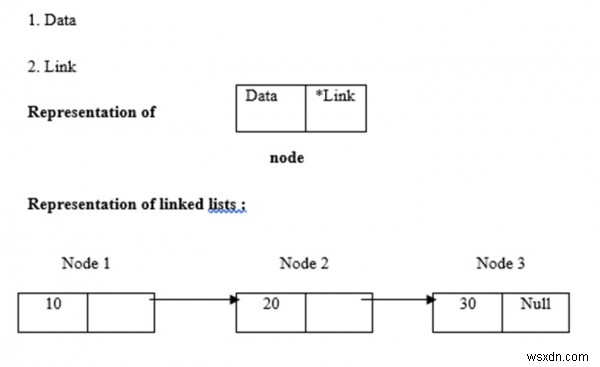
รายการที่เชื่อมโยงใช้การจัดสรรหน่วยความจำแบบไดนามิก กล่าวคือ ขยายและย่อขนาดตามลำดับ พวกมันถูกกำหนดให้เป็นชุดของโหนด ในที่นี้ โหนดมีสองส่วน คือ ข้อมูลและลิงก์ การแสดงข้อมูล ลิงค์ และรายการที่เชื่อมโยงได้รับด้านล่าง -
การดำเนินการกับรายการที่เชื่อมโยง
มีการดำเนินการสามประเภทในรายการเชื่อมโยงในภาษา C ซึ่งมีดังนี้ -
- การแทรก
- การลบ
- การข้ามผ่าน
การแทรก
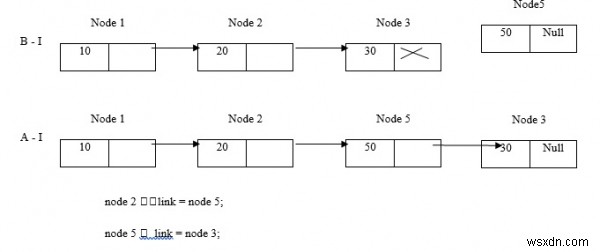
ลองพิจารณาตัวอย่างที่เราแทรกโหนด 5 ระหว่างโหนด 2 และโหนด 3
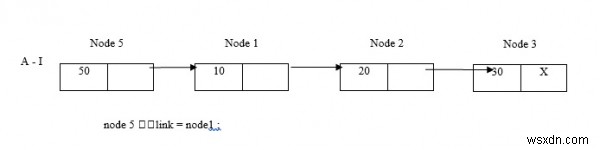
ตอนนี้ แทรกโหนด 5 ที่จุดเริ่มต้น
ใส่โหนด 5 ที่ส่วนท้าย
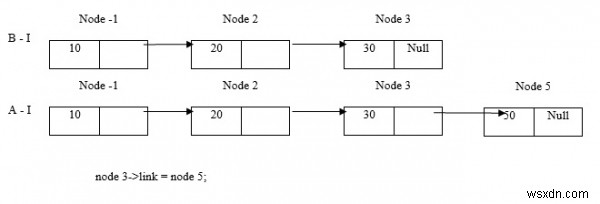
ใส่โหนด 5 ที่ส่วนท้าย
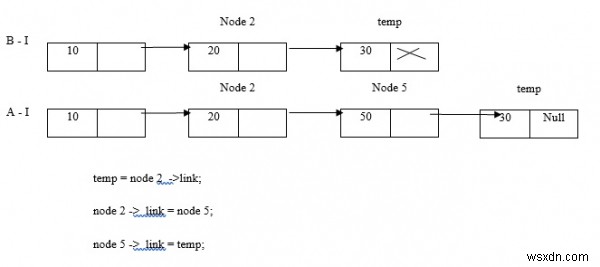
หมายเหตุ:
- เราไม่สามารถแทรกโหนด 5 ก่อนโหนด 2 เนื่องจากไม่มีชื่อโหนด
- เราสามารถแทรกโหนด 5 ก่อน 2 หากระบุตำแหน่ง
โปรแกรม
ต่อไปนี้เป็นโปรแกรม C สำหรับการแทรกองค์ประกอบในรายการที่เชื่อมโยง -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node{
int val;
struct node *next;
};
void print_list(struct node *head){
printf("H->");
while(head){
printf("%d->", head->val);
head = head->next;
}
printf("……\n\n");
}
void insert_front(struct node **head, int value){
struct node * new_node = NULL;
new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (new_node == NULL){
printf(" Out of memory");
}
new_node->val = value;
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
}
void insert_end(struct node **head, int value){
struct node * new_node = NULL;
struct node * last = NULL;
new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (new_node == NULL){
printf(" Out of memory");
}
new_node->val = value;
new_node->next = NULL;
if( *head == NULL){
*head = new_node;
return;
}
last = *head;
while(last->next) last = last->next;
last->next = new_node;
}
void insert_after(struct node *head, int value, int after){
struct node * new_node = NULL;
struct node *tmp = head;
while(tmp) {
if(tmp->val == after) { /*found the node*/
new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (new_node == NULL) {
printf("Out of memory");
}
new_node->val = value;
new_node->next = tmp->next;
tmp->next = new_node;
return;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
void insert_before(struct node **head, int value, int before){
struct node * new_node = NULL;
struct node * tmp = *head;
new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (new_node == NULL){
printf("Out of memory");
return;
}
new_node->val = value;
if((*head)->val == before){
new_node->next = *head;
*head = new_node;
return;
}
while(tmp && tmp->next) {
if(tmp->next->val == before) {
new_node->next = tmp->next;
tmp->next = new_node;
return;
}
tmp = tmp->next;
}
/*Before node not found*/
free(new_node);
}
void main(){
int count = 0, i, val, after, before;
struct node * head = NULL;
printf("Enter no: of elements: ");
scanf("%d", &count);
for (i = 0; i < count; i++){
printf("Enter %dth element: ", i);
scanf("%d", &val);
insert_front(&head, val);
}
printf("starting list: ");
print_list(head);
printf("enter front element: ");
scanf("%d", &val);
insert_front(&head, val);
printf("items after insertion: ");
print_list(head);
printf("enter last element: ");
scanf("%d", &val);
insert_end(&head, val);
printf("items after insertion: ");
print_list(head);
printf("Enter an ele to insert in the list: ");
scanf("%d", &val);
printf("Insert after: ");
scanf("%d", &after);
insert_after(head, val, after);
printf("List after insertion: ");
print_list(head);
printf("Enter an ele to insert in the list: ");
scanf("%d", &val);
printf("Insert before: ");
scanf("%d", &before);
insert_before(&head, val, before);
printf("List after insertion: ");
print_list(head);
} ผลลัพธ์
เมื่อโปรแกรมข้างต้นทำงาน มันจะให้ผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้ −
Enter no: of elements: 4 Enter 0th element: 1 Enter 1th element: 2 Enter 2th element: 3 Enter 3th element: 4 starting list: H->4->3->2->1->...... enter front element: 5 items after insertion: H->5->4->3->2->1->...... enter last element: 0 items after insertion: H->5->4->3->2->1->0->...... Enter an ele to insert in the list: 6 Insert after: 0 List after insertion: H->5->4->3->2->1->0->6->...... Enter an ele to insert in the list: 7 Insert before: 5 List after insertion: H->7->5->4->3->2->1->0->6->......


