การสำรวจเส้นทางแบบกว้าง (BFS) เป็นอัลกอริธึมซึ่งใช้เพื่อเข้าชมโหนดทั้งหมดของกราฟที่กำหนด ในอัลกอริธึมการข้ามผ่านนี้ โหนดจะถูกเลือกหนึ่งโหนด จากนั้นโหนดที่อยู่ติดกันทั้งหมดจะถูกเข้าชมทีละโหนด หลังจากเสร็จสิ้นจุดยอดที่อยู่ติดกันทั้งหมดแล้ว มันจะเคลื่อนที่ต่อไปเพื่อตรวจสอบจุดยอดอีกจุดหนึ่งและตรวจสอบจุดยอดที่อยู่ติดกันอีกครั้ง
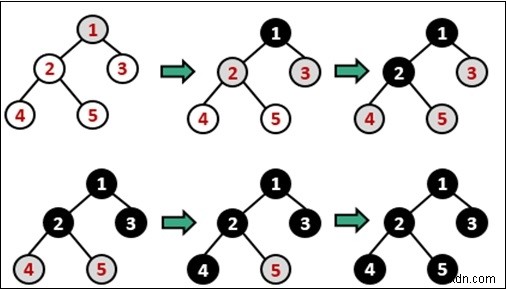
ในการใช้อัลกอริธึมนี้ เราจำเป็นต้องใช้โครงสร้างข้อมูลคิว จุดยอดที่อยู่ติดกันทั้งหมดจะถูกเพิ่มเข้าไปในคิวเมื่อจุดยอดที่อยู่ติดกันทั้งหมดเสร็จสมบูรณ์ หนึ่งรายการจะถูกลบออกจากคิวและเริ่มสำรวจผ่านจุดยอดนั้นอีกครั้ง
ในกราฟบางครั้ง เราอาจได้รับบางรอบ ดังนั้นเราจะใช้อาร์เรย์เพื่อทำเครื่องหมายเมื่อมีการเข้าชมโหนดแล้วหรือไม่
อินพุตและเอาต์พุต
Input: The Adjacency matrix of the graph. A B C D E F A 0 1 1 1 0 0 B 1 0 0 1 1 0 C 1 0 0 1 0 1 D 1 1 1 0 1 1 E 0 1 0 1 0 1 F 0 0 1 1 1 0 Output: BFS Traversal: B A D E C F
อัลกอริทึม
bfs(vertices, start)
อินพุต - รายการจุดยอดและจุดยอดเริ่มต้น
ผลลัพธ์ − ข้ามโหนดทั้งหมดหากเชื่อมต่อกราฟ
Begin define an empty queue que at first mark all nodes status as unvisited add the start vertex into the que while que is not empty, do delete item from que and set to u display the vertex u for all vertices 1 adjacent with u, do if vertices[i] is unvisited, then mark vertices[i] as temporarily visited add v into the queue mark done mark u as completely visited done End
ตัวอย่าง
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#define NODE 6
using namespace std;
typedef struct node {
int val;
int state; //status
}node;
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0}
};
void bfs(node *vert, node s) {
node u;
int i, j;
queue<node> que;
for(i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
vert[i].state = 0; //not visited
}
vert[s.val].state = 1; //visited
que.push(s); //insert starting node
while(!que.empty()) {
u = que.front(); //delete from queue and print
que.pop();
cout << char(u.val+'A') << " ";
for(i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
if(graph[i][u.val]) {
//when the node is non-visited
if(vert[i].state == 0) {
vert[i].state = 1;
que.push(vert[i]);
}
}
}
u.state = 2; //completed for node u
}
}
int main() {
node vertices[NODE];
node start;
char s;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
vertices[i].val = i;
}
s = 'B'; //starting vertex B
start.val = s-'A';
cout << "BFS Traversal: ";
bfs(vertices, start);
cout << endl;
} ผลลัพธ์
BFS Traversal: B A D E C F


