สมมุติว่าเราได้รับพหุนามสองพหุนามและเราต้องหาการบวกพหุนามสองตัว พหุนามจะต้องแสดงเป็นรายการที่เชื่อมโยง เงื่อนไขของพหุนามจะแสดงเป็นโหนดรายการที่เชื่อมโยง โหนดรายการที่เชื่อมโยงแต่ละโหนดจะประกอบด้วยค่าสัมประสิทธิ์ ค่ากำลัง และตัวชี้ไปยังโหนดรายการที่เชื่อมโยงถัดไป เราต้องส่งกลับรายการเชื่อมโยงที่สามซึ่งเป็นการเพิ่มพหุนามของรายการที่เชื่อมโยงสองรายการ
ดังนั้นหากอินพุตเป็นแบบ
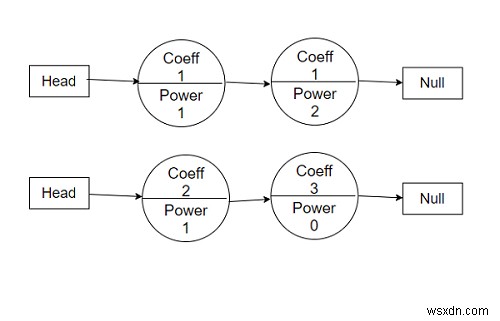
1x^1 + 1x^2 =0 และ 2x^1 + 3x^0 =0,
แล้วผลลัพธ์จะเป็น 3x^1 + 1x^2 + 3x^0 =0
เพื่อแก้ปัญหานี้ เราจะทำตามขั้นตอนเหล่านี้ -
-
dummy :=โหนดพหุนามใหม่
-
โหนด :=โหนดพหุนามใหม่
-
ในขณะที่ poly1 และ poly2 ไม่ว่างเปล่าให้ทำ
-
ถ้ากำลังของ poly1> กำลังของ poly2 แล้ว
-
ถัดไปของโหนด :=poly1
-
โหนด :=poly1
-
poly1 :=ถัดจาก poly1
-
-
มิฉะนั้นเมื่อกำลังของ poly1 <พลังของ poly2 แล้ว
-
ถัดไปของโหนด :=poly2
-
โหนด :=poly2
-
poly2 :=ถัดจาก poly2
-
-
มิฉะนั้น
-
coef :=สัมประสิทธิ์ของ poly1 + สัมประสิทธิ์ของ poly2
-
ถ้า coef ไม่ใช่ศูนย์ แล้ว
-
poly1 :=ถัดจาก poly1
-
poly2 :=ถัดจาก poly2
-
-
-
-
ถัดไปของโหนด :=poly1 หรือ poly2
-
กลับมาต่อจากดัมมี่
ให้เราดูการใช้งานต่อไปนี้เพื่อความเข้าใจที่ดีขึ้น -
ตัวอย่าง
class polynomial: def __init__(self, coeff = 0, pow = 0, nxt = None): self.coefficient = coeff self.power = pow self.next = nxt def create_poly(expression): head = None for element in expression: if head == None: head = polynomial(element[0], element[1]) else: temp = head while temp.next != None: temp = temp.next if temp.next == None: temp.next = polynomial(element[0], element[1]) return head def show_poly(head): temp = head while temp.next != None: print(str(temp.coefficient) + 'x^' + str(temp.power), end = ' + ') temp = temp.next if temp.next == None: print(str(temp.coefficient) + 'x^' + str(temp.power), end=' = 0') def solve(poly1, poly2): dummy = node = polynomial() while poly1 and poly2: if poly1.power > poly2.power: node.next = node = poly1 poly1 = poly1.next elif poly1.power < poly2.power: node.next = node = poly2 poly2 = poly2.next else: coef = poly1.coefficient + poly2.coefficient if coef: node.next = node = polynomial(coef, poly1.power) poly1 = poly1.next poly2 = poly2.next node.next = poly1 or poly2 return dummy.next poly1 = create_poly([[1,1], [1,2]]) poly2 = create_poly([[2,1], [3, 0]]) poly3 = solve(poly1, poly2) show_poly(poly3)
อินพุต
poly1 = create_poly([[1,1], [1,2]]) poly2 = create_poly([[2,1], [3, 0]])
ผลลัพธ์
3x^1 + 1x^2 + 3x^0 = 0


