การปรับแต่งไฟล์ .bashrc ของคุณสามารถปรับปรุงเวิร์กโฟลว์ของคุณได้อย่างมากและเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการทำงานของคุณ
.bashrc เป็นไฟล์มาตรฐานที่อยู่ในโฮมไดเร็กทอรี Linux ของคุณ ในบทความนี้ ผมจะแสดงตัวเลือก .bashrc ที่มีประโยชน์ นามแฝง ฟังก์ชัน และอื่นๆ ที่เป็นประโยชน์แก่คุณ
ประโยชน์หลักของการกำหนดค่าไฟล์ .bashrc คือ:
- การเพิ่มนามแฝงช่วยให้คุณพิมพ์คำสั่งได้เร็วขึ้น ประหยัดเวลา
- การเพิ่มฟังก์ชันทำให้คุณสามารถบันทึกและรันโค้ดที่ซับซ้อนได้อีกครั้ง
- แสดงข้อมูลระบบที่เป็นประโยชน์
- ปรับแต่งพรอมต์ของ Bash
วิธีเริ่มต้นแก้ไข .bashrc
นี่คือวิธีแก้ไขไฟล์ .bashrc ด้วยโปรแกรมแก้ไขข้อความ:
$ vim ~/.bashrcคุณสามารถเพิ่มการจัดรูปแบบวันที่และเวลาลงในประวัติทุบตีได้
HISTTIMEFORMAT="%F %T "# Output
$ history
1017 20210228 10:51:28 uptime
1019 20210228 10:52:42 free -m
1020 20210228 10:52:49 tree --dirsfirst -F
1018 20210228 10:51:38 xrandr | awk '/\*/{print $1}'เพิ่มบรรทัดนี้เพื่อละเว้นคำสั่งที่ซ้ำกันในประวัติ
HISTCONTROL=ignoredupsหากต้องการกำหนดจำนวนบรรทัดในประวัติการใช้งานและกำหนดจำนวนบรรทัดที่บันทึกไว้ในประวัติ Bash ให้เพิ่มสองบรรทัดนี้
HISTSIZE=2000
HISTFILESIZE=2000
คุณสามารถตั้งค่าประวัติของคุณเพื่อผนวกแทนการเขียนทับประวัติทุบตี shopt ย่อมาจาก "ตัวเลือกเชลล์"
shopt -s histappend
หากต้องการดูตัวเลือกเชลล์เริ่มต้นทั้งหมด ให้เรียกใช้ shopt -p .
# Output
$ shopt -p
shopt -u autocd
shopt -u assoc_expand_once
shopt -u cdable_vars
shopt -u cdspell
shopt -u checkhash
shopt -u checkjobs
shopt -s checkwinsize
[...]สร้างตัวแปรเพื่อเพิ่มสีสันให้กับพรอมต์ของ Bash ดังนี้:
blk='\[\033[01;30m\]' # Black
red='\[\033[01;31m\]' # Red
grn='\[\033[01;32m\]' # Green
ylw='\[\033[01;33m\]' # Yellow
blu='\[\033[01;34m\]' # Blue
pur='\[\033[01;35m\]' # Purple
cyn='\[\033[01;36m\]' # Cyan
wht='\[\033[01;37m\]' # White
clr='\[\033[00m\]' # Resetนี่สำหรับคนรัก Vim สิ่งนี้จะช่วยให้คุณใช้คำสั่ง vim บนบรรทัดคำสั่ง นี่เป็นบรรทัดแรกที่ฉันเพิ่มใน .bashrc เสมอ
set -o viวิธีสร้างนามแฝงใน .bashrc
คุณสามารถใช้นามแฝงสำหรับคำสั่งที่คุณรันเป็นจำนวนมาก การสร้างนามแฝงจะช่วยให้คุณพิมพ์ได้เร็วขึ้น ประหยัดเวลา และเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการทำงาน
ไวยากรณ์สำหรับการสร้างนามแฝงคือ alias <my_alias>='longer command' . หากต้องการค้นหาว่าคำสั่งใดจะสร้างนามแฝงที่ดี ให้เรียกใช้คำสั่งนี้เพื่อดูรายการคำสั่ง 10 อันดับแรกที่คุณเรียกใช้บ่อยที่สุด
$ history | awk '{cmd[$2]++} END {for(elem in cmd) {print cmd[elem] " " elem}}' | sort -n -r | head -10
# Output
171 git
108 cd
62 vim
51 python3
38 history
32 exit
30 clear
28 tmux
28 tree
27 lsเนื่องจากฉันใช้ Git เป็นจำนวนมาก นั่นจึงเป็นคำสั่งที่ดีในการสร้างนามแฝง
# View Git status.
alias gs='git status'
# Add a file to Git.
alias ga='git add'
# Add all files to Git.
alias gaa='git add --all'
# Commit changes to the code.
alias gc='git commit'
# View the Git log.
alias gl='git log --oneline'
# Create a new Git branch and move to the new branch at the same time.
alias gb='git checkout -b'
# View the difference.
alias gd='git diff'ต่อไปนี้เป็นนามแฝงที่มีประโยชน์อื่นๆ:
# Move to the parent folder.
alias ..='cd ..;pwd'
# Move up two parent folders.
alias ...='cd ../..;pwd'
# Move up three parent folders.
alias ....='cd ../../..;pwd'# Press c to clear the terminal screen.
alias c='clear'
# Press h to view the bash history.
alias h='history'
# Display the directory structure better.
alias tree='tree --dirsfirst -F'
# Make a directory and all parent directories with verbosity.
alias mkdir='mkdir -p -v'# View the calender by typing the first three letters of the month.
alias jan='cal -m 01'
alias feb='cal -m 02'
alias mar='cal -m 03'
alias apr='cal -m 04'
alias may='cal -m 05'
alias jun='cal -m 06'
alias jul='cal -m 07'
alias aug='cal -m 08'
alias sep='cal -m 09'
alias oct='cal -m 10'
alias nov='cal -m 11'
alias dec='cal -m 12'# Output
$ mar
March 2021
Su Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa
1 2 3 4 5 6
7 8 9 10 11 12 13
14 15 16 17 18 19 20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27
28 29 30 31
วิธีใช้ฟังก์ชันใน .bashrc
ฟังก์ชันเหมาะสำหรับโค้ดที่ซับซ้อนมากขึ้นเมื่อชื่อแทนใช้ไม่ได้
นี่คือไวยากรณ์ของฟังก์ชันพื้นฐาน:
function funct_name() {
# code;
}นี่คือวิธีที่คุณสามารถค้นหาไฟล์ที่ใหญ่ที่สุดในไดเร็กทอรี:
function find_largest_files() {
du -h -x -s -- * | sort -r -h | head -20;
}
# Output
Downloads $ find_largest_files
709M systemrescue-8.00-amd64.iso
337M debian-10.8.0-amd64-netinst.iso
9.1M weather-icons-master.zip
6.3M Hack-font.zip
3.9M city.list.json.gz
2.8M dvdrental.tar
708K IMG_2600.JPG
100K sql_cheat_sheet_pgsql.pdf
4.0K repeating-a-string.txt
4.0K heart.svg
4.0K Fedora-Workstation-33-1.2-x86_64-CHECKSUM
[...]คุณยังสามารถเพิ่มสีให้กับพรอมต์ Bash และแสดงสาขา Git ปัจจุบันได้ดังนี้:
# Display the current Git branch in the Bash prompt.
function git_branch() {
if [ -d .git ] ; then
printf "%s" "($(git branch 2> /dev/null | awk '/\*/{print $2}'))";
fi
}
# Set the prompt.
function bash_prompt(){
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}'${blu}'$(git_branch)'${pur}' \W'${grn}' \$ '${clr}
}
bash_prompt

Grep (ค้นหา) ผ่านประวัติของคุณสำหรับคำสั่งการเรียกใช้ก่อนหน้า:
function hg() {
history | grep "$1";
}# Output
$ hg vim
305 2021-03-02 16:47:33 vim .bashrc
307 2021-03-02 17:17:09 vim .tmux.confนี่คือวิธีที่คุณเริ่มโครงการใหม่ด้วย Git:
function git_init() {
if [ -z "$1" ]; then
printf "%s\n" "Please provide a directory name.";
else
mkdir "$1";
builtin cd "$1";
pwd;
git init;
touch readme.md .gitignore LICENSE;
echo "# $(basename $PWD)" >> readme.md
fi
}# Output
$ git_init my_project
/home/brandon/my_project
Initialized empty Git repository in /home/brandon/my_project/.git/คุณยังสามารถรับรายงานสภาพอากาศในบรรทัดคำสั่ง ต้องใช้แพ็คเกจ curl , jq และ คีย์ API จาก Openweathermap อ่านเอกสาร Openweathermap API เพื่อกำหนดค่า URL ให้ถูกต้องเพื่อรับสภาพอากาศในตำแหน่งของคุณ
ติดตั้ง curl และ jq ด้วยคำสั่งเหล่านี้:
$ sudo apt install curl jq
# OR
$ sudo dnf install curl jqfunction weather_report() {
local response=$(curl --silent 'https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?id=5128581&units=imperial&appid=<YOUR_API_KEY>')
local status=$(echo $response | jq -r '.cod')
# Check for the 200 response indicating a successful API query.
case $status in
200) printf "Location: %s %s\n" "$(echo $response | jq '.name') $(echo $response | jq '.sys.country')"
printf "Forecast: %s\n" "$(echo $response | jq '.weather[].description')"
printf "Temperature: %.1f°F\n" "$(echo $response | jq '.main.temp')"
printf "Temp Min: %.1f°F\n" "$(echo $response | jq '.main.temp_min')"
printf "Temp Max: %.1f°F\n" "$(echo $response | jq '.main.temp_max')"
;;
401) echo "401 error"
;;
*) echo "error"
;;
esac
}# Output
$ weather_report
Location: "New York" "US"
Forecast: "clear sky"
Temperature: 58.0°F
Temp Min: 56.0°F
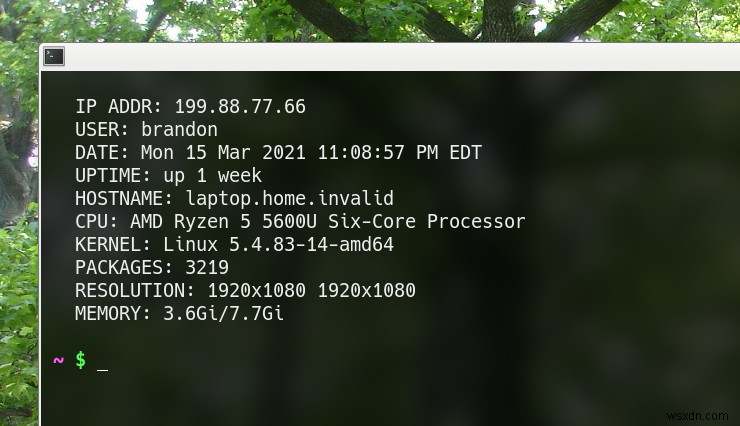
Temp Max: 60.8°Fวิธีพิมพ์ข้อมูลระบบใน .bashrc
คุณสามารถแสดงข้อมูลระบบที่เป็นประโยชน์เมื่อคุณเปิดเทอร์มินัลดังนี้:
clear
printf "\n"
printf " %s\n" "IP ADDR: $(curl ifconfig.me)"
printf " %s\n" "USER: $(echo $USER)"
printf " %s\n" "DATE: $(date)"
printf " %s\n" "UPTIME: $(uptime -p)"
printf " %s\n" "HOSTNAME: $(hostname -f)"
printf " %s\n" "CPU: $(awk -F: '/model name/{print $2}' | head -1)"
printf " %s\n" "KERNEL: $(uname -rms)"
printf " %s\n" "PACKAGES: $(dpkg --get-selections | wc -l)"
printf " %s\n" "RESOLUTION: $(xrandr | awk '/\*/{printf $1" "}')"
printf " %s\n" "MEMORY: $(free -m -h | awk '/Mem/{print $3"/"$2}')"
printf "\n"เอาท์พุต:
แหล่งที่มาของไฟล์ .bashrc เพื่อให้การเปลี่ยนแปลงมีผล:
$ source ~/.bashrcนี่คือการตั้งค่า .bashrc แบบกำหนดเองทั้งหมดเหล่านี้ร่วมกัน ในระบบใหม่ ฉันวางการปรับแต่งใดๆ ด้านล่างโค้ดเริ่มต้นในไฟล์ .bashrc
######################################################################
#
#
# ██████╗ █████╗ ███████╗██╗ ██╗██████╗ ██████╗
# ██╔══██╗██╔══██╗██╔════╝██║ ██║██╔══██╗██╔════╝
# ██████╔╝███████║███████╗███████║██████╔╝██║
# ██╔══██╗██╔══██║╚════██║██╔══██║██╔══██╗██║
# ██████╔╝██║ ██║███████║██║ ██║██║ ██║╚██████╗
# ╚═════╝ ╚═╝ ╚═╝╚══════╝╚═╝ ╚═╝╚═╝ ╚═╝ ╚═════╝
#
#
######################################################################
set -o vi
HISTTIMEFORMAT="%F %T "
HISTCONTROL=ignoredups
HISTSIZE=2000
HISTFILESIZE=2000
shopt -s histappend
blk='\[\033[01;30m\]' # Black
red='\[\033[01;31m\]' # Red
grn='\[\033[01;32m\]' # Green
ylw='\[\033[01;33m\]' # Yellow
blu='\[\033[01;34m\]' # Blue
pur='\[\033[01;35m\]' # Purple
cyn='\[\033[01;36m\]' # Cyan
wht='\[\033[01;37m\]' # White
clr='\[\033[00m\]' # Reset
alias gs='git status'
alias ga='git add'
alias gaa='git add --all'
alias gc='git commit'
alias gl='git log --oneline'
alias gb='git checkout -b'
alias gd='git diff'
alias ..='cd ..;pwd'
alias ...='cd ../..;pwd'
alias ....='cd ../../..;pwd'
alias c='clear'
alias h='history'
alias tree='tree --dirsfirst -F'
alias mkdir='mkdir -p -v'
alias jan='cal -m 01'
alias feb='cal -m 02'
alias mar='cal -m 03'
alias apr='cal -m 04'
alias may='cal -m 05'
alias jun='cal -m 06'
alias jul='cal -m 07'
alias aug='cal -m 08'
alias sep='cal -m 09'
alias oct='cal -m 10'
alias nov='cal -m 11'
alias dec='cal -m 12'
function hg() {
history | grep "$1";
}
function find_largest_files() {
du -h -x -s -- * | sort -r -h | head -20;
}
function git_branch() {
if [ -d .git ] ; then
printf "%s" "($(git branch 2> /dev/null | awk '/\*/{print $2}'))";
fi
}
# Set the prompt.
function bash_prompt(){
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}'${blu}'$(git_branch)'${pur}' \W'${grn}' \$ '${clr}
}
bash_prompt
function git_init() {
if [ -z "$1" ]; then
printf "%s\n" "Please provide a directory name.";
else
mkdir "$1";
builtin cd "$1";
pwd;
git init;
touch readme.md .gitignore LICENSE;
echo "# $(basename $PWD)" >> readme.md
fi
}
function weather_report() {
local response=$(curl --silent 'https://api.openweathermap.org/data/2.5/weather?id=5128581&units=imperial&appid=<YOUR_API_KEY>')
local status=$(echo $response | jq -r '.cod')
case $status in
200) printf "Location: %s %s\n" "$(echo $response | jq '.name') $(echo $response | jq '.sys.country')"
printf "Forecast: %s\n" "$(echo $response | jq '.weather[].description')"
printf "Temperature: %.1f°F\n" "$(echo $response | jq '.main.temp')"
printf "Temp Min: %.1f°F\n" "$(echo $response | jq '.main.temp_min')"
printf "Temp Max: %.1f°F\n" "$(echo $response | jq '.main.temp_max')"
;;
401) echo "401 error"
;;
*) echo "error"
;;
esac
}
clear
printf "\n"
printf " %s\n" "IP ADDR: $(curl ifconfig.me)"
printf " %s\n" "USER: $(echo $USER)"
printf " %s\n" "DATE: $(date)"
printf " %s\n" "UPTIME: $(uptime -p)"
printf " %s\n" "HOSTNAME: $(hostname -f)"
printf " %s\n" "CPU: $(awk -F: '/model name/{print $2}' | head -1)"
printf " %s\n" "KERNEL: $(uname -rms)"
printf " %s\n" "PACKAGES: $(dpkg --get-selections | wc -l)"
printf " %s\n" "RESOLUTION: $(xrandr | awk '/\*/{printf $1" "}')"
printf " %s\n" "MEMORY: $(free -m -h | awk '/Mem/{print $3"/"$2}')"
printf "\n"
บทสรุป
ในบทความนี้ คุณได้เรียนรู้วิธีกำหนดค่าตัวเลือก .bashrc ต่างๆ นามแฝง ฟังก์ชัน และอื่นๆ เพื่อปรับปรุงเวิร์กโฟลว์ของคุณอย่างมากและเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพการทำงานของคุณ
ติดตามฉันบน Github | กำลังพัฒนา


