แนวคิด
สำหรับไบนารีทรีที่กำหนด เราจำเป็นต้องตรวจสอบว่ามีคุณสมบัติฮีปหรือไม่ ต้นไม้ไบนารีต้องเป็นไปตามเงื่อนไขสองข้อต่อไปนี้สำหรับการเป็นฮีป –
-
ต้นไม้ไบนารีควรเป็นต้นไม้ที่สมบูรณ์ (เช่น ทุกระดับยกเว้นสุดท้ายควรเต็ม)
-
ค่าทุกโหนดของทรีไบนารีควรมากกว่าหรือเท่ากับโหนดย่อย (พิจารณาจาก max-heap)
ตัวอย่าง
จากตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้ ต้นไม้นี้มีคุณสมบัติฮีป –
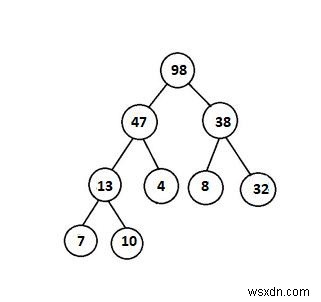
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้ไม่มีคุณสมบัติฮีป –
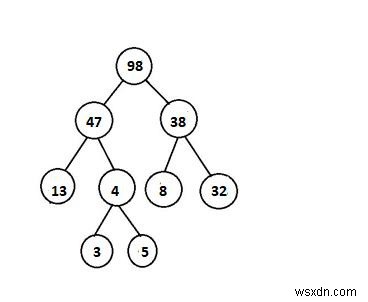
วิธีการ
จำเป็นต้องตรวจสอบแต่ละเงื่อนไขข้างต้นแยกกัน สำหรับการตรวจสอบความสมบูรณ์ isComplete (ฟังก์ชันนี้จะตรวจสอบว่าไบนารีทรีเสร็จสมบูรณ์หรือไม่) และสำหรับการตรวจสอบฟังก์ชัน heap isHeapUtil ถูกเขียนขึ้น
ในส่วนที่เกี่ยวกับการเขียนฟังก์ชัน isHeapUtil เราพิจารณาสิ่งต่อไปนี้ –
-
แต่ละโหนดสามารถมีลูกได้ 2 ลูก, ลูก 0 ลูก (โหนดระดับสุดท้าย) หรือลูก 1 ลูก (มีโหนดดังกล่าวได้สูงสุดหนึ่งโหนด)
-
หากพบว่า Node ไม่มีลูก แสดงว่าโหนดปลายสุดและคืนค่าเป็น true (กรณีฐาน)
-
หากพบว่าโหนดมีลูกหนึ่งคน (ต้องทิ้งลูกเพราะเป็นต้นไม้ที่สมบูรณ์) เราต้องเปรียบเทียบโหนดนี้กับโหนดลูกเดียวเท่านั้น
-
หากพบว่าโหนดมีลูกทั้งคู่ ให้ตรวจสอบคุณสมบัติฮีปที่โหนดที่เกิดซ้ำสำหรับทรีย่อยทั้งสอง
ตัวอย่าง
/* C++ program to checks if a binary tree is max heap or not */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node1{
int key;
struct Node1 *left;
struct Node1 *right;
};
struct Node1 *newNode(int k){
struct Node1 *node1 = new Node1;
node1->key = k;
node1->right = node1->left = NULL;
return node1;
}
unsigned int countNodes(struct Node1* root1){
if (root1 == NULL)
return (0);
return (1 + countNodes(root1->left) + countNodes(root1->right));
}
bool isCompleteUtil (struct Node1* root1, unsigned int index1, unsigned int number_nodes){
if (root1 == NULL)
return (true);
if (index1 >= number_nodes)
return (false);
// Recur for left and right subtrees
return (isCompleteUtil(root1->left, 2*index1 + 1, number_nodes) && isCompleteUtil(root1->right, 2*index1 + 2, number_nodes));
}
bool isHeapUtil(struct Node1* root1){
if (root1->left == NULL && root1->right == NULL)
return (true);
if (root1->right == NULL){
return (root1->key >= root1->left->key);
}
else{
if (root1->key >= root1->left->key &&
root1->key >= root1->right->key)
return ((isHeapUtil(root1->left)) &&
(isHeapUtil(root1->right)));
else
return (false);
}
}
bool isHeap(struct Node1* root1){
unsigned int node_count = countNodes(root1);
unsigned int index1 = 0;
if (isCompleteUtil(root1, index1, node_count) &&
isHeapUtil(root1))
return true;
return false;
}
// Driver program
int main(){
struct Node1* root1 = NULL;
root1 = newNode(10);
root1->left = newNode(9);
root1->right = newNode(8);
root1->left->left = newNode(7);
root1->left->right = newNode(6);
root1->right->left = newNode(5);
root1->right->right = newNode(4);
root1->left->left->left = newNode(3);
root1->left->left->right = newNode(2);
root1->left->right->left = newNode(1);
if (isHeap(root1))
cout << "Given binary tree is a Heap\n";
else
cout << "Given binary tree is not a Heap\n";
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
Given binary tree is a Heap


