แนวคิด
บทความนี้อธิบายวิธีการแก้ปัญหาในการค้นหา LCA ของสองโหนดในทรีโดยลดให้เป็นปัญหา RMQ
ตัวอย่าง
บรรพบุรุษร่วมต่ำที่สุด (LCA) ของสองโหนด a และ b ในทรีที่รูทแล้ว T ถูกกำหนดให้เป็นโหนดที่อยู่ไกลที่สุดจากรูทที่มีทั้ง a และ b เป็นผู้สืบทอด
ตัวอย่างเช่น ตามแผนภาพด้านล่าง LCA ของโหนด D และโหนด I คือโหนด B
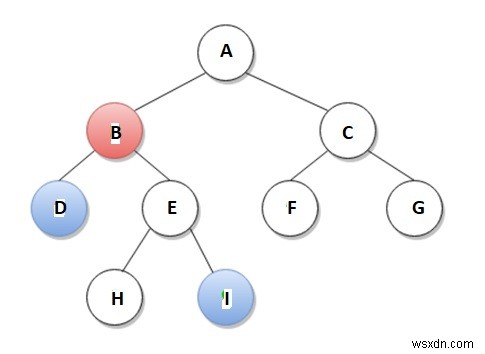
เราสามารถประยุกต์ใช้แนวทางมากมายในการแก้ปัญหา LCA วิธีการเหล่านี้แตกต่างกันไปตามความซับซ้อนของเวลาและพื้นที่
ช่วงการสืบค้นขั้นต่ำ (RMQ) ใช้กับอาร์เรย์เพื่อค้นหาตำแหน่งขององค์ประกอบที่มีค่าต่ำสุดระหว่างสองดัชนีที่ระบุ เราสามารถใช้แนวทางต่างๆ ในการแก้ปัญหา RMQ ตามบทความนี้ จะอธิบายวิธีการตาม Segment Tree ในส่วนของแผนผังเซ็กเมนต์ เวลาก่อนการประมวลผลคือ O(n) และเวลาสำหรับการค้นหาขั้นต่ำของช่วงคือ O(Logn) ในที่นี้ พื้นที่เพิ่มเติมที่ต้องใช้คือ O(n) เพื่อจัดเก็บแผนผังส่วน
การลด LCA เป็น RMQ
เราอธิบายแนวคิดนี้ในการเยี่ยมชมต้นไม้โดยเริ่มจากการรูตโดยทัวร์ออยเลอร์ (เยี่ยมชมโดยไม่ต้องยกดินสอ) ซึ่งเป็นการข้ามผ่านประเภท DFS (การค้นหาระยะลึก) ที่มีลักษณะเฉพาะการข้ามผ่านของการสั่งซื้อล่วงหน้า
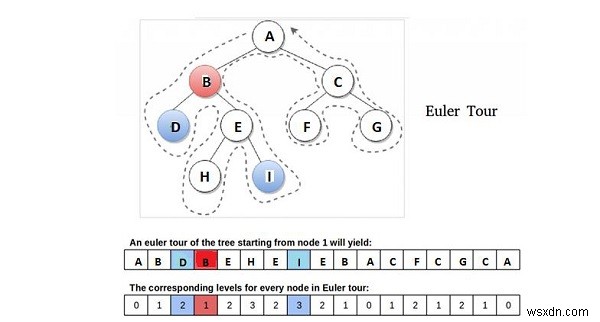
การสังเกต − ตามแผนภาพด้านบน LCA ของโหนด D และ I คือโหนด B ซึ่งบ่งชี้ว่าเป็นโหนดที่ใกล้กับรูทที่สุดในบรรดาทั้งหมดที่พบระหว่างการเยี่ยมชม D และฉัน ระหว่าง DFS ของ T ดังนั้น เราสามารถกล่าวได้ว่าข้อสังเกตนี้ เป็นกุญแจสำคัญในการลด อีกครั้งเราสามารถพูดได้ว่าโหนดของเราเป็นโหนดที่ระดับต่ำสุดและเป็นโหนดเดียวที่ระดับนั้นในบรรดาโหนดทั้งหมดที่เกิดขึ้นระหว่าง a และ b ที่ต่อเนื่องกัน (ใดๆ) ในการทัวร์ออยเลอร์ของ T
เราต้องการสามอาร์เรย์สำหรับการใช้งาน -
-
เยี่ยมชมโหนดตามลำดับทัวร์ออยเลอร์ของ T
-
แต่ละระดับโหนดเข้าเยี่ยมชมในทัวร์ออยเลอร์ของ T
-
ดัชนีการเกิดครั้งแรกของโหนดในทัวร์ออยเลอร์ของ T (หากเกิดเหตุการณ์ใดขึ้นก็ดี เรามาติดตามอันแรกกัน)
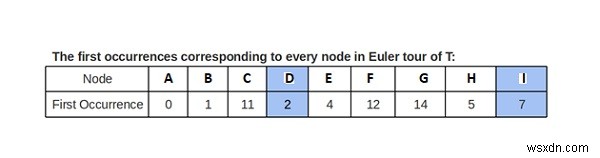
วิธีการ
-
ดำเนินการทัวร์ออยเลอร์บนทรี และเติมออยเลอร์ ระดับ และอาร์เรย์การเกิดขึ้นครั้งแรก
-
ใช้อาร์เรย์การเกิดขึ้นครั้งแรก รับดัชนีที่สอดคล้องกับสองโหนดซึ่งจะเป็นมุมของช่วงในอาร์เรย์ระดับที่ป้อนไปยังอัลกอริธึม RMQ สำหรับค่าต่ำสุด
-
ในขณะที่อัลกอริทึมส่งกลับดัชนีของระดับต่ำสุดในช่วง เราจะใช้มันเพื่อกำหนด LCA โดยใช้ออยเลอร์ทัวร์อาร์เรย์
ตัวอย่าง
/* This C++ Program is implemented to find LCA of u and v by reducing the problem to RMQ */
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define V 9 // indicates number of nodes in input tree
int euler1[2*V - 1]; // indicates for Euler tour sequence
int level1[2*V - 1]; // indicates level of nodes in tour sequence
int firstOccurrence1[V+1]; // indicates first occurrences of nodes in tour
int ind; // indicates variable to fill-in euler and level arrays
//This is a Binary Tree node
struct Node1{
int key;
struct Node1 *left, *right;
};
// Utility function creates a new binary tree node with given key
Node1 * newNode1(int k){
Node1 *temp = new Node1;
temp->key = k;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// indicates log base 2 of x
int Log2(int x){
int ans = 0 ;
while (x>>=1) ans++;
return ans ;
}
/* A recursive function is used to get the minimum value in a given range of array indexes. The following are parameters for this function.
st --> indicates pointer to segment tree
index --> indicates index of current node in the segment tree.
Initially 0 is passed as root is always at index 0
ss & se --> indicate starting and ending indexes of the segment
represented by current node, i.e., st[index]
qs & qe --> indicate starting and ending indexes of query range
*/
int RMQUtil(int index1, int ss1, int se1, int qs1, int qe1, int *st1){
// It has been seen that if segment of this node is a part of given range, then return the min of the segment
if (qs1 <= ss1 && qe1 >= se1)
return st1[index1];
//It has been seen that if segment of this node is outside the given range
else if (se1 < qs1 || ss1 > qe1)
return -1;
// It has been seen that if a part of this segment overlaps with the given range
int mid = (ss1 + se1)/2;
int q1 = RMQUtil(2*index1+1, ss1, mid, qs1, qe1, st1);
int q2 = RMQUtil(2*index1+2, mid+1, se1, qs1, qe1, st1);
if (q1==-1) return q2;
else if (q2==-1) return q1;
return (level1[q1] < level1[q2]) ? q1 : q2;
}
// Return minimum of elements in range from index qs (query start) to
// qe (query end). It mainly uses RMQUtil()
int RMQ(int *st1, int n, int qs1, int qe1){
// Check for erroneous input values
if (qs1 < 0 || qe1 > n-1 || qs1 > qe1){
printf("Invalid Input");
return -1;
}
return RMQUtil(0, 0, n-1, qs1, qe1, st1);
}
// Now a recursive function that constructs Segment Tree for
array[ss1..se1]. // si1 is index of current node in segment tree st
void constructSTUtil(int si1, int ss1, int se1, int arr1[], int *st1){
// When there will be only one element in array, store it in current node of
// segment tree and return
if (ss1 == se1)st1[si1] = ss1;
else{
// It has been seen that if there are more than one
elements, then recur for left and right subtrees and store the
minimum of two values in this node
int mid1 = (ss1 + se1)/2;
constructSTUtil(si1*2+1, ss1, mid1, arr1, st1);
constructSTUtil(si1*2+2, mid1+1, se1, arr1, st1);
if (arr1[st1[2*si1+1]] < arr1[st1[2*si1+2]])
st1[si1] = st1[2*si1+1];
else
st1[si1] = st1[2*si1+2];
}
}
/* Now this function is used to construct segment tree from given
array. This function allocates memory for segment tree and calls
constructSTUtil() to fill the allocated memory */
int *constructST(int arr1[], int n){
// Allocating memory for segment tree
//Indicates height of segment tree
int x = Log2(n)+1;
// Indicates maximum size of segment tree
int max_size = 2*(1<<x) - 1; // 2*pow(2,x) -1
int *st1 = new int[max_size];
// Indicates filling the allocated memory st1
constructSTUtil(0, 0, n-1, arr1, st1);
// Returning the constructed segment tree
return st1;
}
// Indicates recursive version of the Euler tour of T
void eulerTour(Node1 *root, int l){
/* if the passed node exists */
if (root){
euler1[ind] = root->key; // inserting in euler array
level1[ind] = l; // inserting l in level array
ind++; // indicates increment index
/* It has been seen that if unvisited, mark first occurrence*/
if (firstOccurrence1[root->key] == -1)
firstOccurrence1[root->key] = ind-1;
/* touring left subtree if exists, and remark euler
and level arrays for parent on return */
if (root->left){
eulerTour(root->left, l+1);
euler1[ind]=root->key;
level1[ind] = l;
ind++;
}
/* touring right subtree if exists, and remark euler
and level arrays for parent on return */
if (root->right) {
eulerTour(root->right, l+1);
euler1[ind]=root->key;
level1[ind] = l;
ind++;
}
}
}
// Returning LCA of nodes n1, n2 (assuming they are
// present in the tree)
int findLCA(Node1 *root, int u1, int v1){
/* Marking all nodes unvisited. Note that the size of
firstOccurrence is 1 as node values which vary from
1 to 9 are used as indexes */
memset(firstOccurrence1, -1, sizeof(int)*(V+1));
/* To start filling euler and level arrays from index 0 */
ind = 0;
/* Starting Euler tour with root node on level 0 */
eulerTour(root, 0);
/* constructing segment tree on level array */
int *st1 = constructST(level1, 2*V-1);
/*It has been seen that if v before u in Euler tour. For RMQ to
work, first parameter 'u1' must be smaller than second 'v1' */
if (firstOccurrence1[u1]>firstOccurrence1[v1])
std::swap(u1, v1);
// Indicates starting and ending indexes of query range
int qs1 = firstOccurrence1[u1];
int qe1 = firstOccurrence1[v1];
// Indicates query for index of LCA in tour
int index1 = RMQ(st1, 2*V-1, qs1, qe1);
/* returning LCA node */
return euler1[index1];
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main(){
// Let us create the Binary Tree as shown in the diagram.
Node1 * root = newNode1(1);
root->left = newNode1(2);
root->right = newNode1(3);
root->left->left = newNode1(4);
root->left->right = newNode1(5);
root->right->left = newNode1(6);
root->right->right = newNode1(7);
root->left->right->left = newNode1(8);
root->left->right->right = newNode1(9);
int u1 = 4, v1 = 9;
printf("The LCA of node %d and node %d is node %d.\n",
u1, v1, findLCA(root, u1, v1));
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
The LCA of node 4 and node 9 is node 2.


