ต้นไม้ขยายเป็นกราฟย่อยของกราฟที่เชื่อมโยงและไม่มีทิศทางที่เชื่อมต่อจุดยอดทั้งหมด ต้นไม้ที่ทอดยาวหลายต้นสามารถมีอยู่ในกราฟได้ ต้นไม้ทอดข้ามขั้นต่ำ (MST) ในแต่ละกราฟมีน้ำหนักเท่ากันหรือน้อยกว่าต้นไม้ขยายอื่นๆ ทั้งหมด น้ำหนักถูกกำหนดให้กับขอบของต้นไม้ที่ทอดยาว และผลรวมคือน้ำหนักที่กำหนดให้กับแต่ละขอบ เนื่องจาก V คือจำนวนจุดยอดในกราฟ ต้นไม้ที่ทอดข้ามขั้นต่ำจึงมีขอบเป็น (V - 1) โดยที่ V คือจำนวนขอบ
ค้นหาต้นไม้ที่ทอดข้ามขั้นต่ำโดยใช้อัลกอริทึมของ Kruskal
-
ขอบทั้งหมดควรจัดเรียงตามลำดับน้ำหนักที่ไม่ลดต่ำลง
-
เลือกขอบที่เล็กที่สุด ขอบนี้จะรวมอยู่ด้วยหากวัฏจักรไม่เกิด
-
ควรทำขั้นตอนที่ 2 จนกว่าต้นไม้ขยายจะมีขอบ (V-1)
ในสถานการณ์สมมตินี้ เราถูกบอกให้ใช้วิธีการโลภ ตัวเลือกที่โลภคือการเลือกขอบที่มีน้ำหนักน้อยที่สุด ดังภาพประกอบ:ต้นไม้ขยายขั้นต่ำสำหรับกราฟนี้คือ (9-1)=8 ขอบ
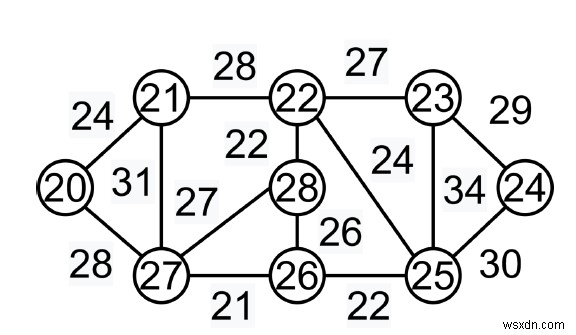
After sorting: Weight Src Dest 21 27 26 22 28 22 22 26 25 24 20 21 24 22 25 26 28 26 27 22 23 27 27 28 28 20 27 28 21 22 29 23 24 30 25 24 31 21 27 34 23 25
ตอนนี้เราต้องเลือกขอบทั้งหมดตามการจัดเรียง
รวมขอบ 26-27-> เนื่องจากไม่มีวงจรเกิดขึ้น
รวมขอบ 28-22-> เนื่องจากไม่มีวงจรเกิดขึ้น
รวมขอบ 26-25-> เนื่องจากไม่มีวงจรเกิดขึ้น
รวมขอบ 20-21-> เนื่องจากไม่มีวงจรเกิดขึ้น
รวมขอบ 22-25-> เนื่องจากไม่มีวงจรเกิดขึ้น
Edge 28-26-> ถูกละทิ้งเมื่อเกิดวงจร
รวมขอบ 22-23-> เนื่องจากไม่มีวงจรเกิดขึ้น
Edge 27-28-> ถูกละทิ้งเมื่อเกิดวงจร
รวมขอบ 20-27-> เนื่องจากไม่มีวงจรเกิดขึ้น
Edge 21-22-> ถูกละทิ้งเมื่อเกิดวงจร
รวมขอบ 23-24-> เนื่องจากไม่มีวงจรเกิดขึ้น
เนื่องจากจำนวนขอบคือ (V-1) ดังนั้นอัลกอริทึมจึงสิ้นสุดที่นี่
ตัวอย่าง
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Edge {
int src, dest, weight;
};
struct Graph {
int V, E;
struct Edge* edge;
};
struct Graph* createGraph(int V, int E){
struct Graph* graph = (struct Graph*)(malloc(sizeof(struct Graph)));
graph->V = V;
graph->E = E;
graph->edge = (struct Edge*)malloc(sizeof( struct Edge)*E);
return graph;
}
struct subset {
int parent;
int rank;
};
int find(struct subset subsets[], int i){
if (subsets[i].parent != i)
subsets[i].parent
= find(subsets, subsets[i].parent);
return subsets[i].parent;
}
void Union(struct subset subsets[], int x, int y){
int xroot = find(subsets, x);
int yroot = find(subsets, y);
if (subsets[xroot].rank < subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[xroot].parent = yroot;
else if (subsets[xroot].rank > subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
else{
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
subsets[xroot].rank++;
}
}
int myComp(const void* a, const void* b){
struct Edge* a1 = (struct Edge*)a;
struct Edge* b1 = (struct Edge*)b;
return a1->weight > b1->weight;
}
void KruskalMST(struct Graph* graph){
int V = graph->V;
struct Edge
result[V];
int e = 0;
int i = 0;
qsort(graph->edge, graph->E, sizeof(graph->edge[0]), myComp);
struct subset* subsets
= (struct subset*)malloc(V * sizeof(struct subset));
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v) {
subsets[v].parent = v;
subsets[v].rank = 0;
}
while (e < V - 1 && i < graph->E) {
struct Edge next_edge = graph->edge[i++];
int x = find(subsets, next_edge.src);
int y = find(subsets, next_edge.dest);
if (x != y) {
result[e++] = next_edge;
Union(subsets, x, y);
}
}
printf("Following are the edges in the constructed MST\n");
int minimumCost = 0;
for (i = 0; i < e; ++i){
printf("%d -- %d == %d\n", result[i].src,
result[i].dest, result[i].weight);
minimumCost += result[i].weight;
}
printf("Minimum Cost Spanning tree : %d",minimumCost);
return;
}
int main(){
/* Let us create the following weighted graph
30
0--------1
| \ |
26| 25\ |15
| \ |
22--------23
24 */
int V = 24;
int E = 25;
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E);
graph->edge[0].src = 20;
graph->edge[0].dest = 21;
graph->edge[0].weight = 30;
graph->edge[1].src = 20;
graph->edge[1].dest = 22;
graph->edge[1].weight = 26;
graph->edge[2].src = 20;
graph->edge[2].dest = 23;
graph->edge[2].weight = 25;
graph->edge[3].src = 21;
graph->edge[3].dest = 23;
graph->edge[3].weight = 35;
graph->edge[4].src = 22;
graph->edge[4].dest = 23;
graph->edge[4].weight = 24;
KruskalMST(graph);
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
Following are the edges in the constructed MST 22 -- 23 == 24 20 -- 23 == 25 20 -- 21 == 30 Minimum Cost Spanning tree : 79
บทสรุป
บทช่วยสอนนี้สาธิตวิธีใช้เมธอดขั้นต่ำ Spanning Tree Algorithm-Greedy ของ Kruskal และโค้ด C++ เพื่อแก้ปัญหานี้ เรายังเขียนโค้ดนี้ในภาษาจาวา ไพธอน และภาษาอื่นๆ ได้ด้วย มันถูกจำลองตามแนวคิดของ Kruskal โปรแกรมนี้ค้นหาแผนผังที่มีความกว้างสั้นที่สุดในกราฟที่กำหนด เราหวังว่าคุณจะพบว่าบทช่วยสอนนี้มีประโยชน์


