งานคือการพิมพ์โหนดด้านซ้ายของไบนารีทรีที่กำหนด ประการแรก ผู้ใช้จะแทรกข้อมูลจึงสร้างไบนารีทรีและพิมพ์มุมมองด้านซ้ายของแผนผังที่เกิดขึ้น
ทุกโหนดสามารถมีลูกได้มากที่สุด 2 คน ดังนั้นที่นี่โปรแกรมจะต้องสำรวจเฉพาะตัวชี้ด้านซ้ายที่เกี่ยวข้องกับโหนด
หากตัวชี้ด้านซ้ายไม่เป็นค่าว่าง หมายความว่าจะมีข้อมูลหรือตัวชี้เชื่อมโยงอยู่ ถ้าไม่เช่นนั้น จะเป็นตัวชี้ด้านซ้ายที่จะพิมพ์และแสดงเป็นเอาต์พุต
ตัวอย่าง
Input : 1 0 3 2 4 Output : 1 0 2
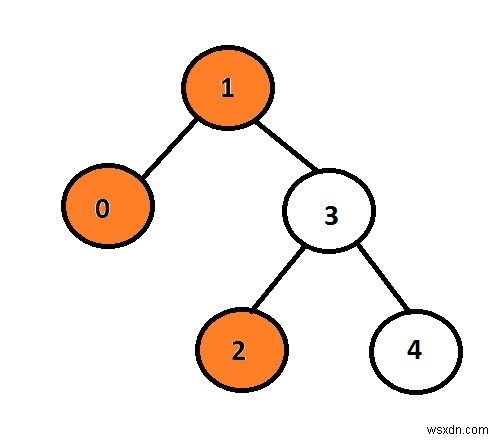
ที่นี่ โหนดสีส้มแสดงถึงมุมมองด้านซ้ายของต้นไม้ไบนารี
ในโหนดรูปที่กำหนดที่มีข้อมูล 1 เป็นโหนดรูท ดังนั้นมันจะถูกพิมพ์มากกว่าที่จะไปที่ลูกด้านซ้าย มันจะพิมพ์ 0 และมากกว่าที่จะไปที่ 3 และพิมพ์ลูกด้านซ้ายซึ่งเป็น 2
เราใช้วิธีการแบบเรียกซ้ำเพื่อเก็บระดับของโหนดและเปลี่ยนไปใช้โหนดอื่นซ้ำๆ
โค้ดด้านล่างแสดงการใช้งาน c ของอัลกอริธึมที่ให้มา
อัลกอริทึม
START Step 1 -> create node variable of type structure Declare int data Declare pointer of type node using *left, *right Step 2 -> create function for inserting node with parameter as new_data Declare temp variable of node using malloc Set temp->data = new_data Set temp->left = temp->right = NULL return temp Step 3 -> declare function void left_view(struct node* root, int level, int* highest_level) IF root = NULL Exit End IF *highest_level < level Print root->data Set *highest_level = level End Recursively call left_view(root->left, level + 1, highest_level) Recursively call left_view(root->right, level + 1, highest_level) Step 4 -> Declare Function void left(struct node* root) Set int highest_level = 0 Call left_view(root, 1, &highest_level) Step 5-> In main() Call New passing value user want to insert as struct node* root = New(1) Call left(root) STOP
ตัวอย่าง
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
//create a structure of a node
struct node {
int data;
struct node *left, *right; //this pointer will point to the nodes attached with a node
};
struct node* New(int new_data) {
struct node* temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
//allocating memory to a pointer dynamically
temp->data = new_data;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
void left_view(struct node* root, int level, int* highest_level) {
if (root == NULL) //if there is no node that means no data
return;
// this function will retrun the root node if there is only root node in a tree
if (*highest_level < level) {
printf("%d\t", root->data);
*highest_level = level;
}
// Recursive function
left_view(root->left, level + 1, highest_level);
left_view(root->right, level + 1, highest_level);
}
void left(struct node* root) {
int highest_level = 0;
left_view(root, 1, &highest_level);
}
int main() {
printf("left view of a binary tree is : ");
struct node* root = New(1);
root->left = New(0);
root->right = New(3);
root->right->left = New(2);
root->right->right = New(4);
left(root);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
หากเรารันโปรแกรมด้านบน มันจะสร้างผลลัพธ์ต่อไปนี้
left view of a binary tree is : 1 0 2


