การใช้อัลกอริธึมการข้ามผ่านแบบ Depth First Search (DFS) ทำให้เราตรวจจับวงจรในกราฟที่กำหนดได้ หากมี self-loop ในโหนดใด ๆ จะถือว่าเป็นวงจร มิฉะนั้นเมื่อโหนดย่อยมีขอบอื่นเพื่อเชื่อมต่อพาเรนต์ก็จะเป็นวงจรด้วย
สำหรับกราฟที่ตัดการเชื่อมต่อ อาจมีต้นไม้ที่แตกต่างกัน เราสามารถเรียกพวกเขาว่าป่า ตอนนี้เราต้องตรวจจับวัฏจักรของต้นไม้ในป่าทั้งหมด
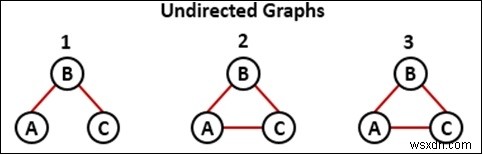
ในแนวทางนี้ เราจะใช้ชุดที่แตกต่างกันเพื่อกำหนดโหนดเพื่อดำเนินการข้ามผ่าน DFS มีสามชุด สีขาว สีเทา และสีดำ เริ่มแรก โหนดทั้งหมดจะถูกเก็บไว้ในชุดสีขาว เมื่อมีการข้ามโหนดใหม่หนึ่งโหนด โหนดนั้นจะถูกเก็บไว้ในชุดสีเทาและนำออกจากโหนดสีขาว และหลังจากย้อนรอยเสร็จแล้ว เมื่อภารกิจนั้นสำหรับโหนดนั้นเสร็จสิ้น จะถูกสลับจากชุดสีเทาเป็นชุดสีดำ
อินพุตและเอาต์พุต
Input: The Adjacency matrix. 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 Output: The graph has cycle.
อัลกอริทึม
dfs(curr, wSet, gSet, bSet)
อินพุต: โหนดปัจจุบัน ชุดสีขาว สีเทา และสีดำ
ผลลัพธ์: เป็นจริงหากมีวัฏจักร
Begin delete curr from the while set and add it to the grey set for all nodes v connected with curr in the graph, do if v is in the black set, then skip next part, and go for next iteration if v is in the grey set, then return true if dfs(v, wSet, gSet, bSet) is true, then return true done delete curr from grey set and add to black set return fasle End
hasCycle(กราฟ)
ป้อนข้อมูล - ให้กราฟ
ผลลัพธ์: เป็นจริงเมื่อกราฟเป็นวงจร
Begin initially insert all nodes into the white set while white set has some elements, do for all nodes v in the graph, do if v is not in the white set, then if dfs(v, wSet, gSet, bSet), then return true done done return false End
ตัวอย่าง
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
#define NODE 5
using namespace std;
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0}
};
bool dfs(int curr, set<int>&wSet, set<int>&gSet, set<int>&bSet) {
//moving curr to white set to grey set.
wSet.erase(wSet.find(curr));
gSet.insert(curr);
for(int v = 0; v < NODE; v++) {
if(graph[curr][v] != 0) { //for all neighbour vertices
if(bSet.find(v) != bSet.end())
continue; //if the vertices are in the black set
if(gSet.find(v) != gSet.end())
return true; //it is a cycle
if(dfs(v, wSet, gSet, bSet))
return true; //cycle found
}
}
//moving v to grey set to black set.
gSet.erase(gSet.find(curr));
bSet.insert(curr);
return false;
}
bool hasCycle() {
set<int> wSet, gSet, bSet; //three set as white, grey and black
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
wSet.insert(i); //initially add all node into the white set
while(wSet.size() > 0) {
for(int current = 0; current < NODE; current++) {
if(wSet.find(current) != wSet.end())
if(dfs(current, wSet, gSet, bSet))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int main() {
bool res;
res = hasCycle();
if(res)
cout << "The graph has cycle." << endl;
else
cout << "The graph has no cycle." << endl;
} ผลลัพธ์
The graph has cycle.


