สมมติว่าเรามีไบนารีทรีที่รูท ความลึกของแต่ละโหนดคือระยะทางที่สั้นที่สุดไปยังรูท โหนดนี้จะลึกที่สุดหากมีความลึกมากที่สุดในบรรดาโหนดใดๆ ในทรีทั้งหมด ทรีย่อยของโหนดคือโหนดนั้น บวกกับชุดของลูกหลานทั้งหมดของโหนดนั้น เราต้องหาโหนดที่มีความลึกมากที่สุดเพื่อให้มีโหนดที่ลึกที่สุดในทรีย่อย ดังนั้นถ้าต้นไม้เป็นเหมือน −
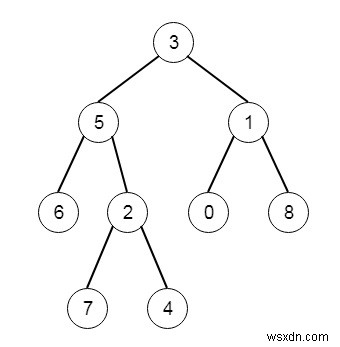
จากนั้นทรีย่อยที่ลึกที่สุดจะเป็น −
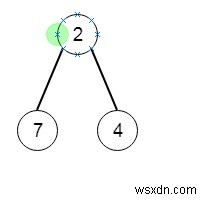
เพื่อแก้ปัญหานี้ เราจะทำตามขั้นตอนเหล่านี้ -
-
กำหนดวิธีการที่เรียกว่า Solve() ซึ่งจะทำการรูทเป็นอินพุต
-
หากรูทเป็นค่าว่าง ให้คืนค่า (null, 0)
-
l :=แก้(ซ้ายของรูท), r :=แก้(ทางขวาของรูท)
-
ถ้าค่าที่สองของ left> ค่าที่สองของ r ให้คืนค่าคู่ (ตัวแรกของ l, 1 + วินาทีของ l)
-
มิฉะนั้น เมื่อค่าที่สองของ left <ค่าที่สองของ r แล้วคืนค่าคู่ (ตัวแรกของ r และ 1 + วินาทีของ r)
-
คืนค่าคู่ (รูท, วินาทีของ l + 1)
-
จากการเรียกเมธอดหลัก Solve(root) แล้วคืนค่าที่สองของมัน
ตัวอย่าง(C++)
ให้เราดูการใช้งานต่อไปนี้เพื่อความเข้าใจที่ดีขึ้น -
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class TreeNode{
public:
int val;
TreeNode *left, *right;
TreeNode(int data){
val = data;
left = right = NULL;
}
};
void insert(TreeNode **root, int val){
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(*root);
while(q.size()){
TreeNode *temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if(!temp->left){
if(val != NULL)
temp->left = new TreeNode(val);
else
temp->left = new TreeNode(0);
return;
} else {
q.push(temp->left);
}
if(!temp->right){
if(val != NULL)
temp->right = new TreeNode(val);
else
temp->right = new TreeNode(0);
return;
} else {
q.push(temp->right);
}
}
}
TreeNode *make_tree(vector<int> v){
TreeNode *root = new TreeNode(v[0]);
for(int i = 1; i<v.size(); i++){
insert(&root, v[i]);
}
return root;
}
void tree_level_trav(TreeNode*root){
if (root == NULL) return;
cout << "[";
queue<TreeNode *> q;
TreeNode *curr;
q.push(root);
q.push(NULL);
while (q.size() > 1) {
curr = q.front();
q.pop();
if (curr == NULL){
q.push(NULL);
} else {
if(curr->left)
q.push(curr->left);
if(curr->right)
q.push(curr->right);
if(curr->val == 0 || curr == NULL){
cout << "null" << ", ";
} else {
cout << curr->val << ", ";
}
}
}
cout << "]"<<endl;
}
class Solution {
public:
pair <TreeNode*, int> solve(TreeNode* root){
if(!root || root->val == 0) return {NULL, 0};
pair <TreeNode*, int> L = solve(root->left);
pair <TreeNode*, int> R = solve(root->right);
if(L.second > R.second)return {L.first, L.second + 1};
else if(L.second < R.second) return {R.first, R.second + 1};
return {root, L.second + 1};
}
TreeNode* subtreeWithAllDeepest(TreeNode* root) {
return solve(root).first;
}
};
main(){
vector<int> v = {3,5,1,6,2,0,8,NULL,NULL,7,4};
TreeNode *root = make_tree(v);
Solution ob;
tree_level_trav(ob.subtreeWithAllDeepest(root)) ;
} อินพุต
{3,5,1,6,2,0,8,NULL,NULL,7,4} ผลลัพธ์
[2,7,4]


