เราได้รับกราฟแบบไม่มีทิศทางและแบบไม่ถ่วงน้ำหนักเป็นอินพุต และภารกิจคือการหาผลคูณของรอบที่เกิดขึ้นในกราฟที่กำหนดและแสดงผล
ตัวอย่าง
ป้อนข้อมูล
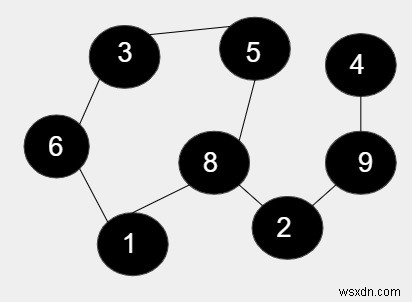
ในรูปมี 8 โหนดและจาก 5 โหนดกำลังสร้างวงจรรวมถึง 1, 6, 3, 5, 8 และส่วนที่เหลือของโหนดจะไม่รวมอยู่ในวงจร ดังนั้น ความยาวของวงจรคือ 5 เนื่องจากมี 5 โหนด ดังนั้น ผลิตภัณฑ์จึงเป็น 5
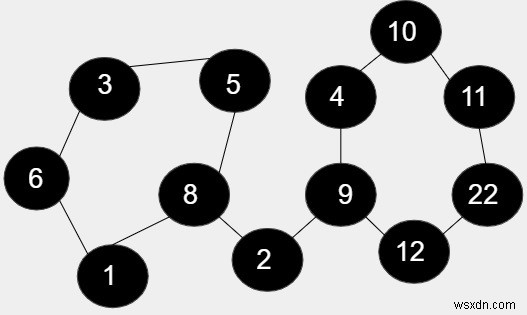
ในรูปมี 12 โหนด และ 11(5 +6) โหนดนั้นกำลังก่อตัว ได้แก่ 1, 6, 3, 5, 8 และ 9, 4, 10, 11, 22, 12 และส่วนที่เหลือ โหนด 2 ไม่รวมอยู่ในวงจร ดังนั้น ความยาวของรอบคือ 5 * 6 =30
แนวทางที่ใช้ในโปรแกรมด้านล่างมีดังนี้ −
- ใส่โหนดสำหรับสร้างวงจร
- สร้างฟังก์ชัน DFS และเรียกให้สำรวจจุดยอดด้วยการระบายสี
- โหนดถูกทำเครื่องหมายว่าเยี่ยมชมอย่างสมบูรณ์หรือเยี่ยมชมบางส่วน
- โหนดที่เข้าชมโดยสมบูรณ์ไม่จำเป็นต้องถูกเข้าชมอีกครั้ง และด้วยเหตุนี้จึงไม่จำเป็นต้องจัดเก็บในขณะที่โหนดที่เข้าชมบางส่วนจำเป็นต้องถูกจัดเก็บเนื่องจากมีการเข้าชมอีกครั้ง
- พิมพ์ผลลัพธ์
อัลกอริทึม
Start Step 1-> declare function to traverse the graph using DFS approach void DFS(int i, int j, int color[], int highlight[], int parent[], int& number) IF color[i] = 2 Return End IF color[i] = 1 Set number++ Declare and set int temp = j Set highlight[temp] = number Loop While temp != i Set temp = parent[temp] Set highlight[temp] = number End Return End Set parent[i] = j Set color[i] = 1 For int k : graph[i] IF k = parent[i] Continue End Call DFS(k, i, color, highlight, parent, number) End Set color[i] = 2 Step 2-> declare function to find product of nodes in cycle int product(int edge, int highlight[], int& number) call unordered_map<int, int> mp Loop For i = 1 and i <= edge and i++ IF (highlight[i] != 0) Set mp[highlight[i]]++ End End Declare and set int temp = 1 Loop For i = 1 and i <= number and i++ Set temp = temp * mp[i] End IF number = 0 Set temp = 0 End return temp Step 3-> In main() Call function as insert(1, 2) to insert a node Declare int color[size], parent[size] Declare int highlight[size] Declare and set int number = 0 Declare and set int edge = 10 Call DFS(1, 0, color, highlight, parent, number) Call print function as product(edge, highlight, number) Stop
ตัวอย่าง
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int size = 100000;
vector<int> graph[size];
//function to traverse the graph using DFS approach
void DFS(int i, int j, int color[], int highlight[], int parent[], int& number) {
// for travered node
if (color[i] == 2) {
return;
}
//not completely visited
if (color[i] == 1) {
number++;
int temp = j;
highlight[temp] = number;
//for backtracking the vertex
while (temp != i) {
temp = parent[temp];
highlight[temp] = number;
}
return;
}
parent[i] = j;
color[i] = 1;
for (int k : graph[i]) {
if (k == parent[i]) {
continue;
}
DFS(k, i, color, highlight, parent, number);
}
color[i] = 2;
}
// function for inserting edges to graph
void insert(int u, int v) {
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
// Find product of nodes in cycle
int product(int edge, int highlight[], int& number) {
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
for (int i = 1; i <= edge; i++) {
if (highlight[i] != 0)
mp[highlight[i]]++;
}
int temp = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= number; i++) {
temp = temp * mp[i];
}
if (number == 0)
temp = 0;
return temp;
}
int main() {
//for inserting a node in the graph
insert(1, 2);
insert(2, 3);
insert(3, 4);
insert(4, 6);
insert(4, 7);
insert(5, 6);
insert(3, 5);
insert(7, 8);
insert(6, 10);
insert(5, 9);
insert(10, 11);
int color[size], parent[size];
int highlight[size];
int number = 0;
int edge = 10;
DFS(1, 0, color, highlight, parent, number);
// function to print the cycles
cout<<"product of all the nodes in the cycle is :"<< product(edge, highlight, number);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
Product of all the nodes in the cycle is :4


