ให้ต้นไม้ไบนารีที่มีลูกซ้ายและขวาและงานคือการพิมพ์ลูกด้านขวาและซ้ายที่แน่นอนของต้นไม้ที่กำหนด
โหนดซ้ายสุดคือโหนดที่สัมพันธ์กันทางด้านซ้ายจากโหนดหลักของทรี และโหนดทางขวาสุดคือโหนดที่เชื่อมโยงทางด้านขวาจากโหนดหลักของรูท
ตัวอย่าง
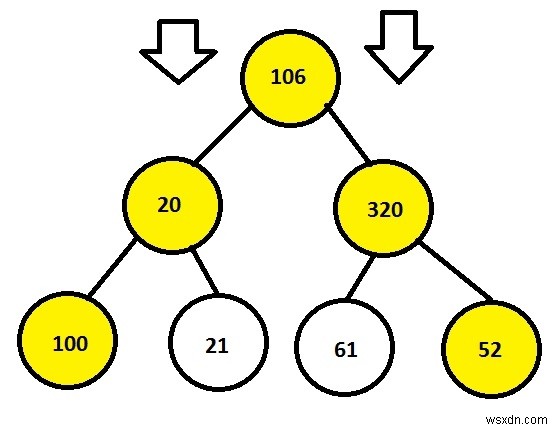
Input: 106 20 320 100 21 61 52 Output: 106 20 320 100 52
อัลกอริทึม
Start Step 1 -> create structure of a node Declare int data Declare struct node *left and *right Step 2 -> create struct node* newNode(int val) Create node* temp=new node Set temp->data = val Set temp->left = temp->right = NULL return (temp) step 3 -> Declare Function void print(node *root) IF root == NULL Return Use STL queue<node*> que Call que.push(root) Use STL vector<int> ans Loop While !que.empty() Set int n = que.size() Loop for int i =0 and i<n and i++ Set node *temp = que.front() Set que.pop() IF i=0 Set ans.push_back(temp->data) End Else IF i=n-1 Set ans.push_back(temp->data) End If temp->left Set que.push(temp->left) End IF temp->right Set que.push(temp->right) End End Loop For auto i : ans Print i End Step 4 -> In main() Declare node *root = newNode(106) to create a node Call print(root) stop
ตัวอย่าง
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//structure of a node {
int data;
struct node* left, *right;
};
//structure to create a new node
struct node* newNode(int val){
node* temp = new node;
temp->data = val;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return (temp);
}
//function to print corner elements of a tree
void print(node *root) {
if(root == NULL)
return;
queue<node*> que;
que.push(root);
vector<int> ans;
while(!que.empty()){
int n = que.size();
for(int i =0;i<n;i++){
node *temp = que.front();
que.pop();
if(i==0)
ans.push_back(temp->data);
else if(i==n-1)
ans.push_back(temp->data);
if(temp->left)
que.push(temp->left);
if(temp->right)
que.push(temp->right);
}
}
for(auto i : ans)
cout << i << " ";
}
int main (){
node *root = newNode(106);
root->left = newNode(20);
root->right = newNode(320);
root->left->left = newNode(100);
root->left->right = newNode(21);
root->right->left = newNode(61);
root->right->right = newNode(52);
print(root);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
หากเรารันโปรแกรมด้านบน มันจะสร้างผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้
106 20 320 100 52


