สมมติว่าเราต้องการสร้างตัววนซ้ำสำหรับไบนารีทรี จะมีสองวิธี วิธี next() เพื่อคืนค่าองค์ประกอบถัดไป และวิธีการ hasNext() เพื่อคืนค่าบูลีน ที่จะระบุว่าองค์ประกอบถัดไปมีอยู่หรือไม่ ดังนั้นถ้าต้นไม้เป็นเหมือน −
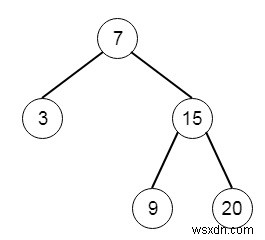
และลำดับของการเรียกใช้ฟังก์ชันคือ [next(), next(), hasNext(), next(), hasNext(),next(), hasNext(),next(), hasNext()] ผลลัพธ์จะเป็น [3,7,true,9,true,15,true,20,false]
เพื่อแก้ปัญหานี้ เราจะทำตามขั้นตอนเหล่านี้ -
- มีสองวิธีถัดไปและ hasNext
- เมธอด next() จะเป็นเช่น −
- curr :=สแต็คองค์ประกอบด้านบนและองค์ประกอบป๊อปด้านบน
- หากสิทธิ์ของสกุลเงินไม่เป็นโมฆะ ให้กดตัวต่อเนื่องตามลำดับจากด้านขวาของโหนด
- คืนค่าของกระแส
- เมธอด hasNext() จะเป็น −
- คืนค่า จริง เมื่อสแต็กไม่ว่างเปล่า มิฉะนั้น จะเป็นเท็จ
ให้เราดูการใช้งานต่อไปนี้เพื่อความเข้าใจที่ดีขึ้น -
ตัวอย่าง
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class TreeNode{
public:
int val;
TreeNode *left, *right;
TreeNode(int data){
val = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
void insert(TreeNode **root, int val){
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(*root);
while(q.size()){
TreeNode *temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if(!temp->left){
if(val != NULL)
temp->left = new TreeNode(val);
else
temp->left = new TreeNode(0);
return;
} else {
q.push(temp->left);
}
if(!temp->right){
if(val != NULL)
temp->right = new TreeNode(val);
else
temp->right = new TreeNode(0);
return;
}else{
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
}
TreeNode *make_tree(vector<int> v){
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(v[0]);
for(int i = 1; i<v.size(); i++){
insert(&root, v[i]);
}
return root;
}
class BSTIterator {
public:
stack <TreeNode*> st;
void fillStack(TreeNode* node){
while(node && node->val != 0){
st.push(node);
node=node->left;
}
}
BSTIterator(TreeNode* root) {
fillStack(root);
}
/** @return the next smallest number */
int next() {
TreeNode* curr = st.top();
st.pop();
if(curr->right && curr->right->val != 0){
fillStack(curr->right);
}
return curr->val;
}
/** @return whether we have a next smallest number */
bool hasNext() {
return !st.empty();
}
};
main(){
vector<int> v = {7,3,15,NULL,NULL,9,20};
TreeNode *root = make_tree(v);
BSTIterator ob(root);
cout << "Next: " << ob.next() << endl;
cout << "Next: " << ob.next() << endl;
cout << ob.hasNext() << endl;
cout << "Next: " << ob.next() << endl;
cout << ob.hasNext() << endl;
cout << "Next: " << ob.next() << endl;
cout << ob.hasNext() << endl;
cout << "Next: " << ob.next() << endl;
cout << ob.hasNext() << endl;
} อินพุต
BSTIterator ob(root); ob.next() ob.next() ob.hasNext() ob.next() ob.hasNext() ob.next() ob.hasNext() ob.next() ob.hasNext()
ผลลัพธ์
Next: 3 Next: 7 1 Next: 9 1 Next: 15 1 Next: 20 0


