โครงสร้างการค้นหาแบบไบนารี (BST) เป็นต้นไม้ชนิดพิเศษซึ่งเป็นไปตามกฎต่อไปนี้ −
- ค่าโหนดลูกด้านซ้ายจะน้อยกว่าหมายเหตุหลักเสมอ
- โหนดย่อยทางขวามีค่ามากกว่าโหนดหลัก
- โหนดทั้งหมดสร้างแผนผังการค้นหาแบบไบนารีแยกกัน
ตัวอย่างของแผนผังการค้นหาแบบไบนารี (BST) -

โครงสร้างการค้นหาแบบไบนารีถูกสร้างขึ้นเพื่อลดความซับซ้อนของการดำเนินการ เช่น การค้นหา ค้นหาค่าต่ำสุดและสูงสุด
การดำเนินการค้นหาใน BST
ดำเนินการค้นหาในแผนผังการค้นหาแบบไบนารี
เราจำเป็นต้องค้นหากุญแจในต้นไม้ สำหรับสิ่งนี้ เราจะเปรียบเทียบคีย์กับโหนดรูทของต้นไม้
หากคีย์เท่ากับรูทโหนด จะพบคีย์
หากค่าของคีย์มากกว่าโหนดรูท ให้ใช้แผนผังย่อยที่ถูกต้องและค้นหาคีย์
หากค่าของคีย์น้อยกว่าโหนดรูท ให้ใช้ทรีย่อยทางซ้ายแล้วค้นหาคีย์
ตัวอย่าง
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node{
int key;
struct node *left, *right;
};
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->key = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void traversetree(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL){
traversetree(root->left);
printf("%d \t", root->key);
traversetree(root->right);
}
}
struct node* search(struct node* root, int key){
if (root == NULL || root->key == key)
return root;
if (root->key < key)
return search(root->right, key);
return search(root->left, key);
}
struct node* insert(struct node* node, int key){
if (node == NULL) return newNode(key);
if (key < node->key)
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
else if (key > node->key)
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
return node;
}
int main(){
struct node *root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 23);
insert(root, 15);
insert(root, 12);
insert(root, 17);
insert(root, 32);
insert(root, 29);
insert(root, 45);
printf("The tree is :\n");
traversetree(root);
printf("\nSearching for 12 in this tree ");
if(search(root , 12))
printf("\nelement found");
else
printf("\nelement not found");
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
The tree is : 12 15 17 23 29 32 45 Searching for 12 in this tree element found
การดำเนินการแทรกใน BST
การดำเนินการแทรกใน BST เกิดขึ้นที่โหนดปลายสุดของต้นไม้สำหรับการแทรก เราจะเริ่มการเปรียบเทียบโหนดกับโหนดรูท และค้นหาตำแหน่งที่ถูกต้องของโหนดแล้วจึงวาง ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้จะทำให้คุณเข้าใจมากขึ้น

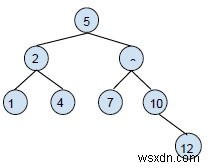
กำลังแทรก 12 ใน BST นี้
เราจะเปรียบเทียบ 12 กับโหนดรูท 12> 5 ซึ่งเป็นของทรีย่อยที่ถูกต้อง
เปรียบเทียบ 12 กับโหนดชายน์ด้านขวา 12> 8 ซึ่งเป็นทางด้านขวาของโหนดย่อยด้านขวา
เปรียบเทียบ 12 กับลูกย่อยด้านขวาของทรีย่อยด้านขวา 12>10 ตำแหน่งของมันคือด้านขวาของโหนดนี้
ต้นไม้ใหม่จะเกิดขึ้น
ตัวอย่าง
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node{
int key;
struct node *left, *right;
};
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->key = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void traversetree(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL){
traversetree(root->left);
printf("%d \t", root->key);
traversetree(root->right);
}
}
struct node* insert(struct node* node, int key){
if (node == NULL) return newNode(key);
if (key < node->key)
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
else if (key > node->key)
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
return node;
}
int main(){
struct node *root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 23);
insert(root, 15);
insert(root, 12);
insert(root, 17);
insert(root, 32);
insert(root, 29);
printf("The tree is :\n");
traversetree(root);
printf("\nInseting 45 to the tree\n");
insert(root, 45);
printf("Tree after insertion is :\n");
traversetree(root);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
The tree is : 12 15 17 23 29 32 Inserting 45 to the tree Tree after insertion is : 12 15 17 23 29 32 45


