รายการที่เชื่อมโยงใช้การจัดสรรหน่วยความจำแบบไดนามิก กล่าวคือ ขยายและย่อขนาดตามลำดับ พวกมันถูกกำหนดให้เป็นชุดของโหนด ในที่นี้ โหนดมีสองส่วน คือ ข้อมูลและลิงก์ การแสดงข้อมูล ลิงค์ และรายการที่เชื่อมโยงได้รับด้านล่าง -
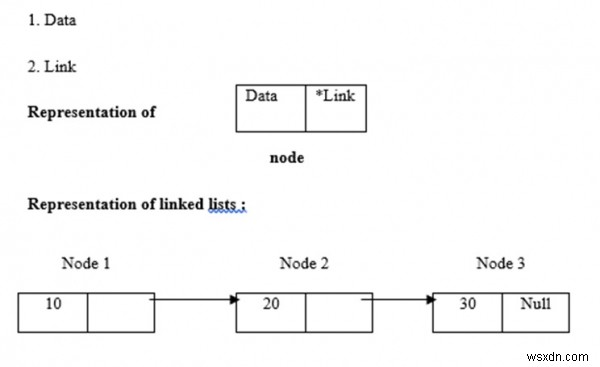
การดำเนินการกับรายการที่เชื่อมโยง
มีการดำเนินการสามประเภทในรายการเชื่อมโยงในภาษา C ซึ่งมีดังนี้ −
- การแทรก
- การลบ
- การข้ามผ่าน
การลบ
ลองพิจารณาตัวอย่างด้านล่าง −
ลบโหนด 2
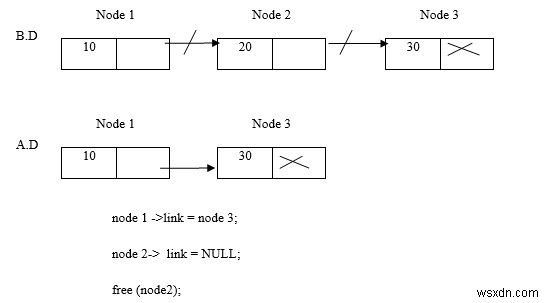
ลบโหนด 1
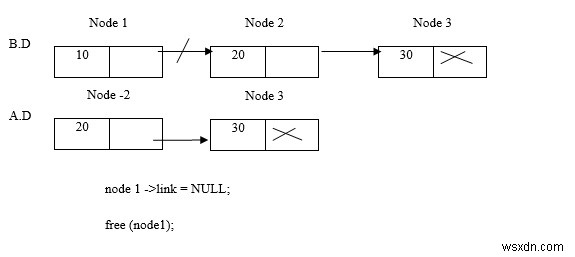
ลบโหนด 3
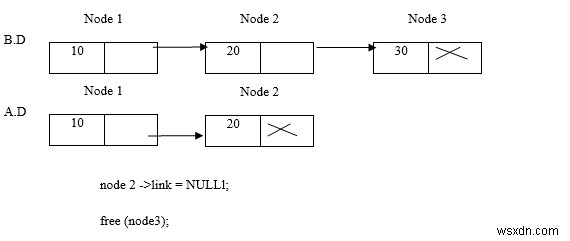
โปรแกรม
ต่อไปนี้เป็นโปรแกรม C สำหรับการลบองค์ประกอบในรายการที่เชื่อมโยง -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data){
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
void deleteNode(struct Node **head_ref, int position){
//if list is empty
if (*head_ref == NULL)
return;
struct Node* temp = *head_ref;
if (position == 0){
*head_ref = temp->next;
free(temp);
return;
}
for (int i=0; temp!=NULL && i<position-1; i++)
temp = temp->next;
if (temp == NULL || temp->next == NULL)
return;
struct Node *next = temp->next->next;
free(temp->next); // Free memory
temp->next = next;
}
void printList(struct Node *node){
while (node != NULL){
printf(" %d ", node->data);
node = node->next;
}
}
int main(){
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 7);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 3);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 8);
puts("Created List: ");
printList(head);
deleteNode(&head, 3);
puts("\n List after Deletion at position 3: ");
printList(head);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
เมื่อโปรแกรมข้างต้นทำงาน มันจะให้ผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้ −
Created List: 8 2 3 1 7 List after Deletion at position 3: 8 2 3 7


