กำหนดไบนารีทรีที่มีน้ำหนักของโหนดเป็นตัวเลข เป้าหมายคือการหาจำนวนโหนดที่มีน้ำหนักจนเป็นตัวเลขฟีโบนักชีตัวเลขในชุดฟีโบนักชีคือ:0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13….n ตัวเลขคือผลรวมของ (n-1) และ (n-2) หากน้ำหนักเท่ากับ 13 แสดงว่าเป็นเลขฟีโบนักชี ดังนั้นโหนดจะถูกนับ
ตัวอย่าง
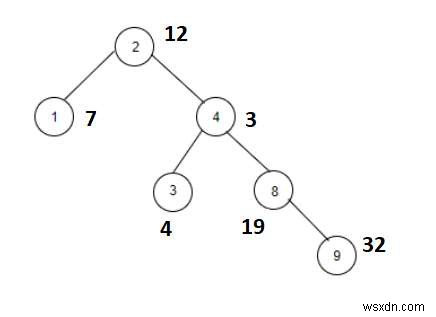
อินพุต
อุณหภูมิ =1. ต้นไม้ที่จะถูกสร้างขึ้นหลังจากป้อนค่าจะได้รับด้านล่าง -
ผลลัพธ์
Count the nodes whose sum with X is a Fibonacci number are: 3
คำอธิบาย
we are given with the tree nodes and the weights associated with each node. Now we check whether the temp+weight is a Fibonacci number or not.
| โหนด | น้ำหนัก | น้ำหนัก+อุณหภูมิ=ฟีโบนักชี | ใช่/ไม่ใช่ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 12 | 12+1=13 | ใช่ |
| 1 | 7 | 7+1=8 | ใช่ |
| 4 | 3 | 3+1=4 | ไม่ |
| 3 | 4 | 4+1=5 | ใช่ |
| 8 | 19 | 19+1=20 | ไม่ |
| 9 | 32 | 32+1=33 | ไม่ |
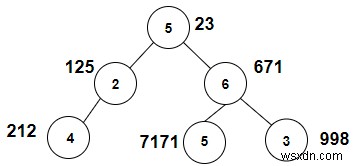
อินพุต
temp =3 ต้นไม้ที่จะถูกสร้างขึ้นหลังจากป้อนค่าจะได้รับด้านล่าง -
ผลลัพธ์
Count the nodes whose sum with X is a Fibonacci number are: 3
คำอธิบาย
we are given with the tree nodes and the weights associated with each node. Now we check whether the temp+weight is a Fibonacci number or not.
| โหนด | น้ำหนัก | น้ำหนัก+อุณหภูมิ=ฟีโบนักชี | ใช่/ไม่ใช่ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 23 | 23+3=26 | ไม่ |
| 2 | 125 | 125+3=128 | ไม่ |
| 6 | 671 | 671+3=674 | ไม่ |
| 4 | 212 | 212+3=215 | ไม่ |
| 5 | 7171 | 7171+3=7174 | ไม่ |
| 3 | 998 | 998+3=1001 | ไม่ |
แนวทางที่ใช้ในโปรแกรมด้านล่างมีดังนี้ −
ในแนวทางนี้ เราจะใช้ DFS บนกราฟของทรีเพื่อสำรวจมัน และตรวจสอบว่าน้ำหนักของโหนดและอุณหภูมิรวมกันเป็นตัวเลขฟีโบนักชีหรือไม่ ใช้ vectorsNode_Weight(100) และ edge_graph[100] สองตัวเพื่อจุดประสงค์นี้
-
เริ่มต้น Node_Weight[] ด้วยน้ำหนักของโหนด
-
สร้างต้นไม้โดยใช้ vector edge_graph
-
หาค่าตัวแปรโกลบอล Fibonacci และเริ่มต้นมันด้วย 0 ใช้ค่าตัวแปรส่วนกลางอื่น ๆ
-
ฟังก์ชัน check_square(long double val) ใช้จำนวนเต็มและคืนค่า จริง หาก val เป็นกำลังสองสมบูรณ์
-
ใช้ val_1 =sqrt(val)
-
ตอนนี้ถ้า (val_1 − floor(val_1) ==0) คืนค่า จริง ผลรวมจะเป็นกำลังสองสมบูรณ์ ให้คืนค่า จริง
-
คืนค่าเท็จมิฉะนั้น
-
ฟังก์ชัน check_Fibonacci(int num) รับค่าตัวเลขและคืนค่า true หากเป็นตัวเลข afibonacci
-
เริ่มต้น fib ด้วย 5*num*num.
-
ถ้า check_square((fib + 4)) || check_square((fib − 4)) ผลลัพธ์เป็น true แล้วคืนค่าเป็น true
-
คืนค่าเท็จมิฉะนั้น
-
ฟังก์ชัน Fibonacci_number(int node, int root) ส่งกลับจำนวนโหนดที่มี X เป็นตัวเลข Fibonacci
-
ถ้า if(check_Fibonacci(Node_Weight[node] + temp)) คืนค่า true แล้ว incrementFibonacci
-
ต้นไม้ขวางใน vector edge_graph[node] ใช้สำหรับวนซ้ำ
-
เรียก Fibonacci_number(it, node) สำหรับโหนดถัดไปในเวกเตอร์
-
ที่ส่วนท้ายของฟังก์ชันทั้งหมด เราจะมีฟีโบนักชีเป็นจำนวนโหนดที่มีน้ำหนักรวมโดยมีอุณหภูมิเป็นตัวเลขฟีโบนักชี
ตัวอย่าง
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> Node_Weight(100);
vector<int> edge_graph[100];
int Fibonacci = 0, temp;
bool check_square(long double val){
long double val_1 = sqrt(val);
if(val_1 − floor(val_1) == 0){
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool check_Fibonacci(int num){
int fib = 5 * num * num;
if(check_square((fib + 4)) || check_square((fib − 4))){
return true;
}
return false;
}
void Fibonacci_number(int node, int root){
if(check_Fibonacci(Node_Weight[node] + temp)){
Fibonacci++;
}
for (int it : edge_graph[node]){
if(it == root){
continue;
}
Fibonacci_number(it, node);
}
}
int main(){
//weight of the nodes
Node_Weight[2] = 6;
Node_Weight[1] = 4;
Node_Weight[4] = 23;
Node_Weight[3] = 5;
Node_Weight[8] = 161;
Node_Weight[9] = 434;
//create graph edge
edge_graph[2].push_back(1);
edge_graph[2].push_back(4);
edge_graph[4].push_back(3);
edge_graph[4].push_back(8);
edge_graph[8].push_back(9);
temp = 3;
Fibonacci_number(2, 2);
cout<<"Count the nodes whose sum with X is a Fibonacci number are: "<<Fibonacci;
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
หากเราเรียกใช้โค้ดข้างต้น มันจะสร้างผลลัพธ์ต่อไปนี้ -
Count the nodes whose sum with X is a Fibonacci number are: 1


