interp1d() ฟังก์ชันของ scipy.interpolate แพ็คเกจใช้เพื่อสอดแทรกฟังก์ชัน 1-D ต้องใช้อาร์เรย์ของค่าต่างๆ เช่น x และ y เพื่อประมาณฟังก์ชันบางอย่าง y =f(x) แล้วใช้การแก้ไขเพื่อหาค่าของคะแนนใหม่
ไวยากรณ์
scipy.interpolate.interp1d(x, y)
โดยที่ x คืออาร์เรย์ 1-D ของค่าจริง และ y คืออาร์เรย์ ND ของค่าจริง ความยาวของ y ตามแกนการแก้ไขต้องเท่ากับความยาวของ x
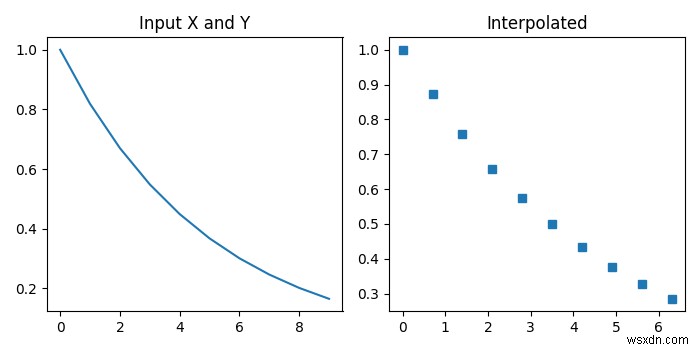
ตัวอย่างที่ 1
ให้เราพิจารณาตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้ −
# Import the required libraries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from scipy import interpolate
# Set the figure size
plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"]=[7.00, 3.50]
plt.rcParams["figure.autolayout"]=True
# Define the values
x = np.arange(0, 10)
y = np.exp(-x/5.0)
# Input Data
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.title("Input X and Y")
plt.plot(x,y)
# Interpolated Data
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.title("Interpolated")
f = interpolate.interp1d(x, y)
x_new = np.arange(0, 7, 0.7)
y_new = f(x_new)
plt.plot(x_new, y_new, 's')
plt.show() ผลลัพธ์
โปรแกรมข้างต้นจะสร้างผลลัพธ์ต่อไปนี้ -
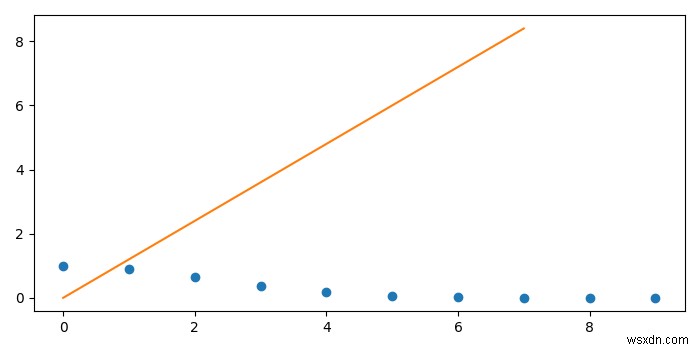
ตัวอย่างที่ 2
เรามาดูตัวอย่างกัน −
# Import the required libraries import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np from scipy import interpolate # Set the figure size plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"]=[7.00, 3.50] plt.rcParams["figure.autolayout"]=True # Define the values x = np.arange(0, 10) y = np.exp(-x **2/9.0) # interpolate function f = interpolate.interp1d(x, y) xnew = np.arange(0, 9, 1.2) plt.plot(x, y, 'o', xnew) plt.show()
ผลลัพธ์
โปรแกรมข้างต้นจะสร้างผลลัพธ์ต่อไปนี้ -