ในปัญหานี้ เราได้รับ N vertex tree และ Q เคียวรีแต่ละรายการประกอบด้วยสองค่า i และ j งานของเราคือการสร้างโปรแกรมเพื่อแก้ปัญหา Query สำหรับความสัมพันธ์บรรพบุรุษ-ลูกหลานในต้นไม้
ในการแก้ปัญหาแต่ละคำถาม เราต้องตรวจสอบว่าโหนด i เป็นบรรพบุรุษของโหนด j ในแผนผังหรือไม่
มาดูตัวอย่างเพื่อทำความเข้าใจปัญหากัน
อินพุต
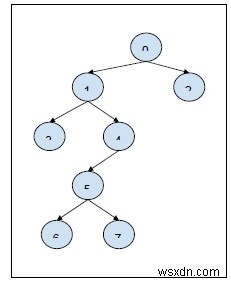
Q = 2, query[][] = {{3, 5}, {1, 6}} ผลลัพธ์
No Yes
คำอธิบาย
i = 3, j = 5: The node 3 is not the ancestor of node 5. Return NO. i = 1, j = 6: The node 1 is the ancestor of node 6. Return YES.
แนวทางการแก้ปัญหา
วิธีแก้ปัญหาคือการใช้เทคนิคการข้ามต้นไม้ซึ่งก็คือ DFS (การค้นหาเชิงลึกก่อน) เราจะสำรวจจากโหนด ith และทำลงไปที่ลูกหลานทั้งหมด จากนั้นตรวจสอบว่าโหนด jth เป็นลูกหลานของโหนดนั้นหรือไม่ วิธีที่มีประสิทธิภาพในการแก้ปัญหาคือการค้นหาเวลาเข้าและหมดเวลาของแต่ละโหนด และตรวจสอบว่ามีความสัมพันธ์แบบบรรพบุรุษ-ทายาทหรือไม่
โปรแกรมเพื่อแสดงการทำงานของโซลูชันของเรา
ตัวอย่าง
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void depthFirstSearch(vector<int> g[], int u, int parent, int entTime[], int exitTime[], int& cnt){
entTime[u] = cnt++;
for (int i = 0; i < g[u].size(); i++) {
int v = g[u][i];
if (v != parent) depthFirstSearch(g, v, u, entTime, exitTime, cnt);
}
exitTime[u] = cnt++;
}
void calcTimeInAndOut(int edges[][2], int V, int entTime[], int exitTime[]){
vector<int> g[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V - 1; i++) {
int u = edges[i][0];
int v = edges[i][1];
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
int cnt = 0; depthFirstSearch(g, 0, -1, entTime, exitTime, cnt);
}
int main(){
int edges[][2] = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 }, { 1, 3 }, { 1, 4 }, { 4, 5 }, { 5, 6 }, { 5, 7 }};
int E = sizeof(edges) / sizeof(edges[0]);
int V = E + 1;
int Q = 2;
int query[Q][2] = {{3, 5}, {1, 6}};
int entTime[V], exitTime[V];
calcTimeInAndOut(edges, V, entTime, exitTime);
for(int i = 0; i < Q; i++){
cout<<"For query "<<(i+1)<<" : "; (entTime[query[i][0]] <= entTime[query[i][1]] && exitTime[query[i][0]] <= exitTime[query[i][1]])? cout<<"is Ancestor\n":cout<<"is not Ancestor\n";
}
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
For query 1 : is Ancestor For query 2 : is not Ancestor


