โครงสร้างข้อมูลคือชุดของข้อมูลที่จัดโครงสร้างในลักษณะที่มีโครงสร้าง โดยแบ่งออกเป็น 2 ประเภท คือ โครงสร้างข้อมูลเชิงเส้นและโครงสร้างข้อมูลแบบไม่เชิงเส้น

โครงสร้างข้อมูลเชิงเส้น − ในที่นี้ ข้อมูลจะถูกจัดระเบียบในลักษณะเชิงเส้น
ตัวอย่างเช่น − อาร์เรย์ โครงสร้าง สแตก คิว รายการเชื่อมโยง
โครงสร้างข้อมูลไม่เป็นเชิงเส้น − ที่นี่ ข้อมูลถูกจัดเป็นลำดับชั้น
ตัวอย่างเช่น − ต้นไม้ กราฟ ชุด ตาราง
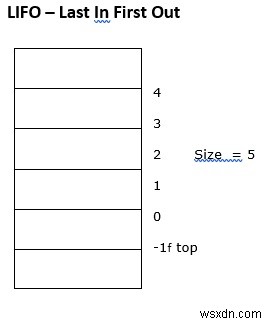
สแต็คในภาษา C
เป็นโครงสร้างข้อมูลเชิงเส้น โดยที่ข้อมูลจะถูกแทรกและนำออกเพียงด้านเดียวเท่านั้น
ปฏิบัติการ
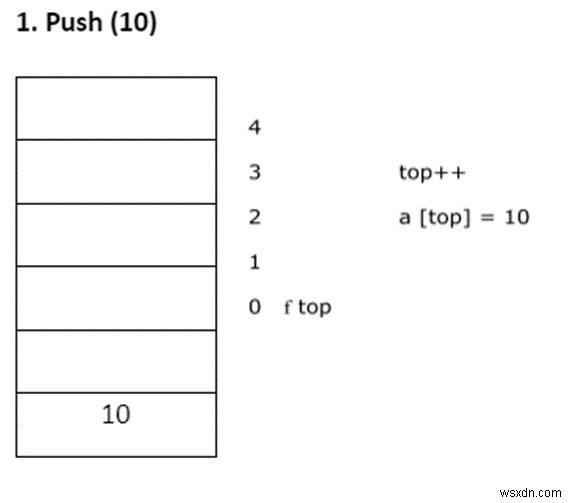
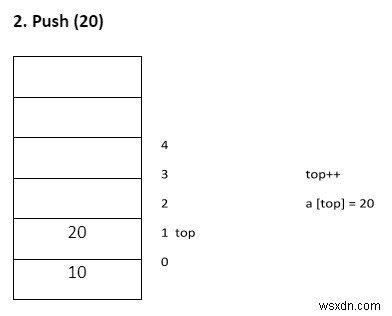
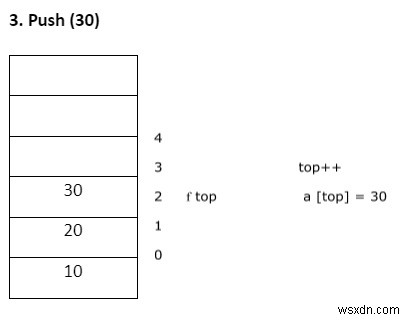
- พุช – การแทรกองค์ประกอบลงในสแต็ก
- ป๊อป – การลบองค์ประกอบออกจากสแต็ก
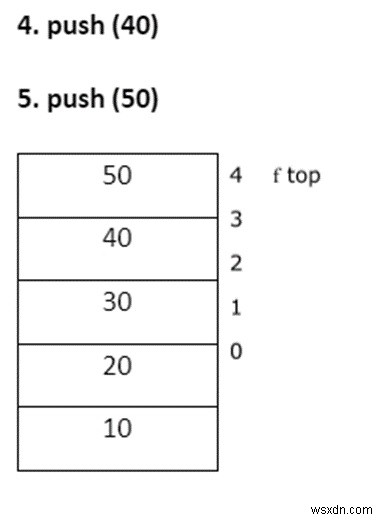
Deleted element = 50 Item = a [top] top --
- pop() ,pop(),pop(), pop()
Deleted element = 40 Deleted element=30 Deleted element=20 Deleted element =10
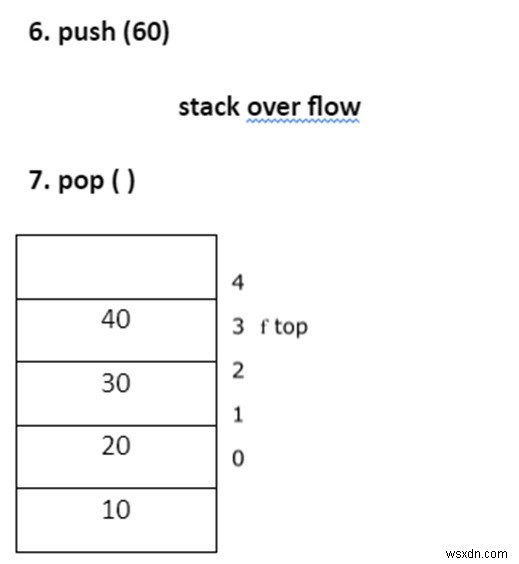
- ป๊อป ( )
กองซ้อนใต้โฟลว์
เงื่อนไข
-
Stack over flow - พยายามแทรกองค์ประกอบลงในสแต็กเต็ม
-
Stack under flow - พยายามลบองค์ประกอบออกจากกองที่ว่างเปล่า
อัลกอริธึมสำหรับการกด ( ), ป๊อป ( ) , การแสดงผล ( )
อัลกอริทึมที่เกี่ยวข้องมีดังนี้ -
ดัน ( )
- ตรวจสอบสแต็กโอเวอร์โฟลว์
if (top = = n-1)
printf("stack over flow”); - มิฉะนั้น ให้แทรกองค์ประกอบลงในสแต็ก
top ++ a[top] = item
ป๊อป ( )
- ตรวจสอบสแต็กอันเดอร์โฟลว์
if ( top = = -1) printf( "stack under flow”);
- มิฉะนั้น ให้ลบองค์ประกอบออกจากสแต็ก
item = a[top] top --
แสดงผล ( )
- ตรวจสอบสแต็กโฟลว์
if (top == -1)
printf ("stack is empty”); - มิฉะนั้น ให้ปฏิบัติตามอัลกอริธึมที่กล่าวถึงด้านล่าง −
for (i=0; i<top; i++)
printf ("%d”, a[i]); ตัวอย่าง
ต่อไปนี้เป็นโปรแกรม C สำหรับการใช้งานสแต็กโดยใช้อาร์เรย์ -
#include<stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int top = -1, n,a[100];
main ( ){
int ch;
void pop ( );
void display ( );
clrscr ( );
printf ("enter the size of the stack”);
scanf ("%d”, &n);
printf("stack implementation\n”);
printf ("1. push \n”);
printf ("2. Pop \n”);
printf ("3. exit \n”);
do{
printf ( "enter ur choice”);
scanf ("%d”, &ch);
switch (ch){
case 1 : push ( );
display ( );
break;
case 2 : push ( );
display ( );
break;
case 3 : exit
}
}while (ch>=1 | | ch<= 3);
getch ( );
}
void push ( ){
int item;
if (top = = n-1)
printf ( "stack over flow”)
else{
printf("enter an element for insertion”)
scanf ("%d”, &item);
top ++;
a[top] = item;
}
}
void pop ( ){
int item;
if (top = = -1);
printf ( "stack under flow”);
else{
item = a[top];
top --;
printf("deleted element = %d”, item);
}
}
void display ( ){
int i;
if (top = = -1)
printf ( "stack is empty”);
else{
printf("contents of the stack are”);
for (i=0; i<top; i++)
printf ("%d \t”, a[i]);
}
} ผลลัพธ์
เมื่อโปรแกรมข้างต้นทำงาน มันจะให้ผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้ −
enter the size of the stack = 5 [given by user] Stack implementation 1. Push 2. Pop 3. exit Enter ur choice : 1 [given by user] Enter an element for insertion : 10 Contents of the stack : 10 Enter ur choice : 1 Enter an element for insertion : 2 Contents of the stack : 10 20 Enter ur choice : 2 Deleted element = 20 Contents of the stack are : 10 Enter ur choice : 2 Deleted element : 10 Contents of the stack are : stack is empty Enter ur choice : 2 Stack underflow. Enter ur choice : 1 Enter an element for insertion : 30 Contents of the stack are : 30


