สมมติว่าเรามีต้นไม้ไบนารี เราจะรวบรวมและลบใบทั้งหมดและทำซ้ำจนกว่าต้นไม้จะว่างเปล่า
ดังนั้นหากอินพุตเป็นแบบ
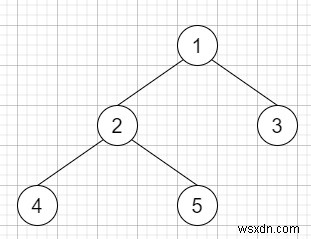
แล้วผลลัพธ์จะเป็น [[4,5,3],[2,[1]]
เพื่อแก้ปัญหานี้ เราจะทำตามขั้นตอนเหล่านี้ -
-
กำหนดหนึ่งแผนที่ sz
-
กำหนดอาร์เรย์ 2D ret หนึ่งรายการ
-
กำหนดฟังก์ชัน dfs() ซึ่งจะใช้โหนด
-
ถ้าโหนดเป็นโมฆะ −
-
sz[val ของโหนด] :=1 + สูงสุดของ dfs (ด้านซ้ายของโหนด) และ dfs (ด้านขวาของโหนด)
-
-
ถ้าขนาดของ ret
-
กำหนดอุณหภูมิอาร์เรย์
-
ใส่ temp ที่ท้าย ret
-
-
แทรก val ของโหนดที่ส่วนท้ายของ ret[sz[val of node] - 1]
-
คืนค่า sz[val ของโหนด]
-
จากวิธีหลัก ให้ทำดังนี้ −
-
dfs(root)
-
รีเทิร์น
ตัวอย่าง
ให้เราดูการใช้งานต่อไปนี้เพื่อความเข้าใจที่ดีขึ้น -
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void print_vector(vector<vector<auto< > v){
cout << "[";
for(int i = 0; i<v.size(); i++){
cout << "[";
for(int j = 0; j <v[i].size(); j++){
cout << v[i][j] << ", ";
}
cout << "],";
}
cout << "]"<<endl;
}
class TreeNode{
public:
int val;
TreeNode *left, *right;
TreeNode(int data){
val = data;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
void insert(TreeNode **root, int val){
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(*root);
while(q.size()){
TreeNode *temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if(!temp->left){
if(val != NULL)
temp->left = new TreeNode(val);
else
temp->left = new TreeNode(0);
return;
}else{
q.push(temp->left);
}
if(!temp->right){
if(val != NULL)
temp->right = new TreeNode(val);
else
temp->right = new TreeNode(0);
return;
}else{
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
}
TreeNode *make_tree(vector<int< v){
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(v[0]);
for(int i = 1; i<v.size(); i++){
insert(&root, v[i]);
}
return root;
}
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map <int, int> sz;
vector < vector <int< > ret;
int dfs(TreeNode* node){
if(!node) return 0;
sz[node->val] = 1 + max(dfs(node->left), dfs(node->right));
if(ret.size() < sz[node->val]){
vector <int< temp;
ret.push_back(temp);
}
ret[sz[node->val] - 1].push_back(node->val);
return sz[node->val];
}
vector<vector<int<> findLeaves(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return ret;
}
};
main(){
Solution ob;
vector<int< v = {1,2,3,4,5};
TreeNode *root = make_tree(v);
print_vector(ob.findLeaves(root));
} อินพุต
{1,2,3,4,5} ผลลัพธ์
[[3, 5, 4, ],[2, ],[1, ],]


