ในปัญหานี้ เราได้รับไบนารีทรี งานของเราคือพิมพ์โหนดทั้งหมดของทรีที่เป็นโหนดเต็ม
ต้นไม้ไบนารี เป็นต้นไม้ที่โหนดสามารถมีโหนดย่อยได้สูงสุด 2 โหนด โหนดหรือจุดยอดต้องไม่มีโหนด โหนดย่อยหนึ่งโหนดหรือโหนดย่อยสองโหนด
ตัวอย่าง −
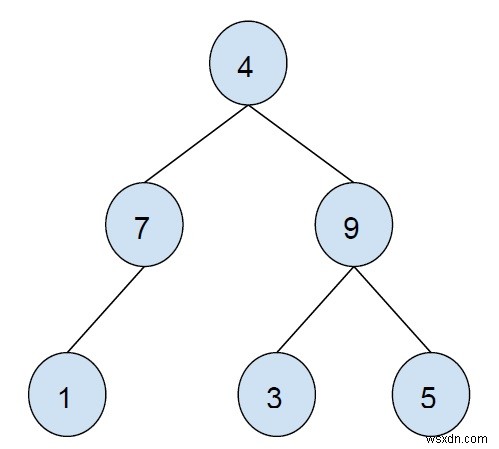
โหนดเต็ม เป็นโหนดที่มีทั้งลูกซ้ายและขวา กล่าวอีกนัยหนึ่ง โหนดที่มีชายด์ด้านซ้ายและขวาเป็นโหนดแบบเต็ม ในไบนารีทรีด้านบน 4 และ 9 เป็นโหนดเต็ม
มาดูตัวอย่างเพื่อทำความเข้าใจปัญหากัน −
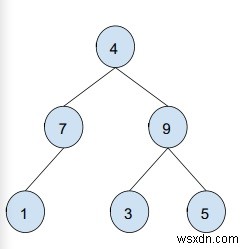
ผลผลิต − 4 9
วิธีที่ง่ายและสะดวกในการแก้ปัญหานี้คือการสำรวจต้นไม้โดยใช้อัลกอริธึมการข้ามผ่านใดๆ ตรวจสอบว่าโหนดปัจจุบันมีลูกหรือโหนดซ้ายและขวา ถ้าใช่ ให้พิมพ์ค่าของโหนดเป็นอย่างอื่น ปล่อยไว้
ตัวอย่าง
โปรแกรมเพื่อแสดงโซลูชันของเรา
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
};
Node *insertNode(int data){
Node *temp = new Node;
temp->data = data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void printFullNode(Node *root){
if (root != NULL){
printFullNode(root->left);
if (root->left != NULL && root->right != NULL)
cout<<root->data<<"\t";
printFullNode(root->right);
}
}
int main(){
Node* root = insertNode(100);
root->left = insertNode(56);
root->right = insertNode(12);
root->left->left = insertNode(89);
root->right->left = insertNode(32);
root->right->right = insertNode(45);
cout<<"All full nodes of the tree are :\n";
printFullNode(root);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
All full nodes of the tree are − 100 12


