สมมติว่าเรามีกราฟที่มีโหนดและขอบที่เชื่อมต่ออยู่ แต่ละขอบมีน้ำหนักไบนารี ดังนั้นน้ำหนักจะเป็น 0 หรือ 1 จุดยอดต้นทางจะได้รับ เราต้องหาเส้นทางที่สั้นที่สุดจากต้นทางไปยังจุดยอดอื่นๆ สมมติว่ากราฟเป็นดังนี้ -
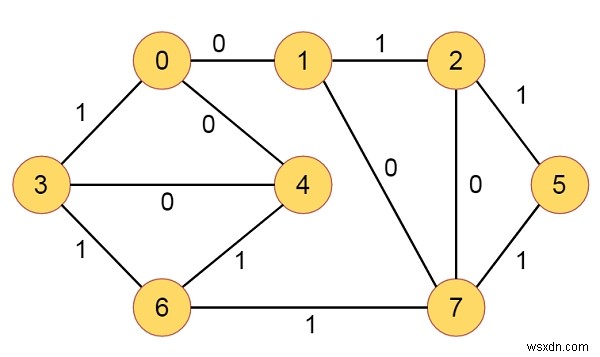
ในอัลกอริธึม BFS ปกติ น้ำหนักขอบทั้งหมดจะเท่ากัน นี่คือบางส่วนเป็น 0 และบางส่วนคือ 1 ในแต่ละขั้นตอน เราจะตรวจสอบเงื่อนไขระยะทางที่เหมาะสมที่สุด ในที่นี้เราจะใช้คิวแบบดับเบิ้ลเอนด์เพื่อจัดเก็บโหนด ดังนั้นเราจะตรวจสอบน้ำหนักขอบ หากเป็น 0 ให้กดที่ด้านหน้า มิฉะนั้น ให้กดที่ด้านหลัง ให้เราตรวจสอบอัลกอริทึมเพื่อให้ได้แนวคิดที่ดีขึ้น
อัลกอริทึม
binaryBFS(src) -
begin define dist array to store source to vertex i into dist[i]. Initially fill with infinity dist[src] := 0 insert src into queue Q. v := first element from Q, and delete it from queue while Q is not empty, do for all connected edge e of v, do if the weight of v to next of i > dist[v] + weight of v to i weight, then update the weight if the weight is 0, then store to front, otherwise back end if done done print all distance from dist array end
ตัวอย่าง
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<deque>
#define V 8
using namespace std;
struct node {
int next, weight;
};
vector <node> edges[V];
void binaryBFS(int src) {
int dist[V];
for (int i=0; i<V; i++) //initially set as infinity
dist[i] = INT_MAX;
deque <int> Q;
dist[src] = 0; //distance from source to source is 0
Q.push_back(src);
while (!Q.empty()) {
int v = Q.front(); //delete first vertex, and store to v
Q.pop_front();
for (int i=0; i<edges[v].size(); i++) {
//check optimal distance
if (dist[edges[v][i].next] > dist[v] + edges[v][i].weight) {
dist[edges[v][i].next] = dist[v] + edges[v][i].weight;
if (edges[v][i].weight == 0) //0 weight edge is stored at front, otherwise at back
Q.push_front(edges[v][i].next);
else
Q.push_back(edges[v][i].next);
}
}
}
for (int i=0; i<V; i++)
cout << dist[i] << " ";
}
void addEdge(int u, int v, int wt) {
edges[u].push_back({v, wt});
edges[v].push_back({u, wt});
}
int main() {
addEdge(0, 1, 0);
addEdge(0, 3, 1);
addEdge(0, 4, 0);
addEdge(1, 2, 1);
addEdge(1, 7, 0);
addEdge(2, 5, 1);
addEdge(2, 7, 0);
addEdge(3, 4, 0);
addEdge(3, 6, 1);
addEdge(4, 6, 1);
addEdge(5, 7, 1);
addEdge(6, 7, 1);
int src = 6;
binaryBFS(src);
} ผลลัพธ์
1 1 1 1 1 2 0 1


