เราต้องพิมพ์ข้อมูลของโหนดของรายการที่เชื่อมโยงที่ดัชนีที่กำหนด ซึ่งแตกต่างจากรายการที่เชื่อมโยงอาร์เรย์โดยทั่วไปไม่มีดัชนี ดังนั้นเราจึงต้องสำรวจรายการที่เชื่อมโยงทั้งหมดและพิมพ์ข้อมูลเมื่อเราไปถึงรายการใดรายการหนึ่ง
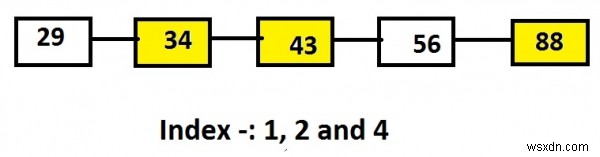
สมมติว่ารายการมีโหนด 29, 34, 43, 56 และ 88 และค่าของดัชนีคือ 1, 2 และ 4 กว่าผลลัพธ์จะเป็นโหนดที่ดัชนีเหล่านี้คือ 34, 43 และ 88
ตัวอย่าง
Linked list: 29->34->43->56->88 Input: 1 2 4 Output: 34 43 88
ในการแสดงด้านบนของ Linked List โหนดที่ไฮไลต์สีเหลืองคือโหนดที่จะพิมพ์หรือโหนดที่อยู่ในดัชนีเฉพาะ
วิธีการที่ใช้ในที่นี้เกี่ยวข้องกับการใช้ตัวชี้หนึ่งตัวและตัวแปรตัวนับหนึ่งตัวที่กำหนดค่าเริ่มต้นเป็น 1 ซึ่งจะเพิ่มขึ้นเมื่อใดก็ตามที่โหนดถูกสำรวจ ตัวนับจะจับคู่กับค่าคีย์ เมื่อคีย์ตรงกับค่าตัวนับ ตัวชี้ที่ชี้ไปที่โครงสร้างโหนดจะพิมพ์ข้อมูลของโหนดและเพิ่มขึ้นไปยังโหนดถัดไป ซึ่งจะทำให้โหนดที่คีย์นั้น ๆ ให้เราทราบ
โค้ดด้านล่างแสดงการใช้งาน c ของอัลกอริทึมที่กำหนด
อัลกอริทึม
START Step 1 -> create node variable of type structure Declare int data Declare pointer of type node using *next Step 2 -> create struct node* intoList(int data) Create newnode using malloc Set newnode->data = data newnode->next = NULL return newnode step 3 -> Declare function void displayList(struct node *catchead) create struct node *temp IF catchead = NULL Print list is empty return End Set temp = catchead Loop While (temp != NULL) print temp->data set temp = temp->next End Step 4 -> Declare Function int search(int key,struct node *head) Set int index Create struct node *newnode Set index = 0 and newnode = head Loop While (newnode != NULL & newnode->data != key) Set index++ Set newnode = newnode->next End return (newnode != NULL) ? index : -1 step 5 -> In Main() create node using struct node* head = intoList(9) call displayList(head) set index = search(24,head) IF (index >= 0) Print index Else Print not found in the list EndIF STOP
ตัวอย่าง
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//structure of a node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node* intoList(int data) {
struct node* newnode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newnode->data = data;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
//funtion to display list
void displayList(struct node *catchead) {
struct node *temp;
if (catchead == NULL) {
printf("List is empty.\n");
return;
}
printf("elements of list are : ");
temp = catchead;
while (temp != NULL) {
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//function to search element
int search(int key,struct node *head) {
int index;
struct node *newnode;
index = 0;
newnode = head;
while (newnode != NULL && newnode->data != key) {
index++;
newnode = newnode->next;
}
return (newnode != NULL) ? index : -1;
}
int main() {
int index;
struct node* head = intoList(9); //inserting elements into a list
head->next = intoList(76);
head->next->next = intoList(13);
head->next->next->next = intoList(24);
head->next->next->next->next = intoList(55);
head->next->next->next->next->next = intoList(109);
displayList(head);
index = search(24,head);
if (index >= 0)
printf("%d found at position %d\n", 24, index);
else
printf("%d not found in the list.\n", 24);
index=search(55,head);
if (index >= 0)
printf("%d found at position %d\n", 55, index);
else
printf("%d not found in the list.\n", 55);
} ผลลัพธ์
หากเรารันโปรแกรมด้านบน มันจะสร้างผลลัพธ์ต่อไปนี้
elements of list are : 9 76 13 24 55 109 24 found at position 3 55 found at position 4


