เราได้รับโครงสร้างข้อมูลแบบต้นไม้ที่มีจำนวนโหนด 'n' ต้นไม้ที่กำหนดจะมีโหนดรูทและชายน์ตามลำดับซึ่งสามารถเป็นตัวเลขใดก็ได้ และชายด์เพิ่มเติมสามารถมีลูกจำนวนเท่าใดก็ได้ ภารกิจคือการค้นหาจำนวนการวนซ้ำขั้นต่ำที่โหนดรูทของทรีต้องการเพื่อส่งข้อมูลไปยังโหนดทั้งหมดในทรี ในแต่ละครั้ง โหนดสามารถส่งข้อมูลไปยังลูกของตนได้ และโหนดลูกหนึ่งสามารถส่งข้อมูลไปยังโหนดลูกของตน และในขณะเดียวกันโหนดรากสามารถส่งข้อมูลไปยังลูกอีกคนหนึ่งได้
ให้เราดูสถานการณ์อินพุตเอาต์พุตต่างๆ สำหรับสิ่งนี้ -
ใน -
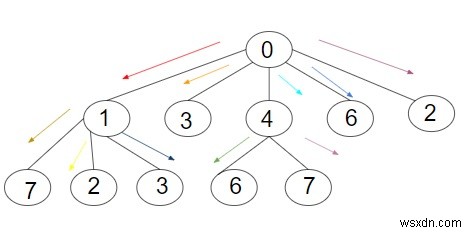
ออก − เลขที่ขั้นต่ำ ของการวนซ้ำเพื่อส่งข้อมูลไปยังโหนดทั้งหมดในทรีคือ:5
คำอธิบาย − เราได้รับต้นไม้ที่มีทั้งหมด 11 โหนด รวมถึงรูทและโหนดอื่นๆ ทั้งหมด โหนดรูทของทรีที่กำหนดคือ 0 ซึ่งจะส่งข้อมูลไปยังโหนด 1 ก่อน เนื่องจากมีโหนดย่อยจำนวนมาก จากนั้นโหนดอื่นๆ โหนดรูทจะส่งข้อมูลไปยังโหนด 4 จากนั้นจึงส่งข้อมูลไปยัง 3 จากนั้นจึงจะผ่าน ข้อมูลเป็น 6 และสุดท้ายจะส่งผ่านข้อมูลไปยัง 2 ดังนั้น โดยรวมการวนซ้ำที่ต้องใช้คือ 5
ใน -
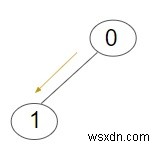
ออก − เลขที่ขั้นต่ำ ของการวนซ้ำเพื่อส่งข้อมูลไปยังโหนดทั้งหมดในทรีคือ:1
คำอธิบาย − :เราได้รับต้นไม้ที่มีทั้งหมด 2 โหนด รวมทั้งรูทและโหนดอื่นๆ ทั้งหมด เนื่องจากมีโหนดย่อยเพียงโหนดเดียวในทรีที่กำหนด ดังนั้นจำนวนการวนซ้ำขั้นต่ำที่ต้องการจะเป็น 1
แนวทางที่ใช้ในโปรแกรมด้านล่างมีดังนี้ −
-
สร้างคลาสเพื่อสร้างทรีและเพิ่มโหนดเป็นสมาชิกข้อมูล และสร้างตัวชี้รายการเป็น List_children และประกาศเมธอดส่วนตัวเป็น void Iteration(int vertices, int arr[]) ประกาศตัวสร้างพารามิเตอร์เป็น Tree(int nodes), void insert_node(int a, int b), int Min_Iteration() และ static int check(const void *a_1, const void *b_1)
-
เรียกตัวสร้างพารามิเตอร์ภายนอกเป็น Tree::Tree(int nodes)
-
ตั้งค่า this->nodes เป็น nodes.
-
ตั้งค่า List_children เป็นรายการใหม่[โหนด]
-
-
เรียกวิธีการของคลาสเป็น void Tree::insert_node(int a, int b)
-
ตั้งค่า List_children[a] เป็น push_back(b)
-
-
เรียกวิธีการเรียนเป็น void Tree::Iteration(int vertices, int arr[])
-
ตั้งค่า arr[vertices] เป็น List_children[vertices].size()
-
ตั้งค่า *ptr เป็น int ใหม่[arr[vertices]]
-
ตั้งค่า temp เป็น 0 และ temp_2 เป็น 0
-
ประกาศ iterator เป็น list::iterator it
-
เริ่มวนซ้ำ FOR จากมันไปที่ List_children[vertices].begin() จนกว่าจะไม่เท่ากับ List_children[vertices].end() และเพิ่มค่าล่วงหน้า ภายในลูปตั้งค่า Iteration(*it, arr) และตั้งค่า ptr[temp++] เป็น arr[*it]
-
โทร qsort(ptr, arr[vertices], sizeof(int) ตรวจสอบ) เพื่อการเรียงลำดับอย่างรวดเร็ว
-
เริ่มวนรอบสำหรับอุณหภูมิถึง 0 และอุณหภูมิน้อยกว่า List_children[vertices].size() และโพสต์อุณหภูมิที่เพิ่มขึ้น ภายในลูป ตั้งค่า temp_2 เป็น ptr[temp] + temp + 1 และ arr[vertices] เป็น max(arr[vertices], temp_2) และ delete[] ptr
-
-
เรียกวิธีการเรียนเป็น int Tree::Min_Iteration()
-
ประกาศตัวชี้เป็น int *ptr =new int[nodes]
-
ประกาศตัวแปรเป็น int temp =-1
-
เริ่มลูป FOR จาก i ถึง 0 จนถึง i
-
เรียก Iteration(0, ptr) และตั้งค่า temp เป็น ptr[0] และ delete[] ptr
-
อุณหภูมิกลับ
-
-
เรียกวิธีการเรียนเป็น int Tree::check(const void * a_1, const void * b_1)
-
ประกาศตัวแปรตามผลลัพธ์เป็น ( *(int*)b_1 - *(int*)a_1 )
-
ส่งคืนผลลัพธ์
-
-
ในฟังก์ชัน main()
-
สร้างวัตถุต้นไม้โดยใช้ตัวสร้างพารามิเตอร์
-
จากนั้นใช้วัตถุของคลาสต้นไม้เรียกเมธอด insert_node() เพื่อแทรกข้อมูลโหนดไปยังทรี
-
เรียกใช้เมธอด Min_Iteration() เพื่อคำนวณจำนวนการวนซ้ำขั้นต่ำเพื่อส่งข้อมูลไปยังโหนดทั้งหมดในทรี
-
ตัวอย่าง
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Tree
{
int nodes;
list<int> *List_children;
void Iteration(int vertices, int arr[]);
public:
//constructor of a class
Tree(int nodes);
//method to insert a node in a tree
void insert_node(int a, int b);
//method to calculate the minimum iterations
int Min_Iteration();
static int check(const void *a_1, const void *b_1);
};
Tree::Tree(int nodes)
{
this->nodes = nodes;
List_children = new list<int>[nodes];
}
void Tree::insert_node(int a, int b)
{
List_children[a].push_back(b);
}
void Tree::Iteration(int vertices, int arr[])
{
arr[vertices] = List_children[vertices].size();
int *ptr = new int[arr[vertices]];
int temp = 0;
int temp_2 = 0;
list<int>::iterator it;
for(it = List_children[vertices].begin(); it!= List_children[vertices].end(); ++it)
{
Iteration(*it, arr);
ptr[temp++] = arr[*it];
}
qsort(ptr, arr[vertices], sizeof(int), check);
for(temp = 0; temp < List_children[vertices].size(); temp++)
{
temp_2 = ptr[temp] + temp + 1;
arr[vertices] = max(arr[vertices], temp_2);
}
delete[] ptr;
}
int Tree::Min_Iteration()
{
int *ptr = new int[nodes];
int temp = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < nodes; i++)
{
ptr[i] = 0;
}
Iteration(0, ptr);
temp = ptr[0];
delete[] ptr;
return temp;
}
int Tree::check(const void * a_1, const void * b_1)
{
}
int main()
{
Tree T_1(8);
T_1.insert_node(0, 1);
T_1.insert_node(0, 3);
T_1.insert_node(0, 4);
T_1.insert_node(0, 6);
T_1.insert_node(0, 2);
T_1.insert_node(1, 7);
T_1.insert_node(1, 2);
T_1.insert_node(1, 3);
T_1.insert_node(4, 6);
T_1.insert_node(4, 7);
cout<<"Minimum no. of iterations to pass information to all nodes in the tree are:"<<T_1.Min_Iteration();
Tree T_2(2);
T_2.insert_node(0, 1);
cout<<"\nMinimum no. of iterations to pass information to all nodes in the tree are:" <<T_1.Min_Iteration();
return 0;
} ผลลัพธ์
ถ้าเรารันโค้ดด้านบน มันจะสร้างผลลัพธ์ต่อไปนี้
Minimum no. of iterations to pass information to all nodes in the tree are: 8 Minimum no. of iterations to pass information to all nodes in the tree are: 8


