ให้ต้นไม้ไบนารี ภารกิจคือสลับโหนดลีฟเป็นคู่ ตัวอย่างเช่น −
อินพุต -
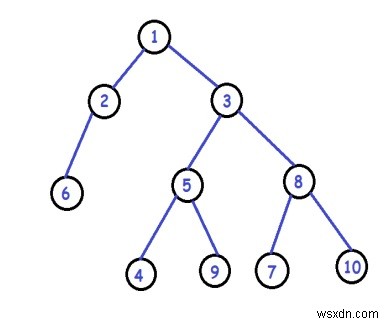
เอาท์พุต -
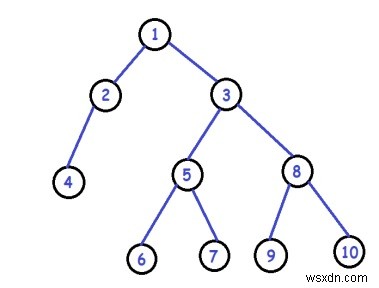
เราจะติดตามตัวชี้สองตัวที่ชี้ไปยังโหนดปลายทั้งสองที่อยู่ติดกัน และสลับค่าของพวกมันในปัญหาที่กำหนด
แนวทางในการหาแนวทางแก้ไข
ในแนวทางนี้ เราสำรวจต้นไม้ ค้นหาโหนดของใบไม้ และติดตามตัวนับของเราเพื่อตรวจสอบจำนวนปัจจุบัน เคล็ดลับหลักคือตัวนับของเราเป็นเลขคี่ ดังนั้นตัวชี้แรกของเราจึงชี้ไปที่โหนดนั้นในตอนนี้ เมื่อตัวนับของเรากลายเป็นคู่ เราจะสลับข้อมูล และด้วยเหตุนี้โหนดปลายสุดของเราจึงถูกสลับ
ตัวอย่าง
รหัส C++ สำหรับแนวทางข้างต้น
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node{ // structure of our tree node
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
void Swap(Node **a, Node **b){ // the swapping utility function
Node * temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
/********Pointers for leaf nodes for swapping********/
Node **firstleaf;
Node **secondleaf;
void SwapTheLeafNodes(Node **root, int &count){//recursive function for
//Swapping leaf nodes
if (!(*root)) // if root is null we return
return;
if(!(*root)->left &&!(*root)->right){ // condition for leaf node
secondleaf = root; // now we firstly make our second pointer point to this node
count++; // we also increment the count
if (count%2 == 0) // now if our count is even that means we have a pair so we can swap them
Swap(firstleaf, secondleaf);
else // if count is odd so that means we only got first node yet
firstleaf = secondleaf;
}
if ((*root)->left)
SwapTheLeafNodes(&(*root)->left, count);
if ((*root)->right)
SwapTheLeafNodes(&(*root)->right, count);
}
Node* newNode(int data){ // function for initializing new node
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void printInorder(Node* node){ // inorder traversal function
if (node == NULL)
return;
printInorder(node->left);
printf("%d ", node->data);
printInorder(node->right);
}
int main(){
/* Creating binary tree*/
Node *root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->right->left = newNode(5);
root->right->right = newNode(8);
root->right->left->left = newNode(6);
root->right->left->right = newNode(7);
root->right->right->left = newNode(9);
root->right->right->right = newNode(10);
cout << "Inorder traversal before swap:\n";
printInorder(root);
cout << "\n";
int count = 0; // out counter for keeping track of leaf nodes
SwapTheLeafNodes(&root, count); // swapping the nodes
cout << "Inorder traversal after swap:\n";
printInorder(root);
cout << "\n";
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
Inorder traversal before swap: 4 2 1 6 5 7 3 9 8 10 Inorder traversal after swap: 6 2 1 4 5 9 3 7 8 10
คำอธิบายของโค้ดด้านบน
ในแนวทางข้างต้น เราเพียงแค่สร้างตัวชี้สองตัวที่จะติดตามโหนดปลายสุดของเรา เราสำรวจต้นไม้เมื่อเราพบโหนดใบ ขั้นแรก ให้ตัวชี้ตัวที่สองชี้ไปที่โหนดนั้น ตอนนี้เราเพิ่มตัวแปรการนับตอนนี้ถ้าการนับของเราเป็นคู่ ดังนั้นเราจึงสลับโหนดและหากการนับเป็นเลขคี่ นั่นหมายความว่าเราพบเพียงองค์ประกอบแรกของคู่ของเราเท่านั้น เราจึง เก็บค่านั้นไว้ในตัวชี้แรก และนี่คือวิธีการทำงานของฟังก์ชันของเรา
บทสรุป
ในบทช่วยสอนนี้ เราจะแก้ปัญหาของโหนดลีฟ Pairwise Swap ในไบนารีทรี นอกจากนี้เรายังได้เรียนรู้โปรแกรม C ++ สำหรับปัญหานี้และแนวทางที่สมบูรณ์ ( Normal และ มีประสิทธิภาพ ) โดยที่เราแก้ไขปัญหานี้ เราสามารถเขียนโปรแกรมเดียวกันในภาษาอื่นๆ เช่น C, java, python และภาษาอื่นๆ เราหวังว่าคุณจะพบว่าบทช่วยสอนนี้มีประโยชน์


