ในปัญหานี้ เราจะได้รับ Binary Tree โดยที่แต่ละโหนดมีค่า หน้าที่ของเราคือสร้างโปรแกรมเพื่อค้นหาผลรวมสูงสุดของโหนดใน Binarytree เพื่อไม่ให้มีสองตัวอยู่ติดกัน โดยใช้ Dynamic Programming
คำอธิบายปัญหา − เราจะเลือกชุดย่อยของไบนารีทรีเพื่อให้ผลรวมสูงสุดในลักษณะที่โหนดไม่ได้เชื่อมต่อโดยตรง
มาดูตัวอย่างเพื่อทำความเข้าใจปัญหากัน
อินพุต
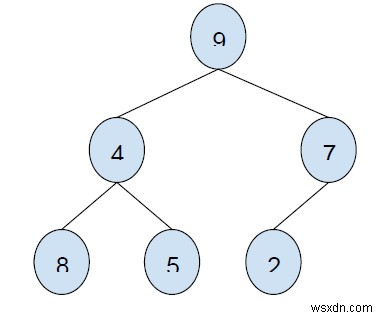
ผลลัพธ์
24
คำอธิบาย
Elements to be taken under consideration are: 8 + 5 + 9 + 2 = 24
แนวทางการแก้ปัญหา
วิธีแก้ปัญหาคือการใช้แผนที่และค้นหาผลรวมของโหนดที่ก่อตัวเป็น maxSum ทั้งโหนดและลูกไม่สามารถ
พิจารณาผลรวมตามเงื่อนไขที่กำหนด ดังนั้น เราต้องตรวจสอบข้อเท็จจริงก่อนว่าก่อนที่จะพิจารณาโหนด เราจำเป็นต้องตรวจสอบว่าแผนผังย่อยของโหนดมีองค์ประกอบที่เป็นผลรวมที่มากกว่าหรือไม่
การค้นหาผลรวมของทรีย่อย parent-child เดียวกันหลายครั้งสำหรับแต่ละโหนดจะเพิ่มค่าใช้จ่ายในการคำนวณ และเพื่อจัดการกับมัน เราจะใช้การท่องจำและเก็บ maxSum ไว้จนถึงโหนดในแผนที่ซึ่งสามารถใช้ได้ในภายหลัง
ตัวอย่าง
โปรแกรมเพื่อแสดงการทำงานของโซลูชันของเรา
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int data;
struct node *left, *right;
};
struct node* newNode(int data){
struct node *temp = new struct node;
temp−>data = data;
temp−>left = temp−>right = NULL;
return temp;
}
int findMaxSumBT(node* node, map<struct node*, int>& nodeSum);
int sumSubTreeNodes(node* node, map<struct node*, int>& nodeSum){
int maxSum = 0;
if (node−>left)
maxSum += findMaxSumBT(node−>left−>left, nodeSum) +
findMaxSumBT(node−>left−>right, nodeSum);
if (node−>right)
maxSum += findMaxSumBT(node−>right−>left, nodeSum) +
findMaxSumBT(node−>right−>right, nodeSum);
return maxSum;
}
int findMaxSumBT(node* node, map<struct node*, int>& nodeSum){
if (node == NULL)
return 0;
if (nodeSum.find(node) != nodeSum.end())
return nodeSum[node];
int sumInclCurr = node−>data + sumSubTreeNodes(node, nodeSum);
int sumExclCurr = findMaxSumBT(node−>left, nodeSum) +
findMaxSumBT(node−>right, nodeSum);
nodeSum[node] = max(sumInclCurr, sumExclCurr);
return nodeSum[node];
}
int main(){
node* root = newNode(9);
root−>left = newNode(4);
root−>right = newNode(7);
root−>left−>left = newNode(8);
root−>left−>right = newNode(5);
root−>right−>left = newNode(2);
map<struct node*, int> nodeSum;
cout<<"Maximum sum of nodes in Binary tree such that no two are
adjacent using Dynamic Programming is "<<findMaxSumBT(root,
nodeSum);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
Maximum sum of nodes in Binary tree such that no two are adjacent using Dynamic Programming is 24


