เราได้รับไบนารีทรีเป็นอินพุต เป้าหมายคือการหาจำนวนต้นไม้การค้นหาแบบไบนารี (BST) ที่มีอยู่เป็นทรีย่อยที่อยู่ภายใน BST เป็นไบนารีทรีที่มีลูกซ้ายน้อยกว่ารูทและลูกขวามากกว่ารูท
ตัวอย่าง
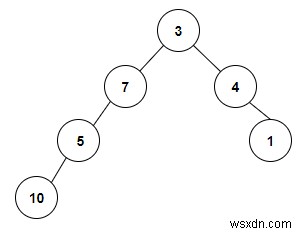
อินพุต
ต้นไม้ที่จะถูกสร้างขึ้นหลังจากป้อนค่าจะได้รับด้านล่าง -
ผลลัพธ์
Count the Number of Binary Search Trees present in a Binary Tree are: 2
คำอธิบาย
เราได้รับอาร์เรย์ของค่าจำนวนเต็มที่ใช้ในการสร้างไบนารีทรีและเราจะตรวจสอบว่ามีทรีการค้นหาแบบไบนารีอยู่ในนั้นหรือไม่ โหนดรากทุกโหนดแสดงถึงแผนผังการค้นหาแบบไบนารี ดังนั้นในไบนารีทรีที่กำหนด เราจะเห็นว่าไม่มีทรีการค้นหาแบบไบนารีอื่นที่มีอยู่ ดังนั้นการนับคือ 2 ซึ่งเป็นจำนวนโหนดลีฟทั้งหมดในทรีไบนารี
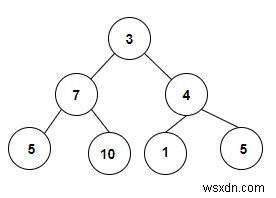
อินพุต
ต้นไม้ที่จะถูกสร้างขึ้นหลังจากป้อนค่าจะได้รับด้านล่าง -
ผลลัพธ์
Count the Number of Binary Search Trees present in a Binary Tree are: 6
คำอธิบาย
เราได้รับอาร์เรย์ของค่าจำนวนเต็มที่ใช้เพื่อสร้างไบนารีทรีและเราจะตรวจสอบว่ามีทรีการค้นหาแบบไบนารีอยู่ในนั้นหรือไม่ ทุกรูตโหนดแสดงถึงแผนผังการค้นหาแบบไบนารี ดังนั้นในไบนารีทรีที่กำหนด เราจะเห็นได้ว่ามีโหนดลีฟ 4 โหนดและทรีย่อยสองทรีซึ่งสร้าง BST ดังนั้นการนับคือ 6
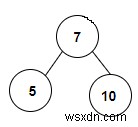
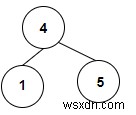
แนวทางที่ใช้ในโปรแกรมด้านล่างมีดังนี้ −
ในวิธีนี้ เราจะหาค่าที่ใหญ่ที่สุดของโหนดในทรีย่อยด้านซ้ายของโหนด N และตรวจสอบว่ามีค่าน้อยกว่า N นอกจากนี้ เราจะหาค่าที่น้อยที่สุดในทรีย่อยด้านขวาของโหนด N และตรวจสอบว่ามีค่ามากกว่า N. ถ้าเป็นจริง แสดงว่าเป็น BST สำรวจไบนารีทรีในลักษณะจากล่างขึ้นบน และตรวจสอบเงื่อนไขด้านบนและจำนวน BST ที่เพิ่มขึ้น
-
โหนดของ node_data ทุกอันมีข้อมูลอย่างเช่น จำนวนของ BST ปัจจุบัน ค่าสูงสุดในทรีนั้น ค่าต่ำสุด บูลีนจริง หากทรีย่อยนั้นเป็น BST
-
ฟังก์ชัน BST_present(struct tree_node* parent) ค้นหาจำนวน BST ที่มีอยู่ภายในไบนารีทรีที่รูทที่พาเรนต์
-
หากพาเรนต์เป็น NULL ให้คืนค่า { 0, min, max, true } โดยที่ min คือ INT-MIN และmax คือ INT_MAX
-
หากลูกซ้ายและขวาเป็นโมฆะ ให้ส่งคืน { 1, parent−>data, parent−>data, true }
-
ตั้งค่า node_data Left =BST_present(parent->left); และ node_data Right =BST_present(parent−>right);
-
ใช้โหนด n1 และตั้งค่า n1.lowest =min(parent−>data, (min(Left.lowest,Right.lowest))) เป็นค่าต่ำสุดในทรีย่อยด้านขวา
-
ตั้งค่า n1.highest =max(parent−>data, (max(Left.highest, Right.highest))); สูงสุดในทรีย่อยด้านซ้าย
-
if(Left.check &&Right.check &&parent−>data> Left.highest &&parent–>data
-
เพิ่มจำนวน bsts เป็น n1.total_bst =1 + Left.total_bst + Right.total_bst;
-
มิฉะนั้น ให้ตั้งค่า n1.check =false และนับเป็น n1.total_bst =Left.total_bst +Right.total_bst
-
ในตอนท้ายให้ส่งคืน n1
ตัวอย่าง
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct tree_node{
struct tree_node* left;
struct tree_node* right;
int data;
tree_node(int data){
this−>data = data;
this−>left = NULL;
this−>right = NULL;
}
};
struct node_data{
int total_bst;
int highest, lowest;
bool check;
};
node_data BST_present(struct tree_node* parent){
if(parent == NULL){
int max = INT_MAX;
int min = INT_MIN;
return { 0, min, max, true };
}
if(parent−>left == NULL){
if(parent−>right == NULL){
return { 1, parent−>data, parent−>data, true };
}
}
node_data Left = BST_present(parent−>left);
node_data Right = BST_present(parent−>right);
node_data n1;
n1.lowest = min(parent−>data, (min(Left.lowest, Right.lowest)));
n1.highest = max(parent−>data, (max(Left.highest, Right.highest)));
if(Left.check && Right.check && parent−>data > Left.highest && parent−>data < Right.lowest){
n1.check = true;
n1.total_bst = 1 + Left.total_bst + Right.total_bst;
} else{
n1.check = false;
n1.total_bst = Left.total_bst + Right.total_bst;
}
return n1;
}
int main(){
struct tree_node* root = new tree_node(3);
root−>left = new tree_node(7);
root−>right = new tree_node(4);
root−>left−>left = new tree_node(5);
root−>right−>right = new tree_node(1);
root−>left−>left−>left = new tree_node(10);
cout<<"Count the Number of Binary Search Trees present in a Binary Tree are: "<<BST_present(root).total_bst;
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
หากเราเรียกใช้โค้ดข้างต้น มันจะสร้างผลลัพธ์ต่อไปนี้ -
Count the Number of Binary Search Trees present in a Binary Tree are: 2


