เพื่อให้เข้าใจแนวคิดนี้ดีขึ้น เรามาสรุปเนื้อหาพื้นฐานที่จำเป็นกันก่อน
รายการที่เชื่อมโยง เป็นโครงสร้างข้อมูลที่จัดเก็บแต่ละองค์ประกอบเป็นวัตถุในโหนดของรายการ ทุกโน้ตจะมีข้อมูลสองส่วน han และลิงก์ไปยังโหนดถัดไป
พหุนาม เป็นนิพจน์ทางคณิตศาสตร์ที่ประกอบด้วยตัวแปรและสัมประสิทธิ์ เช่น x^2 - 4x + 7
ใน รายการเชื่อมโยงพหุนาม สัมประสิทธิ์และเลขชี้กำลังของพหุนามถูกกำหนดให้เป็นโหนดข้อมูลของรายการ
สำหรับการเพิ่มพหุนามสองตัวที่เก็บไว้เป็นรายการที่เชื่อมโยง เราต้องบวกค่าสัมประสิทธิ์ของตัวแปรด้วยกำลังเท่ากัน ในโหนดรายการที่เชื่อมโยงมีสมาชิก 3 ราย ค่าสัมประสิทธิ์จะลิงก์ไปยังโหนดถัดไป
รายการเชื่อมโยงที่ใช้เก็บพหุนามมีลักษณะดังนี้ -
พหุนาม :4x 7 + 12x 2 +45
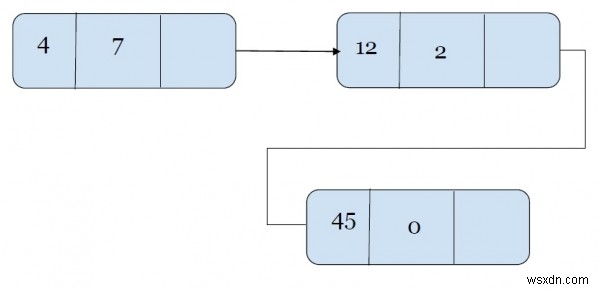
นี่คือลักษณะของรายการเชื่อมโยงที่แสดงพหุนาม
การเพิ่มพหุนามสองตัวที่แสดงโดยรายการที่เชื่อมโยง เราตรวจสอบค่าที่ค่าเลขชี้กำลังของโหนด สำหรับค่าเลขชี้กำลังเดียวกัน เราจะบวกค่าสัมประสิทธิ์
ตัวอย่าง
Input : p1= 13x8 + 7x5 + 32x2 + 54 p2= 3x12 + 17x5 + 3x3 + 98 Output : 3x12 + 13x8 + 24x5 + 3x3 + 32x2 + 152
คำอธิบาย − สำหรับกำลังทั้งหมด เราจะตรวจสอบค่าสัมประสิทธิ์ของเลขชี้กำลังที่มีค่าเลขชี้กำลังเท่ากันและนำมาบวกกัน ส่งคืนพหุนามสุดท้าย
อัลกอริทึม
ป้อนข้อมูล − พหุนาม p1 และ p2 แสดงเป็นรายการที่เชื่อมโยง
Step 1: loop around all values of linked list and follow step 2& 3. Step 2: if the value of a node’s exponent. is greater copy this node to result node and head towards the next node. Step 3: if the values of both node’s exponent is same add the coefficients and then copy the added value with node to the result. Step 4: Print the resultant node.
ตัวอย่าง
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node{
int coeff;
int pow;
struct Node *next;
};
void create_node(int x, int y, struct Node **temp){
struct Node *r, *z;
z = *temp;
if(z == NULL){
r =(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
r->coeff = x;
r->pow = y;
*temp = r;
r->next = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
r = r->next;
r->next = NULL;
} else {
r->coeff = x;
r->pow = y;
r->next = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
r = r->next;
r->next = NULL;
}
}
void polyadd(struct Node *p1, struct Node *p2, struct Node *result){
while(p1->next && p2->next){
if(p1->pow > p2->pow){
result->pow = p1->pow;
result->coeff = p1->coeff;
p1 = p1->next;
}
else if(p1->pow < p2->pow){
result->pow = p2->pow;
result->coeff = p2->coeff;
p2 = p2->next;
} else {
result->pow = p1->pow;
result->coeff = p1->coeff+p2->coeff;
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
}
result->next = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
result = result->next;
result->next = NULL;
}
while(p1->next || p2->next){
if(p1->next){
result->pow = p1->pow;
result->coeff = p1->coeff;
p1 = p1->next;
}
if(p2->next){
result->pow = p2->pow;
result->coeff = p2->coeff;
p2 = p2->next;
}
result->next = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
result = result->next;
result->next = NULL;
}
}
void printpoly(struct Node *node){
while(node->next != NULL){
printf("%dx^%d", node->coeff, node->pow);
node = node->next;
if(node->next != NULL)
printf(" + ");
}
}
int main(){
struct Node *p1 = NULL, *p2 = NULL, *result = NULL;
create_node(41,7,&p1);
create_node(12,5,&p1);
create_node(65,0,&p1);
create_node(21,5,&p2);
create_node(15,2,&p2);
printf("polynomial 1: ");
printpoly(p1);
printf("\npolynomial 2: ");
printpoly(p2);
result = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
polyadd(p1, p2, result);
printf("\npolynomial after adding p1 and p2 : ");
printpoly(result);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
polynomial 1: 41x^7 + 12x^5 + 65x^0 polynomial 2: 21x^5 + 15x^2 polynomial after adding p1 and p2 : 41x^7 + 33x^5 + 15x^2 + 65x^0


