ในการตรวจสอบการเชื่อมต่อของกราฟ เราจะพยายามสำรวจโหนดทั้งหมดโดยใช้อัลกอริธึมการข้ามผ่านใดๆ หลังจากเสร็จสิ้นการข้ามผ่าน หากมีโหนดใดที่ไม่ได้เข้าชม กราฟจะไม่เชื่อมต่อ
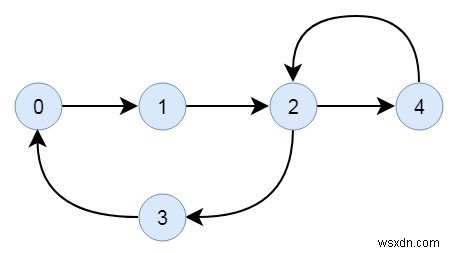
สำหรับกราฟกำกับ เราจะเริ่มสำรวจจากทุกโหนดเพื่อตรวจสอบการเชื่อมต่อ ในบางครั้ง ขอบข้างหนึ่งอาจมีได้เพียงขอบด้านนอกแต่ไม่มีขอบด้านใน ดังนั้นโหนดนั้นจะไม่ถูกเยี่ยมชมจากโหนดเริ่มต้นอื่นๆ
ในกรณีนี้ อัลกอริธึมการข้ามผ่านคือการข้ามผ่าน DFS แบบเรียกซ้ำ
ป้อนข้อมูล − เมทริกซ์ที่อยู่ติดกันของกราฟ
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
ผลผลิต − เชื่อมต่อกราฟแล้ว
อัลกอริทึม
traverse(u, visited) Input: The start node u and the visited node to mark which node is visited. Output: Traverse all connected vertices. Begin mark u as visited for all vertex v, if it is adjacent with u, do if v is not visited, then traverse(v, visited) done End isConnected(graph) Input: The graph. Output: True if the graph is connected. Begin define visited array for all vertices u in the graph, do make all nodes unvisited traverse(u, visited) if any unvisited node is still remaining, then return false done return true End
ตัวอย่าง
#include<iostream>
#define NODE 5
using namespace std;
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {{0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 0, 0, 0}
};
void traverse(int u, bool visited[]){
visited[u] = true; //mark v as visited
for(int v = 0; v<NODE; v++){
if(graph[u][v]){
if(!visited[v])
traverse(v, visited);
}
}
}
bool isConnected(){
bool *vis = new bool[NODE];
//for all vertex u as start point, check whether all nodes are visible or not
for(int u; u < NODE; u++){
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
vis[i] = false; //initialize as no node is visited
traverse(u, vis);
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++){
if(!vis[i]) //if there is a node, not visited by traversal, graph is not connected
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main(){
if(isConnected())
cout << "The Graph is connected.";
else
cout << "The Graph is not connected.";
} ผลลัพธ์
The Graph is connected.


