สมมติว่าเรามีต้นไม้ไบนารี ภารกิจคือการพิมพ์ผลรวมสูงสุดของโหนดทั้งหมดในการข้ามผ่านในแนวตั้ง ดังนั้นถ้าต้นไม้เป็นเหมือนด้านล่าง −
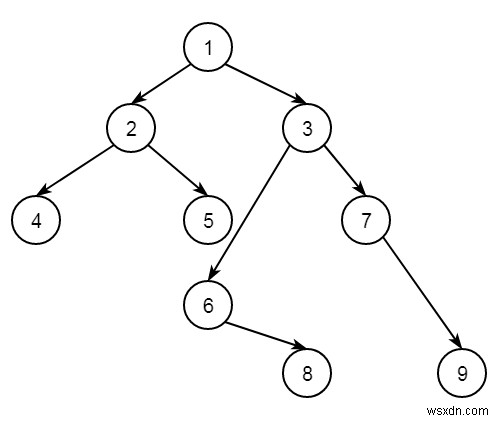
การข้ามผ่านคำสั่งแนวตั้งเป็นเหมือน −
4 2 1 + 5 + 6 = 12 3 + 8 = 11 7 9
ค่าสูงสุดคือ 12 วิธีการนั้นง่าย เราจะทำการข้ามผ่านแนวดิ่ง จากนั้นหาผลรวมและตรวจสอบค่าสูงสุด
ตัวอย่าง
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int key;
Node *left, *right;
};
Node* getNode(int key){
Node* node = new Node;
node->key = key;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
int getMaxSum(Node* root) {
if (!root)
return -1;
int n = 0;
int k_node = -1;
map<int, vector<int> > current_map;
int hd = 0;
queue<pair<Node*, int> > que;
que.push(make_pair(root, hd));
while (!que.empty()) {
pair<Node*, int> temp = que.front();
que.pop();
hd = temp.second;
Node* node = temp.first;
current_map[hd].push_back(node->key);
if (node->left != NULL)
que.push(make_pair(node->left, hd - 1));
if (node->right != NULL)
que.push(make_pair(node->right, hd + 1));
}
map<int, vector<int> >::iterator it;
int maximum = INT_MIN;
for (it = current_map.begin(); it != current_map.end(); it++) {
int temp_sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < it->second.size(); ++i) {
temp_sum += it->second[i];
}
if(maximum < temp_sum){
maximum = temp_sum;
}
}
return maximum;
}
int main() {
Node* root = getNode(1);
root->left = getNode(2);
root->right = getNode(3);
root->left->left = getNode(4);
root->left->right = getNode(5);
root->right->left = getNode(6);
root->right->right = getNode(7);
root->right->left->right = getNode(8);
root->right->right->right = getNode(9);
cout << "Maximum sum of vertical nodes: " << getMaxSum(root);
} ผลลัพธ์
Maximum sum of vertical nodes: 12


