Selection Sort เป็นอัลกอริธึมโจมตีที่ทำงานเพื่อค้นหาตัวเลขที่น้อยที่สุดจากอาร์เรย์แล้ววางลงในตำแหน่งแรก อาร์เรย์ถัดไปที่จะข้ามผ่านจะเริ่มต้นจากดัชนี ถัดจากตำแหน่งซึ่งวางตัวเลขที่น้อยที่สุด
ขั้นตอนการเรียงลำดับการเลือก
-
เลือกองค์ประกอบที่เล็กที่สุดรายการแรกในรายการองค์ประกอบและวางไว้ในตำแหน่งแรก
-
ทำซ้ำเหมือนเดิมสำหรับองค์ประกอบที่เหลือในรายการจนกว่าองค์ประกอบทั้งหมดจะถูกจัดเรียง
พิจารณารายการต่อไปนี้ -
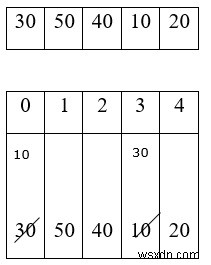
รอบแรก
Sm = a[0] = 30 Sm
a[1]
a[2]
[3]
[4]
a[2]
a[3]
a[4]
[3]
a[4]
a[4] <$\square$ $\square$ sm 50 <40 (F) $\square$ 40 $\square$ แลกเปลี่ยน a[3] ด้วยค่า sm
ดูขั้นตอนด้านล่างสำหรับการเรียงลำดับการเลือก
ต่อไปนี้เป็นโปรแกรม C สำหรับเทคนิคการเรียงลำดับการเลือก -
เมื่อโปรแกรมข้างต้นทำงาน มันจะให้ผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้ −10 50 40 30 20
รอบสอง
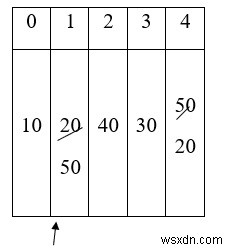
Sm = a[1] = 50 sm
10 20 40 30 50
รอบที่สาม
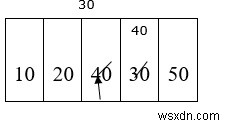
Sm = a[2] = 40 Sm
10 20 30 40 50
รอบที่สี่
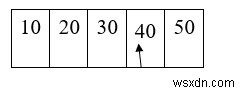
Sm = a[3] = 40 Sm
ขั้นตอน
for (i=0; i<n-1; i++){
sm=i;
for (j=i+1; j<n; j++){
if (a[j] < a[sm])
sm=j;
}
t=a[i];
a[i] = a[sm];
a[sm] = t;
}
} ตัวอย่าง
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int a[50], i,j,n,t,sm;
printf("enter the No: of elements in the list:\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("enter the elements:\n");
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
scanf ("%d", &a[i]);
}
for (i=0; i<n-1; i++){
sm=i;
for (j=i+1; j<n; j++){
if (a[j] < a[sm]){
sm=j;
}
}
t=a[i];
a[i]=a[sm];
a[sm]=t;
}
printf ("after selection sorting the elements are:\n");
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
printf("%d\t", a[i]);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
enter the No: of elements in the list:
4
enter the elements:
45
12
37
68
after selection sorting the elements are:
12 37 45 68


