_set
- total_distance :=total_distance + ระยะทาง
- (x0, y0) :=คะแนน[current_index]
- สำหรับ next_index แต่ละรายการใน points_set ทำ
- (x1, y1) :=คะแนน[next_index]
- แทรก (|x0 - x1| + |y0 - y1| , next_index) ลงในฮีป
- คืนระยะทางทั้งหมด
ตัวอย่าง
ให้เราดูการใช้งานต่อไปนี้เพื่อความเข้าใจที่ดีขึ้น -
import heapq def solve(points): points_set = set(range(len(points))) heap = [(0, 0)] visited_node = set() total_distance = 0 while heap and len(visited_node) < len(points): distance, current_index = heapq.heappop(heap) if current_index not in visited_node: visited_node.add(current_index) points_set.discard(current_index) total_distance += distance x0, y0 = points[current_index] for next_index in points_set: x1, y1 = points[next_index] heapq.heappush(heap, (abs(x0 - x1) + abs(y0 - y1), next_index)) return total_distance points = [(0,0),(3,3),(2,10),(6,3),(8,0)] print(solve(points))
อินพุต
[(0,0),(3,3),(2,10),(6,3),(8,0)]
ผลลัพธ์
22


