ในระบบปฏิบัติการ Linux ไฟล์ที่ถูกลบจะไปอยู่ในถังขยะ เมื่อถังขยะว่างเปล่า ไฟล์จะถูกลบออกจากระบบ อย่างไรก็ตาม ด้วยความต้องการที่เพิ่มขึ้นสำหรับซอฟต์แวร์กู้คืน ไฟล์ที่ถูกลบจากถังขยะสามารถกู้คืนได้ในระดับหนึ่ง ซึ่งหมายความว่าไฟล์ที่ถูกนำออกจากถังขยะจะไม่เคยถูกลบอย่างถาวร แต่จะมองไม่เห็นด้วยตาของคุณ ไฟล์ยังคงอยู่ที่ใดที่หนึ่งบนฮาร์ดไดรฟ์ของคุณซึ่งใช้พื้นที่ที่ไม่จำเป็น และจะถูกลบออกทั้งหมดก็ต่อเมื่อมีการสร้างไฟล์ใหม่และจัดเก็บไว้ในเซกเตอร์เดียวกันของฮาร์ดไดรฟ์ของคุณ ในการกู้คืนพื้นที่ดิสก์อันมีค่าและหลีกเลี่ยงความเสียหายของไฟล์ สิ่งสำคัญคือต้องลบไฟล์ใน Linux อย่างถาวร
ต่อไปนี้เป็นขั้นตอนเล็กๆ น้อยๆ ในการลบไฟล์อย่างถาวรในระบบปฏิบัติการ Linux
เนื่องจากมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงในระบบปฏิบัติการ Linux และ Distros ที่มีอยู่หลายตัว เช่น Ubuntu, Mint, Fedora เป็นต้น ขั้นตอนในการลบไฟล์ใน Linux อาจแตกต่างกันไปตามขั้นตอน แต่แนวคิดพื้นฐานเบื้องหลังการลบไฟล์และโฟลเดอร์ยังคงเหมือนเดิม ขั้นตอนทั่วไปที่สามารถลบไดเร็กทอรีใน Linux อย่างถาวรโดยไม่ต้องฟอร์แมตฮาร์ดดิสก์คือ:
วิธีที่ 1. ลบตัวเลือกถังขยะ
มีตัวเลือกซึ่งเมื่อเลือกแล้ว จะอนุญาตให้ผู้ใช้ลบไฟล์ใน Linux ได้โดยตรงโดยไม่ต้องส่งไปที่ถังขยะ การเปิดใช้งานตัวเลือกนี้จะแตกต่างกันไปใน Linux ประเภทต่างๆ แต่กระบวนการที่ใช้เบื้องหลังฟีเจอร์นี้สามารถเป็นได้ทั้ง 2 อย่างที่กล่าวมาด้านล่าง:
- ลดขีดจำกัดถังขยะ
หาก Linux distro ของคุณรองรับ Dolphin file manager ให้เข้าไปที่ค่ากำหนดและทำเครื่องหมายถูกข้างช่องที่มีข้อความว่า Size และตั้งค่าขีดจำกัดเปอร์เซ็นต์เป็นค่าต่ำสุด เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าไฟล์ทั้งหมดที่มีขนาดใหญ่กว่าขนาดที่ตั้งไว้จะไม่ถูกจัดเก็บไว้ในถังขยะและจะถูกลบอย่างถาวร
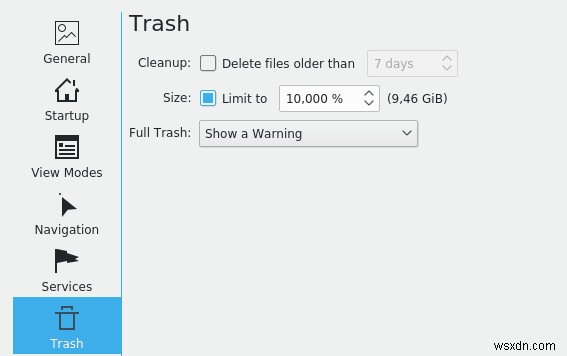
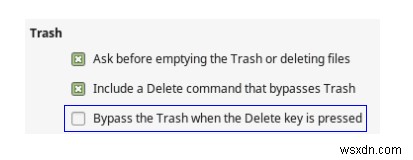
- หาก Linux ของคุณใช้ Nautilus หรือ Nemo file manager คุณจะได้รับตัวเลือกในการตั้งค่า File Manager เพื่อเปิดใช้งาน Bypass the Trash เมื่อกดปุ่ม Delete การดำเนินการนี้จะไม่ย้ายไฟล์ที่ถูกลบไปที่ถังขยะ
วิธีที่ 2 คุณสามารถฉีกไฟล์ได้ตลอดเวลา
Shred เป็นโปรแกรมที่พัฒนาโดย GNU Project ซึ่งฝังอยู่ในระบบปฏิบัติการ Linux ซึ่งสามารถใช้ลบไฟล์ใน Linux อย่างถาวร บรรทัดคำสั่งในการลบไฟล์เอกสารโดยใช้ชื่อ Test using Shred คือ:
shred -uvz -n 2 Test.doc
พารามิเตอร์ “u” จะลบไฟล์ก่อนที่จะเขียนทับ
พารามิเตอร์ “v” แสดงข้อมูลโดยละเอียด
พารามิเตอร์ “z” ป้องกันโอกาสในการกู้คืนข้อมูลที่ถูกลบ
พารามิเตอร์ “-n 2” ระบุการผ่านเพิ่มเติมเพื่อความปลอดภัยเป็นพิเศษ
In case, there are multiple files in a folder by the name of Music and you want to delete all of them, then use this command:
shred -uvz -n 2 Music/*.*
The name of the folder is specified as Music and the Asterix with a period and followed by another Asterix specifies to delete a file in Linux irrespective of their name or extension.
Method 3. Use Wipe.
The Linux Software distribution centre will allow you to install Wipe on your Linux Distro. It is like Shred program and is easy to use. The command line for deleting a file through Wipe is:
wipe Music/song1.mp3
Wipe is more secure than Shred and this means it is time-consuming as well. It also requests a confirmation from the user. To quicken the process, use appropriate flags such as:
f:using this flag will remove the confirmation.
c:wipe the file despite permissions.
q:quicken the process by bypassing all the security passes.
r:delete from a folder in Linux.
The simple Wipe command with all the flags would now appear as:
wipe -rfcq Music/song1.mp3
Method 4. Use Secure Delete.
Another tool that ensures removal of data from a hard drive is SRM, which is bundled in the Secure Delete suite. It is a quite efficient and quick tool and can even delete a directory in Linux. The command to delete a file is:
SRM is one of the tools in the Secure Delete suite of tools that specializes in secure removal of data from your HDD. It’s held by many as the best tool for this job.
Srm Music/song1.mp3
Like Wipe, deleting a file by SRM is a time-consuming process and can be made aster using flags. Some important flags are:
z:your file will be deleted and overwritten by zeros replacing the file for extra security.
v:this flag will provide verbose information about the process.
r:this will enable the recursive mode for subfolders.
1:the number one. This will reduce the time taken to complete the process.
The new command would then be:
srm -rlvz Music/Song1.jpg
Method 5. Install Bleachbit (GUI)
One of the best tools to find and delete unwanted files and even delete folders in Linux operating system is Bleachbit. It is known to free up space by securely erasing data that has not been used for a long time and can be used manually to target a few files that need to be deleted. It can be installed through the software centre by using the following command:
sudo apt install bleachbit
Once installed, run the interface and click on EDIT and choose Preferences. In the General Tab, there would be a list of different options. Place a checkmark in the box beside the option labelled as “Overwrite contents of files to prevent recovery”.
Next, to permanently delete a file on Linux, click File and choose Shred option. A prompt box will appear confirming your action. Click on Delete, and that will the last of the files selected.
The Final Word On Delete A File In Linux.
Although using a Linux operating system is a different experience, it is not difficult. All you must know the functions and features that are embedded in Linux. Being an Open-source, Linux has many options to do the same task, and these are some of the easy ones to delete a file in Linux permanently. Do subscribe to Systweak Blogs and our YouTube Channel for more tech-related updates.


