ตัวชี้เป็นตัวแปรที่เก็บที่อยู่ของตัวแปรอื่น
การประกาศตัวชี้ การเริ่มต้น และการเข้าถึง
พิจารณาข้อความต่อไปนี้ −
int qty = 179;
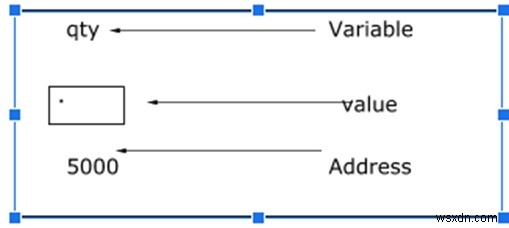
การประกาศตัวชี้
int *p;
'p' คือตัวแปรตัวชี้ที่เก็บที่อยู่ของตัวแปรจำนวนเต็มอื่น
การเริ่มต้นของตัวชี้
ตัวดำเนินการที่อยู่ (&) ใช้เพื่อเริ่มต้นตัวแปรตัวชี้
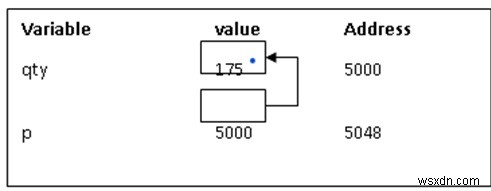
int qty = 175; int *p; p= &qty;
การคำนวณทางคณิตศาสตร์โดยใช้พอยน์เตอร์
ตัวแปรตัวชี้สามารถใช้ในนิพจน์ได้ ตัวอย่างเช่น หากตัวแปรพอยน์เตอร์ได้รับการประกาศและเริ่มต้นอย่างถูกต้อง คำสั่งต่อไปนี้จะถูกต้อง
a) *p1 + *p2 b) *p1- *p2 c) *p1 * *p2 d) *p1/ *p2 Note: There must be a blank space between / and * otherwise it is treated as beginning of comment line e ) p1 + 4 f) p2 - 2 g) p1 - p2 Note: returns the no. of elements in between p1 and p2 if both of them point to same array h) p1++ i) – – p2 j) sum + = *p2 j) p1 > p2 k) p1 = = p2 l) p1 ! = p2 Note: Comparisons can be used meaningfully in handling arrays and strings
ข้อความต่อไปนี้ไม่ถูกต้อง -
a) p1 + p2 b) p1 * p2 c) p1 / p2 d) p1 / 3
โปรแกรม
#include<stdio.h>
main (){
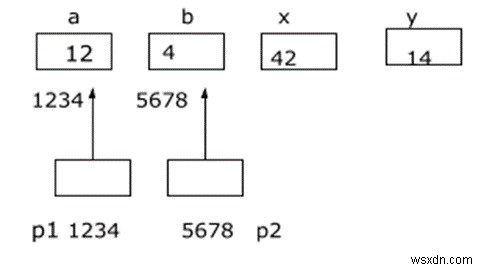
int a,b,x,y,z;
int *p1, *p2;
a =12;
b = 4;
p1= &a;
p2 = &b;
x = *p1 * * p2 – 6;
y= 4 - *p2 / *p1+10;
printf (“Address of a = %d”, p1);
printf (“Address of b = %d”, p2);
printf (“a= %d b =%d”, a,b);
printf (“x= %d y =%d”, x,y);
} ผลลัพธ์
Address of a = 1234 Address of b = 5678 a = 12 b= 4 x = 42 y= 14
คำอธิบาย