ชุดของจำนวนเต็มจะได้รับในลำดับการเรียงลำดับและความถี่อาร์เรย์อื่นเพื่อนับความถี่ งานของเราคือสร้างแผนผังการค้นหาแบบไบนารีที่มีข้อมูลเหล่านั้นเพื่อค้นหาต้นทุนขั้นต่ำสำหรับการค้นหาทั้งหมด
ต้นทุนอาร์เรย์เสริม[n, n] ถูกสร้างขึ้นเพื่อแก้ไขและจัดเก็บวิธีแก้ปัญหาย่อย เมทริกซ์ต้นทุนจะเก็บข้อมูลเพื่อแก้ปัญหาในลักษณะจากล่างขึ้นบน
ป้อนข้อมูล − ค่าคีย์เป็นโหนดและความถี่
Keys = {10, 12, 20}
Frequency = {34, 8, 50} ผลผลิต − ต้นทุนขั้นต่ำคือ 142
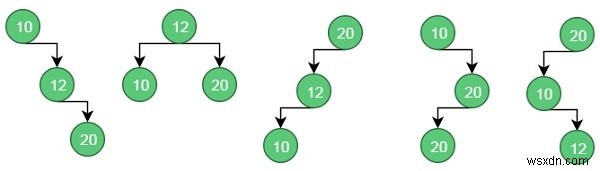
สิ่งเหล่านี้เป็นไปได้ BST จากค่าที่กำหนด
สำหรับกรณีที่ 1 ค่าใช้จ่ายคือ:(34*1) + (8*2) + (50*3) =200
สำหรับกรณีที่ 2 ค่าใช้จ่ายคือ:(8*1) + (34*2) + (50*2) =176
ในทำนองเดียวกัน สำหรับกรณีที่ 5 ค่าใช้จ่ายคือ:(50*1) + (34 * 2) + (8 * 3) =142 (ขั้นต่ำ)
อัลกอริทึม
optCostBst(keys, freq, n) Input: Keys to insert in BST, frequency for each keys, number of keys. Output: Minimum cost to make optimal BST. Begin define cost matrix of size n x n for i in range 0 to n-1, do cost[i, i] := freq[i] done for length in range 2 to n, do for i in range 0 to (n-length+1), do j := i + length – 1 cost[i, j] := ∞ for r in range i to j, done if r > i, then c := cost[i, r-1] else c := 0 if r < j, then c := c + cost[r+1, j] c := c + sum of frequency from i to j if c < cost[i, j], then cost[i, j] := c done done done return cost[0, n-1] End
ตัวอย่าง
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int sum(int freq[], int low, int high){ //sum of frequency from low to high range
int sum = 0;
for (int k = low; k <=high; k++)
sum += freq[k];
return sum;
}
int minCostBST(int keys[], int freq[], int n){
int cost[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) //when only one key, move along diagonal elements
cost[i][i] = freq[i];
for (int length=2; length<=n; length++){
for (int i=0; i<=n-length+1; i++){ //from 0th row to n-length+1 row as i
int j = i+length-1;
cost[i][j] = INT_MAX; //initially store to infinity
for (int r=i; r<=j; r++){
//find cost when r is root of subtree
int c = ((r > i)?cost[i][r-1]:0)+((r < j)?cost[r+1][j]:0)+sum(freq, i, j);
if (c < cost[i][j])
cost[i][j] = c;
}
}
}
return cost[0][n-1];
}
int main(){
int keys[] = {10, 12, 20};
int freq[] = {34, 8, 50};
int n = 3;
cout << "Cost of Optimal BST is: "<< minCostBST(keys, freq, n);
} ผลลัพธ์
Cost of Optimal BST is: 142


