งานคือการพิมพ์โหนดที่ถูกต้องของไบนารีทรีที่กำหนด ประการแรก ผู้ใช้จะแทรกข้อมูลสำหรับสร้างไบนารีทรีและพิมพ์มุมมองขวาของทรีที่ก่อตัวขึ้น
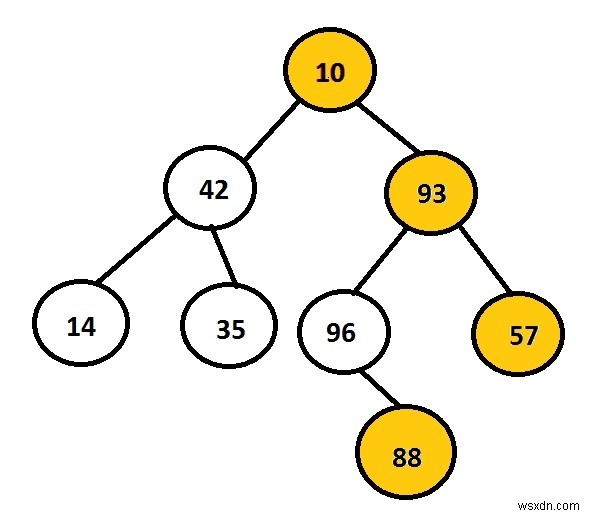
แผนภาพด้านบนแสดงไบนารีทรีที่สร้างด้วยโหนด 10, 42, 93, 14, 35, 96, 57 และ 88 ในบรรดาโหนดเหล่านี้ โหนดที่อยู่ทางด้านขวาของทรีจะถูกเลือกและแสดงบนหน้าจอ ตัวอย่างเช่น 10, 93, 57 และ 88 เป็นโหนดทางขวาสุดของไบนารีทรี
ตัวอย่าง
Input : 10 42 93 14 35 96 57 88 Output : 10 93 57 88
มีพอยน์เตอร์สองตัวที่เชื่อมโยงกับแต่ละโหนด นั่นคือ ซ้ายและขวา ตามคำถามนี้ โปรแกรมต้องสำรวจเฉพาะโหนดทางขวาเท่านั้น ดังนั้นจึงไม่จำเป็นต้องกังวลเกี่ยวกับลูกด้านซ้ายของโหนด
มุมมองขวาเก็บโหนดทั้งหมดที่เป็นโหนดสุดท้ายของระดับ ดังนั้นเราจึงสามารถใช้วิธีการเรียกซ้ำเพื่อจัดเก็บและเข้าถึงโหนดในลักษณะที่ทรีย่อยด้านขวาถูกสำรวจก่อนทรีย่อยด้านซ้าย เมื่อใดก็ตามที่โปรแกรมตรวจพบโหนดที่มีระดับมากกว่าระดับของโหนดก่อนหน้ามากกว่าโหนดก่อนหน้าจะปรากฏขึ้นเนื่องจากจะเป็นโหนดสุดท้ายของระดับ
โค้ดด้านล่างแสดงการใช้งาน c ของอัลกอริธึมที่ให้มา
อัลกอริทึม
START Step 1 -> create node variable of type structure Declare int data Declare pointer of type node using *left, *right Step 2 -> create function for inserting node with parameter as item Declare temp variable of node using malloc Set temp->data = item Set temp->left = temp->right = NULL return temp step 3 -> Declare Function void right_view(struct node *root, int level, int *end_level) IF root = NULL Return IF *end_level < level Print root->data Set *end_level = level Call right_view(root->right, level+1, end_level) Call right_view(root->left, level+1, end_level) Step 4 -> Declare Function void right(struct node *root) Set int level = 0 Call right_view(root, 1, &level) Step 5 -> In Main() Pass the values for the tree nodes using struct node *root = New(10) Call right(root) STOP
ตัวอย่าง
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right;
};
struct node *New(int item) {
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->data = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void right_view(struct node *root, int level, int *end_level) {
if (root == NULL) return;
if (*end_level < level) {
printf("%d\t", root->data);
*end_level = level;
}
right_view(root->right, level+1, end_level);
right_view(root->left, level+1, end_level);
}
void right(struct node *root) {
int level = 0;
right_view(root, 1, &level);
}
int main() {
printf("right view of a binary tree is : ");
struct node *root = New(10);
root->left = New(42);
root->right = New(93);
root->left->left = New(14);
root->left->right = New(35);
root->right->left = New(96);
root->right->right = New(57);
root->right->left->right = New(88);
right(root);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
หากเรารันโปรแกรมด้านบน มันจะสร้างผลลัพธ์ต่อไปนี้
right view of a binary tree is : 10 93 57 88


