Bellman Ford Algorithm เป็นอัลกอริธึมการเขียนโปรแกรมแบบไดนามิกที่ใช้เพื่อค้นหาเส้นทางที่สั้นที่สุดของจุดยอดที่คำนวณจากจุดยอดที่ถือว่าเป็นจุดยอดเริ่มต้น อัลกอริทึมนี้ใช้วิธีวนซ้ำและพยายามค้นหาเส้นทางที่สั้นที่สุดอย่างต่อเนื่อง อัลกอริทึมของ Bellman Ford บนกราฟถ่วงน้ำหนัก
อัลกอริทึมนี้เสนอโดย Alphonso shimbel ในปี 1955 อัลกอริทึมนี้มีการแก้ไขโดย Richard Bellman และ Lester Ford ในปี พ.ศ. 2499 และ พ.ศ. 2501 เนื่องจากอัลกอริธึมนี้มีชื่อว่า Bellman Ford Algorithm . อัลกอริธึมนี้ได้รับการแก้ไขโดย Eward F. Moore ในปี 2500 ซึ่งทำให้ชื่ออัลกอริทึมของ Bellman-Ford-Moore .
อัลกอริธึมนี้ดีกว่าเพราะสามารถรองรับน้ำหนักของขอบได้ แม้ว่าอัลกอริธึมจะช้ากว่าอัลกอริทึมของ Dijkstra แต่ก็เป็นอัลกอริธึมที่ดีกว่าเพราะจัดการกับกราฟประเภทต่างๆ ได้หลากหลายมากขึ้น
อัลกอริทึม
Input : weighted graph and starting vertex Output : shortest distance between all vertices from the src. For negative weight cycle, the same will be returned as the weight cannot be calculated.
อัลกอริทึม
Step 1 : This is the initialisation step, an array is created that stores the distance of all vertices from the initial vertex. The array say dist[] of size equal to the number of vertices in the graph. Step 2 : Calculate the shortest distance of vertex. Loop through step 3 for n-1 number of times ( n is the number of vertices of graph). Step 3 : Follow following steps for each edge i-j Step 3.1 : If dist[v] > dist[u] + weight[uv]. Then, dist[v] = dist[u] + weight[uv]. Step 4 : Check and flag if there is any negative cycle. If step 3.1 executes then there is a negative cycle.
วงจรเชิงลบ :หากมีเส้นทางที่สั้นกว่าการข้ามผ่านขอบปกติ แสดงว่ามีวงจรเชิงลบ
ตัวอย่าง
มาเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับอัลกอริทึมโดยการแก้ปัญหาเกี่ยวกับกราฟ
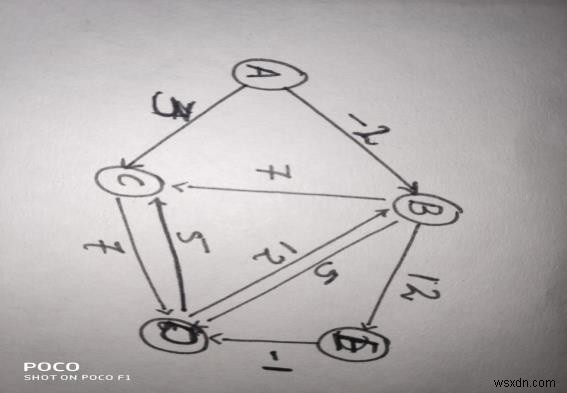
คุณสามารถดูจุดยอดและขอบทั้งหมดของกราฟพร้อมกับน้ำหนักที่เกี่ยวข้องได้
ให้หาระยะทางที่สั้นที่สุดระหว่าง จุดยอด A และจุดยอด E โดยใช้อัลกอริทึม Bellman-ford
ตั้งค่าจุดยอดต้นทาง (A) เป็นศูนย์ 0 และตั้งค่าระยะที่เหลือเป็นอินฟินิตี้ ∞
A B C D E 0 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞
เช็คน้ำหนักขอบ A-B แล้วก็ A-C ,
สำหรับ A- B เรามีเพียงเส้นทางเดียว แต่สำหรับ A-C เรามีเส้นทางสองเส้นทางที่สามารถข้ามได้ และเราจะตรวจสอบว่าเส้นทางใดสั้นที่สุด
A B C D E 0 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ 0 -2 ∞ ∞ ∞ - for (A-B) 0 -2 3 ∞ ∞ - for (A-C)
สำหรับจุดยอดถัดไป เราจะคำนวณและระยะทางที่สั้นที่สุดสำหรับจุดยอดเริ่มต้น
A B C D E 0 ∞ ∞ ∞ ∞ 0 -2 ∞ ∞ ∞ 0 -2 3 3 10
ระยะทางที่สั้นที่สุดจึงใช้อัลกอริทึมคือ 10 การข้ามเส้นทาง A-B-E . การใช้สิ่งนี้ทำให้เราพบว่ามีวงจรเชิงลบ
ตัวอย่าง
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
struct Edge {
int src, dest, weight;
};
struct Graph {
int V, E;
struct Edge* edge;
};
struct Graph* createGraph(int V, int E) {
struct Graph* graph = new Graph;
graph->V = V;
graph->E = E;
graph->edge = new Edge[E];
return graph;
}
void BellmanFord(struct Graph* graph, int src) {
int V = graph->V;
int E = graph->E;
int dist[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
dist[i] = INT_MAX;
dist[src] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < E; j++) {
int u = graph->edge[j].src;
int v = graph->edge[j].dest;
int weight = graph->edge[j].weight;
if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v])
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
int u = graph->edge[i].src;
int v = graph->edge[i].dest;
int weight = graph->edge[i].weight;
if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) {
printf("Graph contains negative weight cycle");
return;
}
}
printf("Vertex :\t\t\t ");
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
printf("%d \t", i);
printf("\nDistance From Source : ");
for (int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
printf("%d \t",dist[i]);
return;
}
int main() {
int V = 5;
int E = 8;
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E);
graph->edge[0].src = 0;
graph->edge[0].dest = 1;
graph->edge[0].weight = -1;
graph->edge[1].src = 0;
graph->edge[1].dest = 2;
graph->edge[1].weight = 4;
graph->edge[2].src = 1;
graph->edge[2].dest = 2;
graph->edge[2].weight = 3;
graph->edge[3].src = 1;
graph->edge[3].dest = 3;
graph->edge[3].weight = 2;
graph->edge[4].src = 1;
graph->edge[4].dest = 4;
graph->edge[4].weight = 2;
graph->edge[5].src = 3;
graph->edge[5].dest = 2;
graph->edge[5].weight = 5;
graph->edge[6].src = 3;
graph->edge[6].dest = 1;
graph->edge[6].weight = 1;
graph->edge[7].src = 4;
graph->edge[7].dest = 3;
graph->edge[7].weight = -3;
BellmanFord(graph, 0);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
Vertex : 0 1 2 3 4 Distance From Source : 0 -1 2 -2 1


