ทุกธุรกิจขึ้นอยู่กับความภักดีของลูกค้า ธุรกิจที่ทำซ้ำจากลูกค้าเป็นหนึ่งในรากฐานที่สำคัญสำหรับการทำกำไรของธุรกิจ ดังนั้นจึงเป็นสิ่งสำคัญที่จะต้องทราบสาเหตุที่ลูกค้าออกจากธุรกิจ ลูกค้าที่จากไปเรียกว่าลูกค้าปั่นป่วน จากการดูแนวโน้มที่ผ่านมา เราสามารถตัดสินได้ว่าปัจจัยใดที่ส่งผลต่อการเลิกราของลูกค้า และวิธีคาดการณ์ว่าลูกค้ารายใดจะออกจากธุรกิจไป ในบทความนี้ เราจะใช้อัลกอริธึม ML เพื่อศึกษาแนวโน้มที่ผ่านมาในการเลิกใช้ของลูกค้า แล้วตัดสินว่าลูกค้ารายใดมีแนวโน้มที่จะเลิกใช้
การเตรียมข้อมูล
เป็นตัวอย่างจะพิจารณาการปั่นของลูกค้าเทเลคอมสำหรับบทความนี้ แหล่งข้อมูลมีอยู่ที่ kaggel URL สำหรับดาวน์โหลดข้อมูลระบุไว้ในโปรแกรมด้านล่าง เราใช้ไลบรารี Pandas เพื่อโหลดไฟล์ csv ลงในโปรแกรม Python และดูตัวอย่างแถวบางแถว
ตัวอย่าง
import pandas as pd
#Loading the Telco-Customer-Churn.csv dataset
#https://www.kaggle.com/blastchar/telco-customer-churn
datainput = pd.read_csv('E:\\Telecom_customers.csv')
print("Given input data :\n",datainput) ผลลัพธ์
การเรียกใช้โค้ดข้างต้นทำให้เราได้ผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้ -
Given input data : customerID gender SeniorCitizen ... MonthlyCharges TotalCharges Churn 0 7590-VHVEG Female 0 ... 29.85 29.85 No 1 5575-GNVDE Male 0 ... 56.95 1889.5 No 2 3668-QPYBK Male 0 ... 53.85 108.15 Yes 3 7795-CFOCW Male 0 ... 42.30 1840.75 No 4 9237-HQITU Female 0 ... 70.70 151.65 Yes ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 7038 6840-RESVB Male 0 ... 84.80 1990.5 No 7039 2234-XADUH Female 0 ... 103.20 7362.9 No 7040 4801-JZAZL Female 0 ... 29.60 346.45 No 7041 8361-LTMKD Male 1 ... 74.40 306.6 Yes 7042 3186-AJIEK Male 0 ... 105.65 6844.5 No [7043 rows x 21 columns]
ศึกษารูปแบบที่มีอยู่
ต่อไปเราจะศึกษาชุดข้อมูลเพื่อค้นหารูปแบบที่มีอยู่เมื่อห่วงโซ่เกิดขึ้น นอกจากนี้เรายังลบบางคอลัมน์จากเพื่อนข้อมูลซึ่งไม่ส่งผลต่อเงื่อนไข ตัวอย่างเช่น คอลัมน์รหัสลูกค้าจะไม่มีผลกระทบต่อการที่ลูกค้าออกจากงานหรือไม่ ดังนั้นเราจึงวางคอลัมน์ดังกล่าวโดยใช้วิธีการดรอปแบบป๊อปทั้งหมด จากนั้นเราพล็อตแผนภูมิแสดงเปอร์เซ็นต์ของโอกาสในชุดข้อมูลที่กำหนด
ตัวอย่างที่ 2
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import rcParams
#Loading the Telco-Customer-Churn.csv dataset
#https://www.kaggle.com/blastchar/telco-customer-churn
datainput = pd.read_csv('E:\\Telecom_customers.csv')
print("Given input data :\n",datainput)
#Dropping columns
datainput.drop(['customerID'], axis=1, inplace=True)
datainput.pop('TotalCharges')
datainput['OnlineBackup'].unique()
data = datainput['Churn'].value_counts(sort = True)
chroma = ["#BDFCC9","#FFDEAD"]
rcParams['figure.figsize'] = 9,9
explode = [0.2,0.2]
plt.pie(data, explode=explode, colors=chroma, autopct='%1.1f%%', shadow=True, startangle=180,)
plt.title('Percentage of Churn in the given Data')
plt.show() ผลลัพธ์
การเรียกใช้โค้ดข้างต้นทำให้เราได้ผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้ -
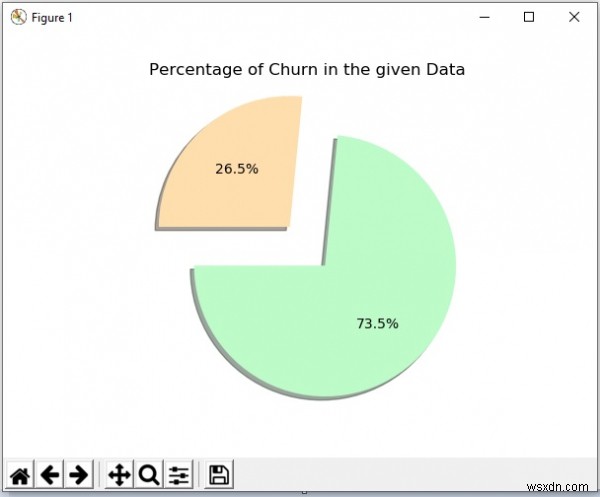
การประมวลผลข้อมูลล่วงหน้า
เพื่อให้ข้อมูลพร้อมใช้งานโดยอัลกอริธึม ML เราติดป้ายกำกับฟิลด์ทั้งหมด เรายังแปลงค่าข้อความเป็นแฟล็กตัวเลข ตัวอย่างเช่น ค่าในคอลัมน์เพศจะเปลี่ยนเป็น 0 และ 1 แทนที่จะเป็นเพศชายและเพศหญิง ซึ่งช่วยในการใช้ฟิลด์เหล่านั้นในการคำนวณและอัลกอริธึมที่จะประเมินผลกระทบของฟิลด์เหล่านี้กับค่าปั่น เราใช้วิธี LabelEncoder จาก sklearn
ตัวอย่างที่ 3
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import preprocessing
label_encoder = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()
datainput['gender'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['gender'])
datainput['Partner'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Partner'])
datainput['Dependents'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Dependents'])
datainput['PhoneService'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['PhoneService'])
datainput['MultipleLines'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['MultipleLines'])
datainput['InternetService'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['InternetService'])
datainput['OnlineSecurity'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['OnlineSecurity'])
datainput['OnlineBackup'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['OnlineBackup'])
datainput['DeviceProtection'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['DeviceProtection'])
datainput['TechSupport'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['TechSupport'])
datainput['StreamingTV'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['StreamingTV'])
datainput['StreamingMovies'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['StreamingMovies'])
datainput['Contract'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Contract'])
datainput['PaperlessBilling'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['PaperlessBilling'])
datainput['PaymentMethod'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['PaymentMethod'])
datainput['Churn'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Churn'])
print("input data after label encoder :\n",datainput)
#separating features(X) and label(y)
datainput["Churn"] = datainput["Churn"].astype(int)
y = datainput["Churn"].values
X = datainput.drop(labels = ["Churn"],axis = 1)
print("\nseparated X and y :")
print("y -",y)
print("X -",X) ผลลัพธ์
การเรียกใช้โค้ดข้างต้นทำให้เราได้ผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้ -
input data after label encoder customerID gender SeniorCitizen ... MonthlyCharges TotalCharges Churn 0 7590-VHVEG 0 0 ... 29.85 29.85 0 1 5575-GNVDE 1 0 ... 56.95 1889.5 0 2 3668-QPYBK 1 0 ... 53.85 108.15 1 3 7795-CFOCW 1 0 ... 42.30 1840.75 0 4 9237-HQITU 0 0 ... 70.70 151.65 1 ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 7038 6840-RESVB 1 0 ... 84.80 1990.5 0 7039 2234-XADUH 0 0 ... 103.20 7362.9 0 7040 4801-JZAZL 0 0 ... 29.60 346.45 0 7041 8361-LTMKD 1 1 ... 74.40 306.6 1 7042 3186-AJIEK 1 0 ... 105.65 6844.5 0 [7043 rows x 21 columns] separated X and y : y - [0 0 1 ... 0 1 0] X - customerID gender ... MonthlyCharges TotalCharges 0 7590-VHVEG 0 ... 29.85 29.85 1 5575-GNVDE 1 ... 56.95 1889.5 2 3668-QPYBK 1 ... 53.85 108.15 3 7795-CFOCW 1 ... 42.30 1840.75 4 9237-HQITU 0 ... 70.70 151.65 ... ... ... ... ... ... 7038 6840-RESVB 1 ... 84.80 1990.5 7039 2234-XADUH 0 ... 103.20 7362.9 7040 4801-JZAZL 0 ... 29.60 346.45 7041 8361-LTMKD 1 ... 74.40 306.6 7042 3186-AJIEK 1 ... 105.65 6844.5 [7043 rows x 20 columns]
การฝึกอบรมและการทดสอบข้อมูล
ตอนนี้เราแบ่งชุดข้อมูลออกเป็นสองส่วน หนึ่งสำหรับการฝึกอบรมและอีกสำหรับการทดสอบ พารามิเตอร์ test_size ใช้เพื่อกำหนดเปอร์เซ็นต์ของชุดข้อมูลที่จะใช้สำหรับการทดสอบเท่านั้น แบบฝึกหัดนี้จะช่วยให้เรามั่นใจในแบบจำลองที่เรากำลังสร้าง จากนั้นเราใช้อัลกอริทึมการถดถอยโลจิสติกและค้นหาค่าที่คาดการณ์ไว้
ตัวอย่าง
import pandas as pd
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
#Loading the Telco-Customer-Churn.csv dataset with pandas
datainput = pd.read_csv('E:\\Telecom_customers.csv')
datainput.drop(['customerID'], axis=1, inplace=True)
datainput.pop('TotalCharges')
datainput['OnlineBackup'].unique()
#LabelEncoder()
from sklearn import preprocessing
label_encoder = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()
datainput['gender'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['gender'])
datainput['Partner'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Partner'])
datainput['Dependents'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Dependents'])
datainput['PhoneService'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['PhoneService'])
datainput['MultipleLines'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['MultipleLines'])
datainput['InternetService'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['InternetService'])
datainput['OnlineSecurity'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['OnlineSecurity'])
datainput['OnlineBackup'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['OnlineBackup'])
datainput['DeviceProtection'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['DeviceProtection'])
datainput['TechSupport'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['TechSupport'])
datainput['StreamingTV'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['StreamingTV'])
datainput['StreamingMovies'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['StreamingMovies'])
datainput['Contract'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Contract'])
datainput['PaperlessBilling'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['PaperlessBilling'])
datainput['PaymentMethod'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['PaymentMethod'])
datainput['Churn'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Churn'])
#print("input data after label encoder :\n",datainput)
#separating features(X) and label(y)
datainput["Churn"] = datainput["Churn"].astype(int)
Y = datainput["Churn"].values
X = datainput.drop(labels = ["Churn"],axis = 1)
#train_test_split method
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2)
#LogisticRegression
classifier=LogisticRegression()
classifier.fit(X_train,Y_train)
Y_pred=classifier.predict(X_test)
print("\npredicted values :\n",Y_pred) ผลลัพธ์
การเรียกใช้โค้ดข้างต้นทำให้เราได้ผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้ -
predicted values : [0 0 1 ... 0 1 0]
การค้นหาพารามิเตอร์การประเมิน
เมื่อระดับความแม่นยำในขั้นตอนข้างต้นเป็นที่ยอมรับ เราจะทำการประเมินแบบจำลองเพิ่มเติมโดยค้นหาพารามิเตอร์ต่างๆ เราใช้ความแม่นยำและเมทริกซ์ความสับสนเป็นพารามิเตอร์ของเราในการตัดสินว่าแบบจำลองนี้ทำงานอย่างแม่นยำเพียงใด เปอร์เซ็นต์ค่าความแม่นยำที่สูงกว่าแนะนำโมเดลว่าเหมาะสมกว่า ในทำนองเดียวกัน เมทริกซ์ความสับสนแสดงเมทริกซ์ของผลบวกจริง ผลลบจริง ผลบวกลวง และผลลบลวง เปอร์เซ็นต์ของค่าจริงที่สูงกว่าเมื่อเปรียบเทียบกับค่าเท็จบ่งชี้ว่าแบบจำลองที่ดีกว่า
ตัวอย่าง
import pandas as pd
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn import metrics
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
#Loading the Telco-Customer-Churn.csv dataset with pandas
datainput = pd.read_csv('E:\\Telecom_customers.csv')
datainput.drop(['customerID'], axis=1, inplace=True)
datainput.pop('TotalCharges')
datainput['OnlineBackup'].unique()
#LabelEncoder()
from sklearn import preprocessing
label_encoder = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()
datainput['gender'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['gender'])
datainput['Partner'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Partner'])
datainput['Dependents'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Dependents'])
datainput['PhoneService'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['PhoneService'])
datainput['MultipleLines'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['MultipleLines'])
datainput['InternetService'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['InternetService'])
datainput['OnlineSecurity'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['OnlineSecurity'])
datainput['OnlineBackup'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['OnlineBackup'])
datainput['DeviceProtection'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['DeviceProtection'])
datainput['TechSupport'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['TechSupport'])
datainput['StreamingTV'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['StreamingTV'])
datainput['StreamingMovies'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['StreamingMovies'])
datainput['Contract'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Contract'])
datainput['PaperlessBilling'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['PaperlessBilling'])
datainput['PaymentMethod'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['PaymentMethod'])
datainput['Churn'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Churn'])
#print("input data after label encoder :\n",datainput)
#separating features(X) and label(y)
datainput["Churn"] = datainput["Churn"].astype(int)
Y = datainput["Churn"].values
X = datainput.drop(labels = ["Churn"],axis = 1)
#train_test_split method
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2)
#LogisticRegression
classifier=LogisticRegression()
classifier.fit(X_train,Y_train)
Y_pred=classifier.predict(X_test)
#Accuracy
LR = metrics.accuracy_score(Y_test, Y_pred) * 100
print("\nThe accuracy score using the LR is -> ",LR)
#confusion matrix
cm=confusion_matrix(Y_test,Y_pred)
print("\nconfusion matrix : \n",cm) ผลลัพธ์
การเรียกใช้โค้ดข้างต้นทำให้เราได้ผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้ -
The accuracy score using the LR is -> 80.8374733853797 confusion matrix : [[928 109] [161 211]]
น้ำหนักของตัวแปร
ต่อไป เราจะตัดสินว่าแต่ละฟิลด์หรือตัวแปรส่งผลต่อค่า churn อย่างไร ซึ่งจะช่วยให้เรากำหนดเป้าหมายตัวแปรเฉพาะที่จะมีผลกระทบมากขึ้นในการปั่นป่วน และพยายามจัดการกับตัวแปรเหล่านั้นในการป้องกันการปั่นของลูกค้า ด้วยเหตุนี้ เราตั้งค่าสัมประสิทธิ์ในตัวแยกประเภทเป็นศูนย์และรับน้ำหนักของตัวแปรแต่ละตัว
ตัวอย่าง
import pandas as pd
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
#Loading the dataset with pandas
datainput = pd.read_csv('E:\\Telecom_customers.csv')
datainput.drop(['customerID'], axis=1, inplace=True)
datainput.pop('TotalCharges')
datainput['OnlineBackup'].unique()
#LabelEncoder()
from sklearn import preprocessing
label_encoder = preprocessing.LabelEncoder()
datainput['gender'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['gender'])
datainput['Partner'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Partner'])
datainput['Dependents'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Dependents'])
datainput['PhoneService'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['PhoneService'])
datainput['MultipleLines'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['MultipleLines'])
datainput['InternetService'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['InternetService'])
datainput['OnlineSecurity'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['OnlineSecurity'])
datainput['OnlineBackup'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['OnlineBackup'])
datainput['DeviceProtection'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['DeviceProtection'])
datainput['TechSupport'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['TechSupport'])
datainput['StreamingTV'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['StreamingTV'])
datainput['StreamingMovies'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['StreamingMovies'])
datainput['Contract'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Contract'])
datainput['PaperlessBilling'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['PaperlessBilling'])
datainput['PaymentMethod'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['PaymentMethod'])
datainput['Churn'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(datainput['Churn'])
#print("input data after label encoder :\n",datainput)
#separating features(X) and label(y)
datainput["Churn"] = datainput["Churn"].astype(int)
Y = datainput["Churn"].values
X = datainput.drop(labels = ["Churn"],axis = 1)
#
#train_test_split method
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2)
#
#LogisticRegression
classifier=LogisticRegression()
classifier.fit(X_train,Y_train)
Y_pred=classifier.predict(X_test)
#weights of all the variables
wt = pd.Series(classifier.coef_[0], index=X.columns.values)
print("\nweight of all the variables :")
print(wt.sort_values(ascending=False)) ผลลัพธ์
การเรียกใช้โค้ดข้างต้นทำให้เราได้ผลลัพธ์ดังต่อไปนี้ -
weight of all the variables : PaperlessBilling 0.389379 SeniorCitizen 0.246504 InternetService 0.209283 Partner 0.067855 StreamingMovies 0.054309 MultipleLines 0.042330 PaymentMethod 0.039134 MonthlyCharges 0.027180 StreamingTV -0.008606 gender -0.029547 tenure -0.034668 DeviceProtection -0.052690 OnlineBackup -0.143625 Dependents -0.209667 OnlineSecurity -0.245952 TechSupport -0.254740 Contract -0.729557 PhoneService -0.950555 dtype: float64


