แนะนำตัว..
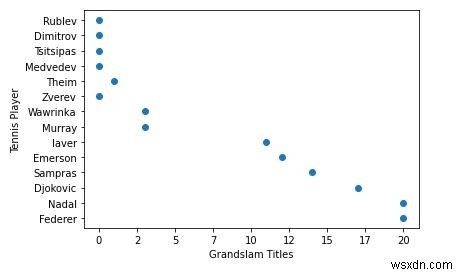
Scatter-plot มีประโยชน์มากเมื่อแสดงข้อมูลที่มีสองมิติเพื่อตรวจสอบว่ามีความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างสองตัวแปรหรือไม่ พล็อตกระจายคือแผนภูมิที่แสดงข้อมูลเป็นจุดที่มีค่า X และ Y
ทำอย่างไร..
1. ติดตั้ง matplotlib โดยทำตามคำสั่ง
pip install matplotlib
2. นำเข้า matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
tennis_stats = (('Federer', 20),('Nadal', 20),('Djokovic', 17),('Sampras', 14),('Emerson', 12),('laver', 11),('Murray', 3),('Wawrinka', 3),('Zverev', 0),('Theim', 1),('Medvedev',0),('Tsitsipas', 0),('Dimitrov', 0),('Rublev', 0)) 3. ขั้นตอนต่อไปคือการจัดเตรียมข้อมูลในรูปแบบอาร์เรย์ใดๆ นอกจากนี้เรายังสามารถอ่านข้อมูลจากฐานข้อมูลหรือจากสเปรดชีตและจัดรูปแบบข้อมูลในรูปแบบด้านล่างได้
titles = [title for player, title in tennis_stats] players = [player for player, title in tennis_stats]
4. พารามิเตอร์สำหรับ .scatter เช่นเดียวกับวิธีการอื่นๆ ของ matplotlib ต้องการอาร์เรย์ของค่า X และ Y
*หมายเหตุ -* ค่า X และ Y ต้องมีขนาดเท่ากัน และข้อมูลจะถูกแปลงเป็นทศนิยมตามค่าเริ่มต้น
plt.scatter(titles, players)
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x28df3684ac0>
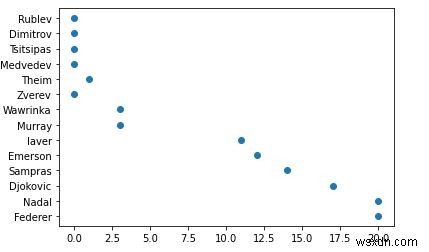
5. โอ้ ชื่อ GrandSlam ของฉันที่พล็อตบนแกน x เป็นแบบทุ่น ฉันจะแปลงเป็นจำนวนเต็มและเพิ่มชื่อสำหรับแกน x และแกน y ในฟังก์ชันด้านล่าง ตัวจัดรูปแบบแกนจะถูกเขียนทับด้วย .set_major_formatter
from matplotlib.ticker import FuncFormatter
def format_titles(title, pos):
return '{}'.format(int(title))
plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_formatter(FuncFormatter(format_titles))
plt.xlabel('Grandslam Titles')
plt.ylabel('Tennis Player')
plt.scatter(titles, players)
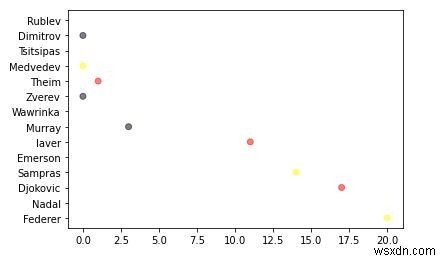
6. อย่าคิดว่าแผนภาพกระจายเป็นเพียงแผนภูมิ 2 มิติ พล็อตกระจายยังสามารถเพิ่มส่วนที่สาม (พื้นที่) และแม้แต่มิติที่สี่ (สี) ให้ฉันอธิบายหน่อยว่าฉันจะทำอะไรอยู่ด้านล่าง
ขั้นแรก เราจะกำหนดสีที่คุณเลือก จากนั้นวนซ้ำโดยการสุ่มเลือกสีและกำหนดมูลค่าการเดินทาง
ค่าอัลฟ่าทำให้แต่ละจุดเป็นแบบกึ่งโปร่งใส ทำให้เราเห็นว่าจุดใดทับซ้อนกัน ยิ่งค่านี้สูง คะแนนก็จะยิ่งโปร่งใสน้อยลงเท่านั้น
import random # define your own color scale. random_colors = ['#FF0000', '#FFFF00', '#FFFFF0', '#FFFFFF', '#00000F'] # set the number of colors similar to our data values color = [random.choice(random_colors) for _ in range(len(titles))] plt.scatter(titles, players, c=color, alpha=0.5)
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x28df2242d00>
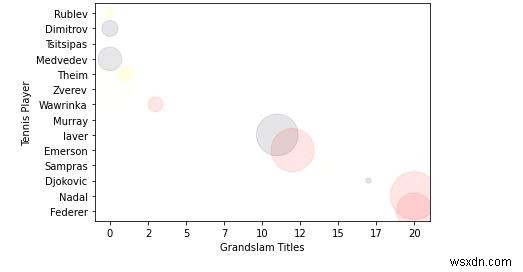
7. ตอนนี้ เรามาทำให้ขนาด/พื้นที่ของการนำเสนอใหญ่ขึ้นอีกหน่อย
import random
# define your own color scale.
random_colors = ['#FF0000', '#FFFF00', '#FFFFF0', '#FFFFFF', '#00000F']
# set the number of colors similar to our data values
color = [random.choice(random_colors) for _ in range(len(titles))]
# set the size
size = [(50 * random.random()) ** 2 for _ in range(len(titles))]
plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_formatter(FuncFormatter(format_titles))
plt.xlabel('Grandslam Titles')
plt.ylabel('Tennis Player')
plt.scatter(titles, players, c=color, s=size, alpha=0.1)
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x28df22e2430>
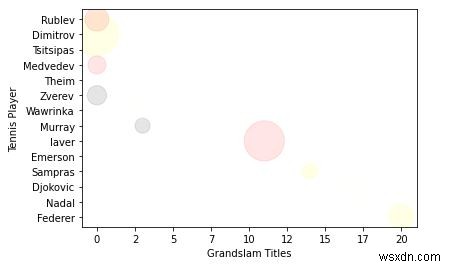
โปรดจำไว้ว่า เป้าหมายสูงสุดของกราฟคือการทำให้ข้อมูลเข้าใจง่าย
ฉันได้แสดงข้อมูลพื้นฐานเกี่ยวกับสิ่งที่คุณสามารถทำได้ด้วยแผนภาพแบบกระจาย คุณสามารถทำสิ่งต่างๆ ได้มากขึ้น เช่น ทำให้สีขึ้นอยู่กับขนาดเพื่อทำให้จุดที่มีขนาดเดียวกันทั้งหมดเป็นสีเดียวกัน ซึ่งอาจช่วยให้เราแยกแยะระหว่างข้อมูลได้
สำรวจเพิ่มเติม - https://matplotlib.org/.
สุดท้ายก็รวมทุกอย่างเข้าด้วยกัน
ตัวอย่าง
# imports
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
# preparing data..
tennis_stats = (('Federer', 20),('Nadal', 20),('Djokovic', 17),('Sampras', 14),('Emerson', 12),('laver', 11),('Murray', 3),('Wawrinka', 3),('Zverev', 0),('Theim', 1),('Medvedev',0),('Tsitsipas', 0),('Dimitrov', 0),('Rublev', 0))
titles = [title for player, title in tennis_stats]
players = [player for player, title in tennis_stats]
# custom function
from matplotlib.ticker import FuncFormatter
def format_titles(title, pos):
return '{}'.format(int(title))
# define your own color scale.
random_colors = ['#FF0000', '#FFFF00', '#FFFFF0', '#FFFFFF', '#00000F']
# set the number of colors similar to our data values
color = [random.choice(random_colors) for _ in range(len(titles))]
# set the size
size = [(50 * random.random()) ** 2 for _ in range(len(titles))]
plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_formatter(FuncFormatter(format_titles))
plt.xlabel('Grandslam Titles')
plt.ylabel('Tennis Player')
plt.scatter(titles, players, c=color, s=size, alpha=0.1)
<matplotlib.collections.PathCollection at 0x2aa7676b670>