อัลกอริทึมของ Ford-Fulkerson ใช้เพื่อตรวจจับการไหลสูงสุดจากจุดยอดเริ่มต้นไปยังจุดยอดจมในกราฟที่กำหนด ในกราฟนี้ ทุกขอบมีความจุ มีจุดยอดสองจุดชื่อ Source และ Sink จุดยอดต้นทางมีขอบด้านนอกทั้งหมด ไม่มีขอบด้านใน และอ่างจะมีขอบเข้าด้านในทั้งหมด ไม่มีขอบด้านนอก
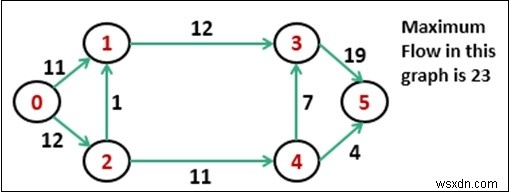
มีข้อจำกัดบางประการ:
- การไหลบนขอบไม่เกินความจุที่กำหนดของกราฟนั้น
- กระแสขาเข้าและขาออกจะเท่ากันทุกขอบ ยกเว้นแหล่งที่มาและซิงก์
อินพุตและเอาต์พุต
Input: The adjacency matrix: 0 10 0 10 0 0 0 0 4 2 8 0 0 0 0 0 0 10 0 0 0 0 9 0 0 0 6 0 0 10 0 0 0 0 0 0 Output: Maximum flow is: 19
อัลกอริทึม
bfs (พลิก เริ่ม จม)
อินพุต: รายการจุดยอด โหนดเริ่มต้น และโหนดซิงก์
ผลลัพธ์ − จริงเมื่อเข้าอ่าง
Begin initially mark all nodes as unvisited state of start as visited predecessor of start node is φ insert start into the queue qu while qu is not empty, do delete element from queue and set to vertex u for all vertices i, in the residual graph, do if u and i are connected, and i is unvisited, then add vertex i into the queue predecessor of i is u mark i as visited done done return true if state of sink vertex is visited End
fordFulkerson(จุดกลับ, ต้นทาง, จม)
ป้อนข้อมูล: รายการจุดยอด จุดยอดต้นทาง และจุดยอดซิงก์
ผลลัพธ์ − การไหลสูงสุดตั้งแต่ต้นจนจบ
Begin create a residual graph and copy given graph into it while bfs(vert, source, sink) is true, do pathFlow := ∞ v := sink vertex while v ≠ start vertex, do u := predecessor of v pathFlow := minimum of pathFlow and residualGraph[u, v] v := predecessor of v done v := sink vertex while v ≠ start vertex, do u := predecessor of v residualGraph[u,v] := residualGraph[u,v] – pathFlow residualGraph[v,u] := residualGraph[v,u] – pathFlow v := predecessor of v done maFlow := maxFlow + pathFlow done return maxFlow End
ตัวอย่าง
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#define NODE 6
using namespace std;
typedef struct node {
int val;
int state; //status
int pred; //predecessor
}node;
int minimum(int a, int b) {
return (a<b)?a:b;
}
int resGraph[NODE][NODE];
/* int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0},
{0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0},
{0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20},
{0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
}; */
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 10, 0, 10, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 4, 2, 8, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 10},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 9, 0},
{0, 0, 6, 0, 0, 10},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
};
int bfs(node *vert, node start, node sink) {
node u;
int i, j;
queue<node> que;
for(i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
vert[i].state = 0; //not visited
}
vert[start.val].state = 1; //visited
vert[start.val].pred = -1; //no parent node
que.push(start); //insert starting node
while(!que.empty()) {
//delete from queue and print
u = que.front();
que.pop();
for(i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
if(resGraph[u.val][i] > 0 && vert[i].state == 0) {
que.push(vert[i]);
vert[i].pred = u.val;
vert[i].state = 1;
}
}
}
return (vert[sink.val].state == 1);
}
int fordFulkerson(node *vert, node source, node sink) {
int maxFlow = 0;
int u, v;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j<NODE; j++) {
resGraph[i][j] = graph[i][j]; //initially residual graph is main graph
}
}
while(bfs(vert, source, sink)) { //find augmented path using bfs algorithm
int pathFlow = 999;//as infinity
for(v = sink.val; v != source.val; v=vert[v].pred) {
u = vert[v].pred;
pathFlow = minimum(pathFlow, resGraph[u][v]);
}
for(v = sink.val; v != source.val; v=vert[v].pred) {
u = vert[v].pred;
resGraph[u][v] -= pathFlow; //update residual capacity of edges
resGraph[v][u] += pathFlow; //update residual capacity of reverse edges
}
maxFlow += pathFlow;
}
return maxFlow; //the overall max flow
}
int main() {
node vertices[NODE];
node source, sink;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
vertices[i].val = i;
}
source.val = 0;
sink.val = 5;
int maxFlow = fordFulkerson(vertices, source, sink);
cout << "Maximum flow is: " << maxFlow << endl;
} ผลลัพธ์
Maximum flow is: 19


